Skull - USMF
... second visceral arch, and it has two nuclei of ossification (one before birth and another at 2 years of age). Fusion of the parts of the temporal bone, begin after birth and continue until 13 years of age. The styloid process unites with temporal bone beginning with 2 years and lasted until 12 years ...
... second visceral arch, and it has two nuclei of ossification (one before birth and another at 2 years of age). Fusion of the parts of the temporal bone, begin after birth and continue until 13 years of age. The styloid process unites with temporal bone beginning with 2 years and lasted until 12 years ...
Posterior abdominal wall
... The lumbar lymph trunks are formed by vessels draining from the lateral aortic nodes. Thus, either directly or after traversing intermediary groups, they carry lymph from: the lower limbs, the full thickness of the pelvic, perineal and infra-umbilical abdominal walls, the deep tissues of most of the ...
... The lumbar lymph trunks are formed by vessels draining from the lateral aortic nodes. Thus, either directly or after traversing intermediary groups, they carry lymph from: the lower limbs, the full thickness of the pelvic, perineal and infra-umbilical abdominal walls, the deep tissues of most of the ...
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10e (Marieb)
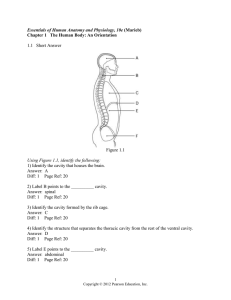
... A) femoral, popliteal, patellar B) brachial, antecubital, carpal C) nasal, oral, occipital D) acromial, sacral, gluteal E) pelvic, pubic, inguinal Answer: B Diff: 2 Page Ref: 16 ...
... A) femoral, popliteal, patellar B) brachial, antecubital, carpal C) nasal, oral, occipital D) acromial, sacral, gluteal E) pelvic, pubic, inguinal Answer: B Diff: 2 Page Ref: 16 ...
26-arches+venous&lymphatics2008-05
... 1-superficial circumflex iliac vein. 2-superficial epigastric vein. 3-superficial external pudendal vein. Another tributary is known as accessory vein, usually joins the great saphenous vein about the middle of the thigh. Many small veins on medial& lateral sides of the thigh drain into great saph ...
... 1-superficial circumflex iliac vein. 2-superficial epigastric vein. 3-superficial external pudendal vein. Another tributary is known as accessory vein, usually joins the great saphenous vein about the middle of the thigh. Many small veins on medial& lateral sides of the thigh drain into great saph ...
The Pterional Port in Dual-Port Endoscopy: A 2D and 3D
... the bone that was formed at the medial junction of the parasellar carotid canal and the optic canal. This was a critical landmark in locating the optic nerve canal as it joined the middle clinoid process and represented the pneumatization of the middle clinoid process and the lateral aspects of the ...
... the bone that was formed at the medial junction of the parasellar carotid canal and the optic canal. This was a critical landmark in locating the optic nerve canal as it joined the middle clinoid process and represented the pneumatization of the middle clinoid process and the lateral aspects of the ...
OMM06-ExternalOsteologyCranium
... Continue towards the vertex of the skull in the midline, and you will reach a depression about 1/3 of the way posteriorly on the vertex.—Translation: move about 1 – 2 ” behind the hair line (for most) and find a little depression. This is the start of the sagittal suture. The bregma is the junct ...
... Continue towards the vertex of the skull in the midline, and you will reach a depression about 1/3 of the way posteriorly on the vertex.—Translation: move about 1 – 2 ” behind the hair line (for most) and find a little depression. This is the start of the sagittal suture. The bregma is the junct ...
Hand Shao-Yang San
... • Location: On the dorsal side of the forearm and on the line connection Yangchi(SJ4) and the tip of the olecranon, 2 cun proximal to the dorsal crease of the wrist, between the radius and ulna. • Luo-Connecting point • Master point of Yang-Wei (Linking) Vessel ...
