Units 3-4 Review
... 1. Be able to break down classical and operant conditioning / differentiate between the two a. US, UR, NS, CS, CR b. Positive vs. Negative Reinforcement / Punishment c. Voluntary vs. Involuntary 2. Know the difference between observational and latent conditioning: a. Be able to describe the followin ...
... 1. Be able to break down classical and operant conditioning / differentiate between the two a. US, UR, NS, CS, CR b. Positive vs. Negative Reinforcement / Punishment c. Voluntary vs. Involuntary 2. Know the difference between observational and latent conditioning: a. Be able to describe the followin ...
introduction to psychology - Faculty Information System
... processes, whether the emotion was generated by everyday experiences (biases in recall of positive versus negative information) or generated by clinical disorders (schizophrenia, depression, posttraumatic stress disorder, etc.). We will read relevant journal articles and discuss/critique the article ...
... processes, whether the emotion was generated by everyday experiences (biases in recall of positive versus negative information) or generated by clinical disorders (schizophrenia, depression, posttraumatic stress disorder, etc.). We will read relevant journal articles and discuss/critique the article ...
Chapter 14
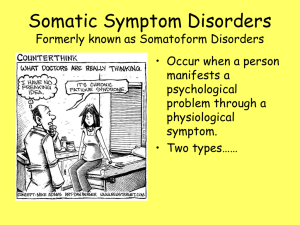
... Conversion disorder – voluntary motor or sensory dysfunction with psychological cause. Hypochondriasis – fear of illness. Pain disorder – pain whose onset, severity and maintenance have a psychological cause. ...
... Conversion disorder – voluntary motor or sensory dysfunction with psychological cause. Hypochondriasis – fear of illness. Pain disorder – pain whose onset, severity and maintenance have a psychological cause. ...
Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
... • A disorder in which a person experiences alterations in memory, identity, or consciousness – Very rare ...
... • A disorder in which a person experiences alterations in memory, identity, or consciousness – Very rare ...
Social
... males and females. The test showed that 30 percent of the sample was androgynous. This finding is most relevant to which of the following propositions? – (A) genotypic sex exerts the greatest influence on gender identity – (B) gender roles become less differentiated after puberty, as hormone levels ...
... males and females. The test showed that 30 percent of the sample was androgynous. This finding is most relevant to which of the following propositions? – (A) genotypic sex exerts the greatest influence on gender identity – (B) gender roles become less differentiated after puberty, as hormone levels ...
DISSOCIATIVE DISORDERS
... gain, obtaining drugs, avoiding work, prosecution, duty, or improving physical wellbeing. ...
... gain, obtaining drugs, avoiding work, prosecution, duty, or improving physical wellbeing. ...
Video-EEG Monitoring in Childhood Epilepsy
... Psychogenic seizures Psychosis Somatoform disorders Rage attacks ...
... Psychogenic seizures Psychosis Somatoform disorders Rage attacks ...
Module 49 Dissociative and Personality Disorders Outline
... a. Localized amnesia is present in an individual who has no memory of specific events that took place, usually traumatic. The loss of memory is localized with a specific window of time. For example, a survivor of a car wreck who has no memory of the experience until two days later is experiencing lo ...
... a. Localized amnesia is present in an individual who has no memory of specific events that took place, usually traumatic. The loss of memory is localized with a specific window of time. For example, a survivor of a car wreck who has no memory of the experience until two days later is experiencing lo ...
Module 69 - Dissociative Disorders
... • Mild dissociative experiences are quite common and completely normal (daydreaming) ...
... • Mild dissociative experiences are quite common and completely normal (daydreaming) ...
Dissociative Disorders - Weber State University
... A somatoform Disorder characterized by reported pain of sufficient duration and severity to cause significant life disruption and the absence of medical pathology that would explain the experienced pain. Subjectivity of Pain ...
... A somatoform Disorder characterized by reported pain of sufficient duration and severity to cause significant life disruption and the absence of medical pathology that would explain the experienced pain. Subjectivity of Pain ...
Before Milgram`s study on obedience, a team of psychiatrists
... b) changed its properties after it was recorded such that it was eventually accessible. c) Often, parents and their adult children disagree on the details of past events. d) Asking a leading question such as ‘what was the speed of the car before it smashed?’ results in some subjects falsely recallin ...
... b) changed its properties after it was recorded such that it was eventually accessible. c) Often, parents and their adult children disagree on the details of past events. d) Asking a leading question such as ‘what was the speed of the car before it smashed?’ results in some subjects falsely recallin ...
Dissociative Identity Disorder
... ones customary place of work, with inability to recall one’s past. Confusion about personal identity or assumes new identity (partial or complete) Not due to another dissociative disorder or direct effects of substances or GMC Causes significant distress or impairment in imp areas of functioni ...
... ones customary place of work, with inability to recall one’s past. Confusion about personal identity or assumes new identity (partial or complete) Not due to another dissociative disorder or direct effects of substances or GMC Causes significant distress or impairment in imp areas of functioni ...
Section 3: Dissociative Disorders
... from conscious thought – Somewhat common – Becomes a disorder when used to avoid stressful events or feelings – Lose memory of an event, forget identity ...
