BODY SYSTEMS
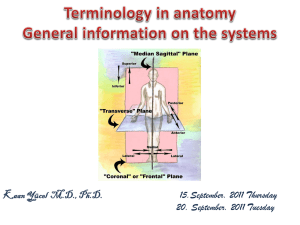
... ****Remember it cuts the body into front and back TRANSVERSE PLANE – a horizontal cut that divides the body into upper and lower parts, usually at the umbilicus (belly button) ...
... ****Remember it cuts the body into front and back TRANSVERSE PLANE – a horizontal cut that divides the body into upper and lower parts, usually at the umbilicus (belly button) ...
PowerPoint Sunusu
... • Oral and digestive – mouth and cavities of the digestive organs • Nasal –located within and posterior to the nose • Orbital – house the eyes • Middle ear – contain bones (ossicles) that transmit sound vibrations • Synovial – joint cavities ...
... • Oral and digestive – mouth and cavities of the digestive organs • Nasal –located within and posterior to the nose • Orbital – house the eyes • Middle ear – contain bones (ossicles) that transmit sound vibrations • Synovial – joint cavities ...
Phylum: Annelida
... -cylindrical elongated segmented bodies; segments divided by septa -well developed true coelom -closed circulatory system with one to several hearts and dorsal and ventral vessels -more efficient excretory system of nephridia -well developed muscular system with circular and longitudinal muscle laye ...
... -cylindrical elongated segmented bodies; segments divided by septa -well developed true coelom -closed circulatory system with one to several hearts and dorsal and ventral vessels -more efficient excretory system of nephridia -well developed muscular system with circular and longitudinal muscle laye ...
ANIMAL KINGDOM
... b) Osteichthyes - bony fish with scales - when they spawn large numbers of eggs & sperm are released into the water & few will reach adulthood marine & aquatic - bass & catfish c) Amphibia - frogs, toads, salamanders - aquatic & terrestrial - eggs are fertilized externally, have no shells, & are lai ...
... b) Osteichthyes - bony fish with scales - when they spawn large numbers of eggs & sperm are released into the water & few will reach adulthood marine & aquatic - bass & catfish c) Amphibia - frogs, toads, salamanders - aquatic & terrestrial - eggs are fertilized externally, have no shells, & are lai ...
Section 29-2 - Pearson School
... 24. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about invertebrate reproduction. a. Most invertebrates reproduce sexually in one part of their life cycle. b. Asexual reproduction maintains genetic diversity in a population. c. Asexual reproduction includes budding and division in two. d. Most in ...
... 24. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about invertebrate reproduction. a. Most invertebrates reproduce sexually in one part of their life cycle. b. Asexual reproduction maintains genetic diversity in a population. c. Asexual reproduction includes budding and division in two. d. Most in ...
body systems - Mr. McKittrick`s Website
... 4. Endocrine System endocrine glands • produces hormones (chemical messengers) • hormones secrete into blood and are carried to every cell in body • hormones regulate the activity of specific tissues and organs ...
... 4. Endocrine System endocrine glands • produces hormones (chemical messengers) • hormones secrete into blood and are carried to every cell in body • hormones regulate the activity of specific tissues and organs ...
Sample
... a. Outer surface of the skin (including the eye). Interior surface for all body cavities. ...
... a. Outer surface of the skin (including the eye). Interior surface for all body cavities. ...
Animal Diversity Part I
... respiratory and reproductive tracts; the mesoderm layer, sandwiched between the other two, eventually gives rise to muscle, organs, and supportive tissues. Triploblastic animals, those possessing three tissue layers, are further classified by whether or not they have a body cavity called a coelom (p ...
... respiratory and reproductive tracts; the mesoderm layer, sandwiched between the other two, eventually gives rise to muscle, organs, and supportive tissues. Triploblastic animals, those possessing three tissue layers, are further classified by whether or not they have a body cavity called a coelom (p ...
Question Bank Kingdom Animalia
... These are the first truly terrestrial animals among the higher group of vertebrates (Reptilia, Aves, Mammalia). These show following characteristic features : (i) Body is divisible into head, neck and trunk. Tail is well developed in some, while it is reduced in others. (ii) Two pairs of pentadactyl ...
... These are the first truly terrestrial animals among the higher group of vertebrates (Reptilia, Aves, Mammalia). These show following characteristic features : (i) Body is divisible into head, neck and trunk. Tail is well developed in some, while it is reduced in others. (ii) Two pairs of pentadactyl ...
Embryology And Anatomy Of The Eye And Ocular
... The sclera • The sclera, also known as the white of the eye, is the opaque, fibrous, protective, outer layer of the eye containing collagen and elastic fiber. • It is of variable thickness, 1 mm around the optic nerve head and 0.3 mm just posterior to the muscle insertions. ...
... The sclera • The sclera, also known as the white of the eye, is the opaque, fibrous, protective, outer layer of the eye containing collagen and elastic fiber. • It is of variable thickness, 1 mm around the optic nerve head and 0.3 mm just posterior to the muscle insertions. ...
Arthropods
... nerves that send incoming and outgoing messages. They have sophisticated sense organs and can see and taste ...
... nerves that send incoming and outgoing messages. They have sophisticated sense organs and can see and taste ...
upper limb
... radiate out from the nipple The main duct from each lobe opens separately on the summit of the nipple called Ampulla Base of nipple is surrounded by AREOLA Tiny tubercles on the areola produced by the underlying areolar glands ...
... radiate out from the nipple The main duct from each lobe opens separately on the summit of the nipple called Ampulla Base of nipple is surrounded by AREOLA Tiny tubercles on the areola produced by the underlying areolar glands ...
