Characteristics
... – Herbivores are animals that eat plants, including roots, stems, leaves, flowers and fruits. – Carnivores feed on other animals. – Filter feeders are aquatic animals that strain tiny floating plants and animals from the water around them. – Detrivores are animals that feed on pieces of decaying pla ...
... – Herbivores are animals that eat plants, including roots, stems, leaves, flowers and fruits. – Carnivores feed on other animals. – Filter feeders are aquatic animals that strain tiny floating plants and animals from the water around them. – Detrivores are animals that feed on pieces of decaying pla ...
Animals
... backbones. Other chordates are the tunicates (sea squirts) and lancelets. Chordates are bilaterally symmetric, coelomate, deuterostomes. They are characterized by having a notochord, a long rod of stiffened tissue that supports the body and runs along the back. In many chordates (including us), the ...
... backbones. Other chordates are the tunicates (sea squirts) and lancelets. Chordates are bilaterally symmetric, coelomate, deuterostomes. They are characterized by having a notochord, a long rod of stiffened tissue that supports the body and runs along the back. In many chordates (including us), the ...
Animals - NIU Department of Biological Sciences
... backbones. Other chordates are the tunicates (sea squirts) and lancelets. Chordates are bilaterally symmetric, coelomate, deuterostomes. They are characterized by having a notochord, a long rod of stiffened tissue that supports the body and runs along the back. In many chordates (including us), the ...
... backbones. Other chordates are the tunicates (sea squirts) and lancelets. Chordates are bilaterally symmetric, coelomate, deuterostomes. They are characterized by having a notochord, a long rod of stiffened tissue that supports the body and runs along the back. In many chordates (including us), the ...
animalintro - Otterville R
... (folds inward at one point) • Called Gastrulation • The opening is called the blastopore • The center is the primitive gut or Archenteron ...
... (folds inward at one point) • Called Gastrulation • The opening is called the blastopore • The center is the primitive gut or Archenteron ...
ZOO 261
... The Porifera are asymmetrical or radially symmetrical, aquatic (mostly marine), sedantry animals, but have a ciliated larva. The body is perforated by numerous pores serving for the igress and egress of water, with a single body cavity (the paragaster) which is lined with peculiar collared-cells, an ...
... The Porifera are asymmetrical or radially symmetrical, aquatic (mostly marine), sedantry animals, but have a ciliated larva. The body is perforated by numerous pores serving for the igress and egress of water, with a single body cavity (the paragaster) which is lined with peculiar collared-cells, an ...
Science Grade 7 Unit 08: Structure and Function oI Living Systems
... A student is investigating the effect of length of exercise time on heart rate. She performed three trials over a period of three days. Based on her data, she concluded that exercising for longer times results in a continued increase in heart rate. Which of the following data tables accurately repre ...
... A student is investigating the effect of length of exercise time on heart rate. She performed three trials over a period of three days. Based on her data, she concluded that exercising for longer times results in a continued increase in heart rate. Which of the following data tables accurately repre ...
arthropoda general characters
... Phlyum Arlhropoda was established by Von Sicbold. Arlhropoda constitute about 80% of the known animal species. Insecta constitutes the largest class in the animal kingdom. They exhibit the greatest adaptive radiation. Athropods are the most successful of all the known animal groups. it is due to Pre ...
... Phlyum Arlhropoda was established by Von Sicbold. Arlhropoda constitute about 80% of the known animal species. Insecta constitutes the largest class in the animal kingdom. They exhibit the greatest adaptive radiation. Athropods are the most successful of all the known animal groups. it is due to Pre ...
Introduction to Animals
... (folds inward at one point) • Called Gastrulation • The opening is called the blastopore • The center is the primitive gut or Archenteron ...
... (folds inward at one point) • Called Gastrulation • The opening is called the blastopore • The center is the primitive gut or Archenteron ...
Jeopardy Game Template
... In the CNS; Controls involuntary functions such as breathing and heart rate next ...
... In the CNS; Controls involuntary functions such as breathing and heart rate next ...
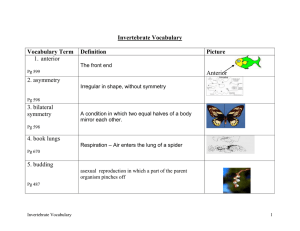
Invertebrate Vocabulary
... A carbohydrate that forms part of the exoskeleton of arthropods and other organisms, such as insects, crustaceans, fungi and some algae. ...
... A carbohydrate that forms part of the exoskeleton of arthropods and other organisms, such as insects, crustaceans, fungi and some algae. ...
Basic Human Anatomy - The Brookside Associates
... (2) As serous membranes, simple squamous epithelial tissue lines the cavities of the abdomen (peritoneal lining) and the chest (pleural lining). Serous membranes are membranes which secrete a lubricating fluid. (3) Epithelial tissue forms the secretory part of glands and also parts of the various se ...
... (2) As serous membranes, simple squamous epithelial tissue lines the cavities of the abdomen (peritoneal lining) and the chest (pleural lining). Serous membranes are membranes which secrete a lubricating fluid. (3) Epithelial tissue forms the secretory part of glands and also parts of the various se ...
File
... 4. Which body system contains the brain and the spinal cord? 5. Name the type of connective tissue that holds the bone together at the joints. 6. Which abdominal region is above the hypogastric region? 7. Define the suffix -megaly. 8. What is the function of the sagittal/mid-sagittal plane? 9. Which ...
... 4. Which body system contains the brain and the spinal cord? 5. Name the type of connective tissue that holds the bone together at the joints. 6. Which abdominal region is above the hypogastric region? 7. Define the suffix -megaly. 8. What is the function of the sagittal/mid-sagittal plane? 9. Which ...
