Clavicle Fracture
... Most commonly a fall onto an outstretched arm from standing height Younger patient typically present after high energy trauma such as MVA ...
... Most commonly a fall onto an outstretched arm from standing height Younger patient typically present after high energy trauma such as MVA ...
Localisation of hypogastric nerves and pelvic plexus in relation to
... autonomic nerves in adults and their implications in pelvic surgery. Despite advances in nerve-sparing surgery, the pelvic plexus remains liable to iatrogenic injury due to the small size of the individual nerve fibers, the depth and narrowness of the pelvis, which can hinder precise surgical access ...
... autonomic nerves in adults and their implications in pelvic surgery. Despite advances in nerve-sparing surgery, the pelvic plexus remains liable to iatrogenic injury due to the small size of the individual nerve fibers, the depth and narrowness of the pelvis, which can hinder precise surgical access ...
Block 2 Unit 3 Objectives
... iv. Innervated by the afferent loop of the glossopharyngeal n. (CN IX) AND vagus n. (CN X) AND cervical sympathetic nn. Nerves and Plexuses 4. Describe the cervical and branchial plexuses in the neck. a. Cervical plexus (ventral rami C1-C4) i. Motor nerves 1. Superior root of ansa cervicalis (C1) a. ...
... iv. Innervated by the afferent loop of the glossopharyngeal n. (CN IX) AND vagus n. (CN X) AND cervical sympathetic nn. Nerves and Plexuses 4. Describe the cervical and branchial plexuses in the neck. a. Cervical plexus (ventral rami C1-C4) i. Motor nerves 1. Superior root of ansa cervicalis (C1) a. ...
MAXILLARy SWING APPROACH TO THE NASOPHARyNX
... important that the holes avoid the roots of the teeth by positioning the miniplates above or between the teeth roots if the height of the maxilla is inadequate. ...
... important that the holes avoid the roots of the teeth by positioning the miniplates above or between the teeth roots if the height of the maxilla is inadequate. ...
The Forearm 2
... extensor carpi radialis longus in the extensor compartment *Other books mention that the lateral compartment contain the Brachioradialis and the extensor carpi radialis longus because the origin of the two muscles is above the lateral epicondyle (common extensor origin/tendon) exactly from the later ...
... extensor carpi radialis longus in the extensor compartment *Other books mention that the lateral compartment contain the Brachioradialis and the extensor carpi radialis longus because the origin of the two muscles is above the lateral epicondyle (common extensor origin/tendon) exactly from the later ...
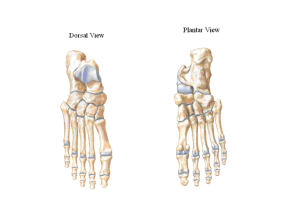
Sole - GMCH
... •O- Plantar from its own metatarsal ,dorsal from two metatarsal •I- Plantar – 3,4,5 digits dorsal extensor expansions •Dorsal-each arises by two metatarsal. - 2 are inserted on 2nd toe. -3,4 are inserted on 3rd and 4th toe. -Proximal phalanges & dorsal extensor expansion •N- lateral plantar nerve ...
... •O- Plantar from its own metatarsal ,dorsal from two metatarsal •I- Plantar – 3,4,5 digits dorsal extensor expansions •Dorsal-each arises by two metatarsal. - 2 are inserted on 2nd toe. -3,4 are inserted on 3rd and 4th toe. -Proximal phalanges & dorsal extensor expansion •N- lateral plantar nerve ...
1. Sympathetic fibers in the greater thoracic splanchnic nerve arise
... sympathetic fibers join spinal nerves at the cervical and lumbar levels, which are above and below the lateral horn. Third, some preganglionic fibers do not synapse in the trunk and, instead, form splanchnic nerves. These nerves descend into the abdomen and synapse in other ganglia. You really need ...
... sympathetic fibers join spinal nerves at the cervical and lumbar levels, which are above and below the lateral horn. Third, some preganglionic fibers do not synapse in the trunk and, instead, form splanchnic nerves. These nerves descend into the abdomen and synapse in other ganglia. You really need ...
The Neck
... • The skin overlying the trapezius muscle and that on the back of the scalp as high as the vertex, is supplied segmentally by the posterior rami of cervical nerves 25. • The skin of the front and sides of the neck is supplied by the anterior rami of the cervical nerves 2-4 through branches of the ce ...
... • The skin overlying the trapezius muscle and that on the back of the scalp as high as the vertex, is supplied segmentally by the posterior rami of cervical nerves 25. • The skin of the front and sides of the neck is supplied by the anterior rami of the cervical nerves 2-4 through branches of the ce ...