... • Location: On the dorsal side of the forearm and on the line connection Yangchi(SJ4) and the tip of the olecranon, 2 cun proximal to the dorsal crease of the wrist, between the radius and ulna. • Luo-Connecting point • Master point of Yang-Wei (Linking) Vessel ...
Variations in portal and hepatic vein branching of the liver
... c, d: On 3DCT, the round ligament of liver (yellow) is not connected to the umbilical portion but to the right portal vein branch (red arrow) (c: image viewed from the right side, d: image viewed from the caudal side). ...
... c, d: On 3DCT, the round ligament of liver (yellow) is not connected to the umbilical portion but to the right portal vein branch (red arrow) (c: image viewed from the right side, d: image viewed from the caudal side). ...
a comparative study of the pterygopalatine fossa and its ganglion in
... Blocking the contents of the pterygopalatine fossa (PPF) is a highly effective method in alleviating pain in trigeminal neuralgia (TN) and other facial pain syndromes. This, however, is not a widely used technique, due to the difficulty in locating the PPF which is obscured by bony and soft tissue s ...
... Blocking the contents of the pterygopalatine fossa (PPF) is a highly effective method in alleviating pain in trigeminal neuralgia (TN) and other facial pain syndromes. This, however, is not a widely used technique, due to the difficulty in locating the PPF which is obscured by bony and soft tissue s ...
PART II • LARYNX • TRACHEA • PHARYNX • ESOPHAGUS
... superior laryngeal nerve through the thyrohyoid membrane and branches to supply the internal surface of the larynx. The cricothyroid artery, a small branch of the superior thyroid artery, supplies the cricothyroid muscle. The inferior laryngeal artery (branch of the inferior thyroid artery fr ...
... superior laryngeal nerve through the thyrohyoid membrane and branches to supply the internal surface of the larynx. The cricothyroid artery, a small branch of the superior thyroid artery, supplies the cricothyroid muscle. The inferior laryngeal artery (branch of the inferior thyroid artery fr ...
An anatomic study of the positional relationships between the lateral
... the innervating branches (twig) to the lateral pterygoid muscle. The black square indicates the branch (twig) to the temporalis. A: The lateral pterygoid muscle is innervated by twigs from the anterior and middle deep temporal nerves and from the fork of the anterior deep temporal nerve and the main ...
... the innervating branches (twig) to the lateral pterygoid muscle. The black square indicates the branch (twig) to the temporalis. A: The lateral pterygoid muscle is innervated by twigs from the anterior and middle deep temporal nerves and from the fork of the anterior deep temporal nerve and the main ...
Movements of the Upper Cervical Assembly and Strain in the
... The Structure of Cervical Vertebrae It is easiest to start with the typical lower cervical vertebra and then to consider the special structure of the atlas and axis. ...
... The Structure of Cervical Vertebrae It is easiest to start with the typical lower cervical vertebra and then to consider the special structure of the atlas and axis. ...
Respiratory System Anatomy
... -supplies the nasopharynx especially the glands there 4) Nasal Branches: pass through sphenopalatine foramen to nasal cavity - 7 or 8 small nerves ...
... -supplies the nasopharynx especially the glands there 4) Nasal Branches: pass through sphenopalatine foramen to nasal cavity - 7 or 8 small nerves ...
Arteries of the Head and Neck
... – Supply the frontal part of the skull medially – Anastomose with the superficial temporal artery establishing a free communication between the internal and external carotid arteries ...
... – Supply the frontal part of the skull medially – Anastomose with the superficial temporal artery establishing a free communication between the internal and external carotid arteries ...
Pelvic Viscera
... The internal iliac artery gives rise to a complex network of arteries that anastomose around the uterus. This anastomosis network derives from the uterine arteries and supplies the uterus. There is some degree of overlap between the uterine arteries and ovarian artery descending from the abdominal a ...
