Chapter 3-2
... Serous membranes line body cavities that are not exposed to the outside and also cover the organs within the cavities. There are 2 layers with a space between them. Parietal layer = attached to body wall Visceral layer = covers and attaches to organs Serous fluid = clear fluid between two la ...
... Serous membranes line body cavities that are not exposed to the outside and also cover the organs within the cavities. There are 2 layers with a space between them. Parietal layer = attached to body wall Visceral layer = covers and attaches to organs Serous fluid = clear fluid between two la ...
Chapter 1 study guide
... ▪ right and left lungs located here Abdominopelvic cavity ▪ Abdominal cavity contains stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, and lowest part of intestine ▪ Pelvic cavity contains reproductive organs, urinary bladder, pancreas, and spleen Dorsal cavity Cranial cavity contains brain Spinal cav ...
... ▪ right and left lungs located here Abdominopelvic cavity ▪ Abdominal cavity contains stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, and lowest part of intestine ▪ Pelvic cavity contains reproductive organs, urinary bladder, pancreas, and spleen Dorsal cavity Cranial cavity contains brain Spinal cav ...
GuideSheet unit 9 “the human Body” (SyStemS)
... Study Guide Questions for Test: Upon completion of the activities, go through these: 1. What are the four tissue types that are found in the integumentary system? (Pg. 936) 2. What are the functions of the integumentary system? (Pg. 938-939) 3. What are the two layers of skin composed of? (Pg. 936-9 ...
... Study Guide Questions for Test: Upon completion of the activities, go through these: 1. What are the four tissue types that are found in the integumentary system? (Pg. 936) 2. What are the functions of the integumentary system? (Pg. 938-939) 3. What are the two layers of skin composed of? (Pg. 936-9 ...
Chapter 14 - Angelo State University
... than protozoans to the extreme elongation seen in tapeworms which can be 10 to 15 m, but most are small to moderate size. • Most are white or colorless or owe their color to the food they ingest; Free-living worms are often gray, brown or black (when not white), but some are brightly colored. ...
... than protozoans to the extreme elongation seen in tapeworms which can be 10 to 15 m, but most are small to moderate size. • Most are white or colorless or owe their color to the food they ingest; Free-living worms are often gray, brown or black (when not white), but some are brightly colored. ...
worms - Quia
... • Example: Planaria – Scavenger – Transparent – 3 layers ectoderm – protection; mesoderm – nerves and muscle; endoderm – internal organs – Acoelomate –no body cavity b/t body wall and digestive tube – Mouth – round opening at end of pharynx • Located half way down on ventral (underside) side ...
... • Example: Planaria – Scavenger – Transparent – 3 layers ectoderm – protection; mesoderm – nerves and muscle; endoderm – internal organs – Acoelomate –no body cavity b/t body wall and digestive tube – Mouth – round opening at end of pharynx • Located half way down on ventral (underside) side ...
There are approximately 206 bones in your body and 22* of them
... There are approximately 206 bones in your body and 22* of them belong to your skull. These bones, all irregular in shape, fit together like puzzle pieces. *Except your teeth. While teeth are bone-like structures and are located in the skull, they are not counted. ...
... There are approximately 206 bones in your body and 22* of them belong to your skull. These bones, all irregular in shape, fit together like puzzle pieces. *Except your teeth. While teeth are bone-like structures and are located in the skull, they are not counted. ...
Organ Systems
... A. Tissue, Cell, Organ, Organ System, Organism B. Cell, Tissue, Organ System, Organ, Organism C. Cell, Tissue, Organ, Organ System, Organism D. Cell, Organ, Tissue, Organ System, Organism ...
... A. Tissue, Cell, Organ, Organ System, Organism B. Cell, Tissue, Organ System, Organ, Organism C. Cell, Tissue, Organ, Organ System, Organism D. Cell, Organ, Tissue, Organ System, Organism ...
Cells - busadmin
... median plane that divides the body into left and the right sides. Any plane parallel to the midsagittal or median plane is called a parasagittal or paramedian plane (para meaning besides). The second plane is a horizontal cut which illustrates the horizontal or transverse plane. This is the equivale ...
... median plane that divides the body into left and the right sides. Any plane parallel to the midsagittal or median plane is called a parasagittal or paramedian plane (para meaning besides). The second plane is a horizontal cut which illustrates the horizontal or transverse plane. This is the equivale ...
lecture notes ch32 Intro Animal Evolution
... sides. Some Bilateria have radial symmetry as adults (e.g. sea stars, sea cucumbers), but all are bilateral at some point during early development. Bilateria are triploblastic: they have endoderm, ectoderm, and they also have a mesoderm and the tissues that develop from the mesoderm. 11) Bilateral s ...
... sides. Some Bilateria have radial symmetry as adults (e.g. sea stars, sea cucumbers), but all are bilateral at some point during early development. Bilateria are triploblastic: they have endoderm, ectoderm, and they also have a mesoderm and the tissues that develop from the mesoderm. 11) Bilateral s ...
File
... b) Give an example of an animal that would have an open system, and one that would have a closed one. 2. How is a fish’s heart different from a human’s? 3. a) How many chambers does an amphibian’s heart have? b) What does this mean then? ...