1 1 Phylum Platyhelminthes They exhibit bilateral symmetry
... They exhibit bilateral symmetry, cephalization, bodies are dorsoventrally flattened. Acoelomates with 3 germ layers The mesoderm gives rise to muscles, various organs systems, and the parenchyma Evolutionary Relationships among Flatworms What all flatworms have in common, apart from their flatness, ...
... They exhibit bilateral symmetry, cephalization, bodies are dorsoventrally flattened. Acoelomates with 3 germ layers The mesoderm gives rise to muscles, various organs systems, and the parenchyma Evolutionary Relationships among Flatworms What all flatworms have in common, apart from their flatness, ...
simple animals
... • Sponges consist of a noncellular mesohyl layer between two cell layers • Amoebocytes are found in the mesohyl and play roles in digestion and structure • Most sponges are hermaphrodites: Each individual functions as both male and female • Some sponges produce asexual reproductive bodies called ge ...
... • Sponges consist of a noncellular mesohyl layer between two cell layers • Amoebocytes are found in the mesohyl and play roles in digestion and structure • Most sponges are hermaphrodites: Each individual functions as both male and female • Some sponges produce asexual reproductive bodies called ge ...
Anatomical Terms Worksheet
... the human skeleton is made up of two main sections the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton the axial skeleton is made up of bones that lie around the long axis of your body these bones include your ribs sternum skull and spinal column the appendicular skeleton contains the bones of your lim ...
... the human skeleton is made up of two main sections the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton the axial skeleton is made up of bones that lie around the long axis of your body these bones include your ribs sternum skull and spinal column the appendicular skeleton contains the bones of your lim ...
LT 6 Anatomical Terms
... the human skeleton is made up of two main sections the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton the axial skeleton is made up of bones that lie around the long axis of your body these bones include your ribs sternum skull and spinal column the appendicular skeleton contains the bones of your lim ...
... the human skeleton is made up of two main sections the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton the axial skeleton is made up of bones that lie around the long axis of your body these bones include your ribs sternum skull and spinal column the appendicular skeleton contains the bones of your lim ...
Section 25.2 Summary – pages 680
... independently. However, they are not totally independent of each other because materials pass from one segment to another through a circulatory and nervous system that connects them. • Therefore, they have great flexibility and mobility. • Each segment repeats many of the organs in the adjacent segm ...
... independently. However, they are not totally independent of each other because materials pass from one segment to another through a circulatory and nervous system that connects them. • Therefore, they have great flexibility and mobility. • Each segment repeats many of the organs in the adjacent segm ...
Biology\Fish Unit
... Dorsal Fins (usually 2) – are on top of fish’s back; the front fin is the anterior dorsal fin, the back fin is the posterior dorsal fin (posterior dorsal fin has rays-other fin has spines) Anal fin – on ventral surface (helps keep fish upright and moving in straight line) Pelvic fins (paired) – foun ...
... Dorsal Fins (usually 2) – are on top of fish’s back; the front fin is the anterior dorsal fin, the back fin is the posterior dorsal fin (posterior dorsal fin has rays-other fin has spines) Anal fin – on ventral surface (helps keep fish upright and moving in straight line) Pelvic fins (paired) – foun ...
Biology 320 Invertebrate Zoology Fall 2005
... ► Invagination of exoskeleton which contains many smaller invaginations (large SA) ► Exchange occurs between surfaces of book lungs and blood ...
... ► Invagination of exoskeleton which contains many smaller invaginations (large SA) ► Exchange occurs between surfaces of book lungs and blood ...
Chapter 03 IR
... 1. List some of the different systems of the human body and give an example of a fluid dynamic element of each of these systems. Answer: The skin has a normal flow rate of 8% of the total blood volume that can increase to 30% when the body is trying to cool itself. The heart pumps approximately 3,60 ...
... 1. List some of the different systems of the human body and give an example of a fluid dynamic element of each of these systems. Answer: The skin has a normal flow rate of 8% of the total blood volume that can increase to 30% when the body is trying to cool itself. The heart pumps approximately 3,60 ...
Vital Functions for Human Life
... However, this is just one of several roles that the urinary system plays in maintaining homeostasis of body fluids, so it will be explored more extensively in the next vital function category involving body fluids. ...
... However, this is just one of several roles that the urinary system plays in maintaining homeostasis of body fluids, so it will be explored more extensively in the next vital function category involving body fluids. ...
ST110 Organ Systems_BB
... Identify the primary functions of each system Identify and discuss the major subdivisions of the reproductive system ...
... Identify the primary functions of each system Identify and discuss the major subdivisions of the reproductive system ...
File
... oxygen our bodies need and gets rid of the carbon dioxide so that it does not build up in our bodies and poison us. ...
... oxygen our bodies need and gets rid of the carbon dioxide so that it does not build up in our bodies and poison us. ...
Anatomical Planes
... regions, such as the thorax and abdomen. Systemic anatomy ;is the method of studying the body by systems, for example, the circulatory and reproductive systems. ...
... regions, such as the thorax and abdomen. Systemic anatomy ;is the method of studying the body by systems, for example, the circulatory and reproductive systems. ...
Organ Systems in Plants and Animals
... 4. Explain how the respiratory, circulatory, and nervous systems maintain homeostasis while you are playing outside on a sunny day. 5. Explain how the muscular and skeletal systems work together to maintain homeostasis while you are playing outside on a sunny day. ...
... 4. Explain how the respiratory, circulatory, and nervous systems maintain homeostasis while you are playing outside on a sunny day. 5. Explain how the muscular and skeletal systems work together to maintain homeostasis while you are playing outside on a sunny day. ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.