File - Anatomy & Physiology
... Epithelium: layers of cells that line the cavity and cover flat surfaces Basement membrane: Basal Lamina (protein scaffolding) secreted by epithelial cells Reticular Lamina (crossed collagen fiber network) that support and anchor the epithelium ...
... Epithelium: layers of cells that line the cavity and cover flat surfaces Basement membrane: Basal Lamina (protein scaffolding) secreted by epithelial cells Reticular Lamina (crossed collagen fiber network) that support and anchor the epithelium ...
vertebrates - Cloudfront.net
... What is a “vertebrate?” • Animal that has a backbone, or a vertebral column • All are part of the Chordate Phylum ...
... What is a “vertebrate?” • Animal that has a backbone, or a vertebral column • All are part of the Chordate Phylum ...
Structure and Movement
... Chapter 17 Notes Section 1 The Skeletal System A. All the bones in your body make up your skeletal system, which has five major functions. 1. Your skeleton gives shape and support to your body. 2. Your bones protect your internal organs. 3. Major muscles are attached to your bones. 4. Blood cells ar ...
... Chapter 17 Notes Section 1 The Skeletal System A. All the bones in your body make up your skeletal system, which has five major functions. 1. Your skeleton gives shape and support to your body. 2. Your bones protect your internal organs. 3. Major muscles are attached to your bones. 4. Blood cells ar ...
Mader/Biology, 11/e – Chapter Outline
... 4) Fertilized eggs are enclosed in a cocoon and hatch in two to three weeks into tiny worms. d. Nervous system 1) Planarias have a ladder-type nervous system. 2) Paired ganglia function as a brain in the head region. 3) The head is bluntly arrow-shaped; side extensions (auricles) are sensory organs ...
... 4) Fertilized eggs are enclosed in a cocoon and hatch in two to three weeks into tiny worms. d. Nervous system 1) Planarias have a ladder-type nervous system. 2) Paired ganglia function as a brain in the head region. 3) The head is bluntly arrow-shaped; side extensions (auricles) are sensory organs ...
invertebrate zoology..
... enzymatic digestion of food particles). Intestine and anus present. Chapter 13 Phylum Mollusca - means soft 1) True coelomic animals 2) Belong protostomates have blastopore 3) All organ systems present and well-developed 4) Tcochophore larva: Free-swimming ciliated marine larva Biological Contributi ...
... enzymatic digestion of food particles). Intestine and anus present. Chapter 13 Phylum Mollusca - means soft 1) True coelomic animals 2) Belong protostomates have blastopore 3) All organ systems present and well-developed 4) Tcochophore larva: Free-swimming ciliated marine larva Biological Contributi ...
Name Nick DiMucci
... The condition known as jaundice (yellow skin and eyes) is a result of a build-up of bilirubin and is usually a sign of liver malfunction. Newborn human infants often go through a period of fetal jaundice in which they turn yellow. This usually reflects not a liver malfunction, but rather the destruc ...
... The condition known as jaundice (yellow skin and eyes) is a result of a build-up of bilirubin and is usually a sign of liver malfunction. Newborn human infants often go through a period of fetal jaundice in which they turn yellow. This usually reflects not a liver malfunction, but rather the destruc ...
Anatomical Terminology
... Parietal portion of the serous membrane from the OUTER wall of the body cavity Visceral portion covers surfaces of the internal organs where they protrude into the body cavity. Consider a Peanut… • Shell is the body wall, fibrous membrane attached to the inside of the shell is the parietal mem ...
... Parietal portion of the serous membrane from the OUTER wall of the body cavity Visceral portion covers surfaces of the internal organs where they protrude into the body cavity. Consider a Peanut… • Shell is the body wall, fibrous membrane attached to the inside of the shell is the parietal mem ...
UNIT
... 1. Describe the major organs and functions of the various systems of the human body. 2. Explain how all the parts of each system work together to perform a specific functions (movement, digesting food, filtering wastes, circulation of blood, obtaining and using oxygen, reproduction, etc.) 3. Describ ...
... 1. Describe the major organs and functions of the various systems of the human body. 2. Explain how all the parts of each system work together to perform a specific functions (movement, digesting food, filtering wastes, circulation of blood, obtaining and using oxygen, reproduction, etc.) 3. Describ ...
animal-notes-ch-32
... * Belzer said: In most other groups, the blastula undergoes more complicated rearrangement. It first invaginates to form a gastrula with a digestive chamber, and two separate germ layers - an external ectoderm and an internal endoderm. In most cases, a mesoderm also develops between them. These germ ...
... * Belzer said: In most other groups, the blastula undergoes more complicated rearrangement. It first invaginates to form a gastrula with a digestive chamber, and two separate germ layers - an external ectoderm and an internal endoderm. In most cases, a mesoderm also develops between them. These germ ...
Introduction to the Human body/Chapter I
... describes the consequences of the improper functioning of body parts. ...
... describes the consequences of the improper functioning of body parts. ...
PowerPoint to accompany Hole`s Human Anatomy and Physiology
... – Why is that? Because they perform different ______________________________________ ...
... – Why is that? Because they perform different ______________________________________ ...
Animal Evolution
... Arthropoda), has a left side and a right side. Only one imaginary cut divides the animal into mirror-image halves. ...
... Arthropoda), has a left side and a right side. Only one imaginary cut divides the animal into mirror-image halves. ...
Skeletal System Webquest
... 4. What is the job of the rib cage? How many pairs of ribs do humans have? ...
... 4. What is the job of the rib cage? How many pairs of ribs do humans have? ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.