... b) Give an example of an animal that would have an open system, and one that would have a closed one. 2. How is a fish’s heart different from a human’s? 3. a) How many chambers does an amphibian’s heart have? b) What does this mean then? ...
Animal Kingdom Webquest
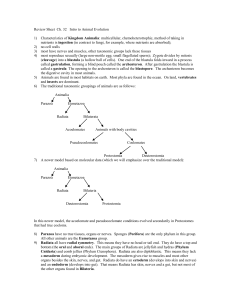
... 15. (http://mansfield.osu.edu/~sabedon/campbl32.htm) In organisms that are triploblastic and contain the mesodermal layer of cells, this mesoderm layer can interact with the endoderm layer in one of three ways to create three distinct groups of organisms. Describe them: i. acoelomates: _____________ ...
... 15. (http://mansfield.osu.edu/~sabedon/campbl32.htm) In organisms that are triploblastic and contain the mesodermal layer of cells, this mesoderm layer can interact with the endoderm layer in one of three ways to create three distinct groups of organisms. Describe them: i. acoelomates: _____________ ...
In animal embryos, the ectoderm gives rise to ______.
... kinds of spiders bite humans and other animals when threatened the spider's segments are fused into three sections: the forebody, the abdomen, and the hindbody spiders have a closed circulatory system with a heart which pumps blood into tissues and back to book lungs for oxygenation spiders do not h ...
... kinds of spiders bite humans and other animals when threatened the spider's segments are fused into three sections: the forebody, the abdomen, and the hindbody spiders have a closed circulatory system with a heart which pumps blood into tissues and back to book lungs for oxygenation spiders do not h ...
Period 1 -Human Body Systems Name: Reproductive System
... Function: Controls the whole body – controls interactions and responses to the outside world. Parts – brain, spinal cord, nerves Secondary Systems – Skeletal – brain protected by skull Muscular – receives messages to contract and produce movement Urinary – regulates ions that are used to make a nerv ...
... Function: Controls the whole body – controls interactions and responses to the outside world. Parts – brain, spinal cord, nerves Secondary Systems – Skeletal – brain protected by skull Muscular – receives messages to contract and produce movement Urinary – regulates ions that are used to make a nerv ...
Phylum Annelida
... with blood • Complete digestive tract with mouthparts as modified appendages • Open circulatory system with dorsal contractile heart ...
... with blood • Complete digestive tract with mouthparts as modified appendages • Open circulatory system with dorsal contractile heart ...
Lower Extremity Anatomy
... • Tibial Plateau – widened medial and lateral surfaces for articulation with femur • Intercondylar eminence (Tibial Spine) – between the plateaus with two peaks (tubercles) • Tibial Tuberosity – site of attachment of patellar ligament anteriorly ...
... • Tibial Plateau – widened medial and lateral surfaces for articulation with femur • Intercondylar eminence (Tibial Spine) – between the plateaus with two peaks (tubercles) • Tibial Tuberosity – site of attachment of patellar ligament anteriorly ...
Animal Taxonomy
... Chordates have a tail posterior to the anus In many species, the tail is lost during embryonic development; if not it can often be used for movement Urochordates and cephalochordates Although invertebrates, are more closely related to vertebrates Tunicates and lancelets: marine filter feeders Ja ...
... Chordates have a tail posterior to the anus In many species, the tail is lost during embryonic development; if not it can often be used for movement Urochordates and cephalochordates Although invertebrates, are more closely related to vertebrates Tunicates and lancelets: marine filter feeders Ja ...
Developmental Issues - Core Constellations
... and communications system. Its main function is gathering and integrating information. Organs: Skin (outer layer), nervous system, sense organs, brain. Body-mind Function: Think & perceive (“mental-intellectual”) Facing. Mesoderm Definition: Middle (= “meso-“) layer of three primary germ layers of ...
... and communications system. Its main function is gathering and integrating information. Organs: Skin (outer layer), nervous system, sense organs, brain. Body-mind Function: Think & perceive (“mental-intellectual”) Facing. Mesoderm Definition: Middle (= “meso-“) layer of three primary germ layers of ...
tissues - Immaculateheartacademy.org
... A tissue is a group of cells that have a similar structure and function The microscopic study of tissues is called histology ...
... A tissue is a group of cells that have a similar structure and function The microscopic study of tissues is called histology ...
human_body_systems_thyne
... • The blood then returns to the heart where the left side pumps it to the rest of the body ...
... • The blood then returns to the heart where the left side pumps it to the rest of the body ...
1 Name: ______ __ Date: ______ Block: ______ Classification
... The phylum Cnidaria includes jellyfish, corals, sea pens, sea anemones, and hydras. This phylum contains the most venomous marine creature; the Australian box jellyfish. It is known to kill more people than sharks, crocodiles, and stonefish combined. It can cause shock and heart failure within minut ...
... The phylum Cnidaria includes jellyfish, corals, sea pens, sea anemones, and hydras. This phylum contains the most venomous marine creature; the Australian box jellyfish. It is known to kill more people than sharks, crocodiles, and stonefish combined. It can cause shock and heart failure within minut ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.