TUBERCLE OF ZUCKERKANDL Mean size(mm)
... makes the posterior extension in intimate relation with RLN and inferior thyroid artery10. Presence of TZ in patients is confirming the importance of TZ as a common anatomical part of thyroid gland. Incidence of TZ in more than 50% patients have been reported by many authors. Mohapatra et al 68%11, ...
... makes the posterior extension in intimate relation with RLN and inferior thyroid artery10. Presence of TZ in patients is confirming the importance of TZ as a common anatomical part of thyroid gland. Incidence of TZ in more than 50% patients have been reported by many authors. Mohapatra et al 68%11, ...
Spring 2002 3B
... 23) Cutting the _____ nerve could result in the condition known as wrist drop? a) radial nerve b) musculocutaneous nerve c) axillary nerve d) ulnar nerve e) median nerve 24) Which of the following is NOT true concerning Erb-Duchenne palsy? a) damage to spinal nerves C8 and T1 b) dropped shoulder c) ...
... 23) Cutting the _____ nerve could result in the condition known as wrist drop? a) radial nerve b) musculocutaneous nerve c) axillary nerve d) ulnar nerve e) median nerve 24) Which of the following is NOT true concerning Erb-Duchenne palsy? a) damage to spinal nerves C8 and T1 b) dropped shoulder c) ...
11_chapter 7
... infra-orbital rim - the rim situated beneath the orbit of the eye. the lower part of the bony eye socket rim. infra-tip lobule - The portion of the lobule between the tip defining points and the columellar-lobular angle. integument - an enveloping layer (as a skin or membrane) of an organism or one ...
... infra-orbital rim - the rim situated beneath the orbit of the eye. the lower part of the bony eye socket rim. infra-tip lobule - The portion of the lobule between the tip defining points and the columellar-lobular angle. integument - an enveloping layer (as a skin or membrane) of an organism or one ...
Spring 2002 3A
... 59) When we say that the lesser occipital nerve is derived from C2, and C3 spinal nerves we actually mean it is directly derived from _______________ of the spinal nerves a) the ventral roots b) the dorsal roots c) the ventral rami d) the meningeal ramus e) the dorsal rami 60) A spinal nerve root i ...
... 59) When we say that the lesser occipital nerve is derived from C2, and C3 spinal nerves we actually mean it is directly derived from _______________ of the spinal nerves a) the ventral roots b) the dorsal roots c) the ventral rami d) the meningeal ramus e) the dorsal rami 60) A spinal nerve root i ...
Three Dimensional Microanatomy of the Ophthalmic Artery
... maximum intensity projection. In the present study, we used the OsiriX software to process DICOM images. This software may show the basal cerebral arteries and OphA together with the bone structure of the cranial base and orbital cavity. The OphA enters the orbital cavity through the optic foramen. ...
... maximum intensity projection. In the present study, we used the OsiriX software to process DICOM images. This software may show the basal cerebral arteries and OphA together with the bone structure of the cranial base and orbital cavity. The OphA enters the orbital cavity through the optic foramen. ...
pdf
... The deep cervical lymph nodes lie along the course of the internal jugular vein. The vein passes deep to the interval between the two heads of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Level III contains the middle jugular lymph nodes located around the middle third of the IJV. It is the caudal extension of l ...
... The deep cervical lymph nodes lie along the course of the internal jugular vein. The vein passes deep to the interval between the two heads of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Level III contains the middle jugular lymph nodes located around the middle third of the IJV. It is the caudal extension of l ...
2 m – 23. Х, ХI, ХII pairs of cranial nerves
... 1.1. Describe and demonstrate the localization of the branches of the vagus nerve, accessory and hepoglossal nerves and their relation to anatomical organs of the head and neck. 1.2. Determine the function of nuclei of the vagus nerve, accessory and hypoglossal nerves. 1.3. Be able to determine the ...
... 1.1. Describe and demonstrate the localization of the branches of the vagus nerve, accessory and hepoglossal nerves and their relation to anatomical organs of the head and neck. 1.2. Determine the function of nuclei of the vagus nerve, accessory and hypoglossal nerves. 1.3. Be able to determine the ...
NATIONAL GUIDANCE FOR IMRT IN ANAL CANCER
... Patient Simulation and Immobilisation: Standard position: supine with immobilisation for popliteal fossa and feet. Prior to pre-treatment scan, the clinician will assess the diagnostic imaging and ascertain whether the tumour is adequately bolused by the surrounding buttocks ie. 5mm of tissue su ...