... The internal iliac artery gives rise to a complex network of arteries that anastomose around the uterus. This anastomosis network derives from the uterine arteries and supplies the uterus. There is some degree of overlap between the uterine arteries and ovarian artery descending from the abdominal a ...
Development of the Inguinal Canal
... deep inguinal ring downward and medially to the superficial inguinal ring. It lies parallel to and immediately above the inguinal ligament. In the newborn child, the deep ring lies almost directly posterior to the superficial ring so that the canal is considerably shorter at this age. Later, as the ...
... deep inguinal ring downward and medially to the superficial inguinal ring. It lies parallel to and immediately above the inguinal ligament. In the newborn child, the deep ring lies almost directly posterior to the superficial ring so that the canal is considerably shorter at this age. Later, as the ...
Comprehensive Review Cranial Mechanics
... • All Midline individual bones are said to either Flex or Extend around a transverse axis • All Paired bones are said to either internally rotate or externally rotate • During Flexion Phase all midline bones Flex • During Flexion Phase all paired bones Externally Rotate • During Extension phase all ...
... • All Midline individual bones are said to either Flex or Extend around a transverse axis • All Paired bones are said to either internally rotate or externally rotate • During Flexion Phase all midline bones Flex • During Flexion Phase all paired bones Externally Rotate • During Extension phase all ...
Knee Anatomy
... Originates at the adductor hiatus and passes through the popliteal fossa, then deep to the fibrous arch over the soleus muscle Divides into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries at the distal aspect of the popliteus muscle ...
... Originates at the adductor hiatus and passes through the popliteal fossa, then deep to the fibrous arch over the soleus muscle Divides into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries at the distal aspect of the popliteus muscle ...
Manual Therapy for Motion Loss at the Knee
... I. Posterior tibial glide grade I-II* -Patient supine: knee flexed to 10-25 degrees with towel roll under knee -Posterior glide to tibia up to grade II slack zone only II. Traction -Patient prone: knee slightly flexed, stabilize femur with belt or hand -Distraction force along long axis of the tibia ...
... I. Posterior tibial glide grade I-II* -Patient supine: knee flexed to 10-25 degrees with towel roll under knee -Posterior glide to tibia up to grade II slack zone only II. Traction -Patient prone: knee slightly flexed, stabilize femur with belt or hand -Distraction force along long axis of the tibia ...
düzce tip dergi̇si̇
... which arises from medial cord. There was a communicating accessory branch 2.5 cm long running obliquely between the cords which formed the median nerve. Coracobrachialis muscle was innervated by a thin branch arising from lateral cord. Median nerve given two branches at a point 9 cm distal to its fo ...
... which arises from medial cord. There was a communicating accessory branch 2.5 cm long running obliquely between the cords which formed the median nerve. Coracobrachialis muscle was innervated by a thin branch arising from lateral cord. Median nerve given two branches at a point 9 cm distal to its fo ...
Multiple inflammatory arthropathies can affect the TMJ
... Sagittal PD-weighted images of the TMJ in the closed and open mouth positions. In the closed mouth position the mandibular condyle is concentrically seated within the glenoid fossa. However, the posterior margin of the posterior disc is situated far anterior to the 12 o’clock position (arrow), and t ...
... Sagittal PD-weighted images of the TMJ in the closed and open mouth positions. In the closed mouth position the mandibular condyle is concentrically seated within the glenoid fossa. However, the posterior margin of the posterior disc is situated far anterior to the 12 o’clock position (arrow), and t ...
CERVICO-AURICULAR FISTULAE
... arches on the dorsal end of the first groove which lies between. By growth and fusion, the tubercles and the immediately surrounding area give rise to the primitive pinna. This is situated around the end of the developing external auditory meatus. The tragus and its immediate area is derived from th ...
... arches on the dorsal end of the first groove which lies between. By growth and fusion, the tubercles and the immediately surrounding area give rise to the primitive pinna. This is situated around the end of the developing external auditory meatus. The tragus and its immediate area is derived from th ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.