... from conscious thought – Somewhat common – Becomes a disorder when used to avoid stressful events or feelings – Lose memory of an event, forget identity ...
Dissociative disorders
... the loss of identity and travel to a new location • From the DSM-IV: • Sudden, unexpected travel away from home or one's customary place of work, with inability to recall one's past, • Confusion about personal identity, or the assumption of a new identity, or significant distress or impairment. http ...
... the loss of identity and travel to a new location • From the DSM-IV: • Sudden, unexpected travel away from home or one's customary place of work, with inability to recall one's past, • Confusion about personal identity, or the assumption of a new identity, or significant distress or impairment. http ...
Psychological Disorders
... • Selective amnesia happens when a person can recall only small parts of events that took place in a defined period of time. For example, an abuse victim may recall only some parts of the series of events around the abuse. • Generalized amnesia is diagnosed when a person's amnesia encompasses his or ...
... • Selective amnesia happens when a person can recall only small parts of events that took place in a defined period of time. For example, an abuse victim may recall only some parts of the series of events around the abuse. • Generalized amnesia is diagnosed when a person's amnesia encompasses his or ...
Dissociative Disorders
... Extreme and rare, involves flight from home and the assumption of a new identity, with amnesia for past identity and events. A. Sudden, unexpected travel away from home or one’s customary place of work, with inability to recall one’s past B. Confusion about personal identity or assumption of a new i ...
... Extreme and rare, involves flight from home and the assumption of a new identity, with amnesia for past identity and events. A. Sudden, unexpected travel away from home or one’s customary place of work, with inability to recall one’s past B. Confusion about personal identity or assumption of a new i ...
Chap16
... A feeling of detachment or estrangement from one’s self. A person may feel like an observer of their own mental processes or body. Includes sensory anesthesia, lack of affect, a feeling of lack of control of one’s actions. Voluntarily induced in religious and trance ...
... A feeling of detachment or estrangement from one’s self. A person may feel like an observer of their own mental processes or body. Includes sensory anesthesia, lack of affect, a feeling of lack of control of one’s actions. Voluntarily induced in religious and trance ...
What Is Amnesia? What Causes Amnesia? When people lose their
... Anterograde amnesia - the patient cannot remember new information. Things that happened recently, information that should be stored into short-term memory disappear. This is usually caused by brain trauma (brain damage from a blow to the head, for example). However, a patient with anterograde amnesi ...
... Anterograde amnesia - the patient cannot remember new information. Things that happened recently, information that should be stored into short-term memory disappear. This is usually caused by brain trauma (brain damage from a blow to the head, for example). However, a patient with anterograde amnesi ...
Syllabus
... COURSE DESCRIPTION: Psychology is a regular level class for students who are interested in an introduction to the science of Psychology. This course will study major topics in Psychology through lectures, group projects, discussions, and independent research. Students will be expected to demonstrate ...
... COURSE DESCRIPTION: Psychology is a regular level class for students who are interested in an introduction to the science of Psychology. This course will study major topics in Psychology through lectures, group projects, discussions, and independent research. Students will be expected to demonstrate ...
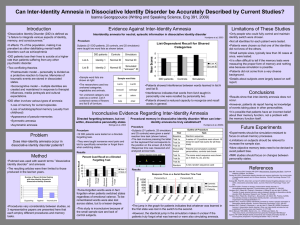
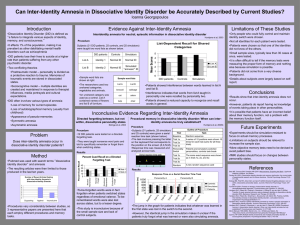
Conflicting Views on Inter-Identity Amnesia in Patients
... occur. •However, patients do report having no knowledge of events taking place in other personalities. •It is possible that patients have an incorrect belief about their memory function, not a problem with the memory function itself. ...
... occur. •However, patients do report having no knowledge of events taking place in other personalities. •It is possible that patients have an incorrect belief about their memory function, not a problem with the memory function itself. ...
Can Inter-Identity Amnesia in Dissociative Identity
... occur. •However, patients do report having no knowledge of events taking place in other personalities. •It is possible that patients have an incorrect belief about their memory function, not a problem with the memory function itself. ...
... occur. •However, patients do report having no knowledge of events taking place in other personalities. •It is possible that patients have an incorrect belief about their memory function, not a problem with the memory function itself. ...
DISSOCIATIVE DISORDER
... Dissociative Amnesia Characterized by inability to remember information, usually related to stressful or ...
... Dissociative Amnesia Characterized by inability to remember information, usually related to stressful or ...
Lec 18 - Forgetting
... Decay theory Decay theory states that when something new is learned, a neurochemical, physical "memory trace" is formed in the brain and over time this trace tends to disintegrate, unless it is occasionally used. Definitions and Controversy Forgetting can have very different causes than simply remov ...
... Decay theory Decay theory states that when something new is learned, a neurochemical, physical "memory trace" is formed in the brain and over time this trace tends to disintegrate, unless it is occasionally used. Definitions and Controversy Forgetting can have very different causes than simply remov ...