... Patient Simulation and Immobilisation: Standard position: supine with immobilisation for popliteal fossa and feet. Prior to pre-treatment scan, the clinician will assess the diagnostic imaging and ascertain whether the tumour is adequately bolused by the surrounding buttocks ie. 5mm of tissue su ...
Dr.Kaan Yücel yeditepeanatomyfhs122.wordpress.com Vertebral
... Cervical vertebrae form the skeleton of the neck. The smallest of the 24 movable vertebrae, the cervical vertebrae are located between the cranium and the thoracic vertebrae. Their smaller size reflects the fact that they bear less weight than do the larger inferior vertebrae. The most distinctive f ...
... Cervical vertebrae form the skeleton of the neck. The smallest of the 24 movable vertebrae, the cervical vertebrae are located between the cranium and the thoracic vertebrae. Their smaller size reflects the fact that they bear less weight than do the larger inferior vertebrae. The most distinctive f ...
BIL 226, General Botany – Krempels Study Guide for Final (non
... What's interesting about our only North American Gnetophyte, Ephedra? What about Gnetum and Welwitschia? The Anthophytes: Introduction Know the synapomorphies that set Anthophytes apart from the other Spermatopsida. Know the parts of a flower, and from what each is derived. Know all the flower's ana ...
... What's interesting about our only North American Gnetophyte, Ephedra? What about Gnetum and Welwitschia? The Anthophytes: Introduction Know the synapomorphies that set Anthophytes apart from the other Spermatopsida. Know the parts of a flower, and from what each is derived. Know all the flower's ana ...
CHAPTER 10
... course of the fibers toward their insertion brings the medial pterygoid to lie on the same sagittal plane as the lateral pterygoid. In general direction, the fibers of the medial pterygoid are the internal counterpart of the superficial masseter (see Fig.10-1B). (The medial pterygoid and superficial ...
... course of the fibers toward their insertion brings the medial pterygoid to lie on the same sagittal plane as the lateral pterygoid. In general direction, the fibers of the medial pterygoid are the internal counterpart of the superficial masseter (see Fig.10-1B). (The medial pterygoid and superficial ...
TEKS 7.9 A Body Systems
... Teacher Background: There are twelve major organ systems in the human body (i.e., circulatory, skeletal, respiratory, excretory, integumentary, nervous, digestive, endocrine, reproductive, immune, lymphatic, and muscular systems). In this TEKS, we will introduce students to the common structures of ...
... Teacher Background: There are twelve major organ systems in the human body (i.e., circulatory, skeletal, respiratory, excretory, integumentary, nervous, digestive, endocrine, reproductive, immune, lymphatic, and muscular systems). In this TEKS, we will introduce students to the common structures of ...
Anatomy of the temporomandibular joint
... involving TMJ and the masticatory musculature. Muscle disorders result especially when functional activity involves such factors as proprioceptive and sensory feedback ...
... involving TMJ and the masticatory musculature. Muscle disorders result especially when functional activity involves such factors as proprioceptive and sensory feedback ...
Surgery of Skull Base Tumors Extending to the Orbit, Paranasal
... It should be noted that there is no anatomical concept of the "craniofacial region". The term "craniofacial tumor" is conditional. It means a neoplasm of the skull base extending both intracranially and to extracranial structures of the facial skeleton [7, 10]. Upon that, the source of growth may be ...
... It should be noted that there is no anatomical concept of the "craniofacial region". The term "craniofacial tumor" is conditional. It means a neoplasm of the skull base extending both intracranially and to extracranial structures of the facial skeleton [7, 10]. Upon that, the source of growth may be ...
pdf
... table, with the knee flexed and the sole of the foot resting on the surface of the table. Fig. 1 on page 9 a) Tendons and retinacula: The tendons here are gliding tendons, which are surrounded by a synovial sheath.. The tendons are derived from muscles located in the anterolateral portion of the leg ...
... table, with the knee flexed and the sole of the foot resting on the surface of the table. Fig. 1 on page 9 a) Tendons and retinacula: The tendons here are gliding tendons, which are surrounded by a synovial sheath.. The tendons are derived from muscles located in the anterolateral portion of the leg ...
File - Jamison Spencer, DMD, MS
... lateral movement can be made at any given degree of jaw separation (GPT1) 4: The most posterior relation of the lower to the upper jaw from which lateral movements can be made at a given vertical dimension (Boucher) 5: a maxilla to mandible relationship in which the condyles and disks are thought to ...
... lateral movement can be made at any given degree of jaw separation (GPT1) 4: The most posterior relation of the lower to the upper jaw from which lateral movements can be made at a given vertical dimension (Boucher) 5: a maxilla to mandible relationship in which the condyles and disks are thought to ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.