Document
... force tries bend the knee in a lateral direction • The ligament getting stretched is the one that gets injured ...
... force tries bend the knee in a lateral direction • The ligament getting stretched is the one that gets injured ...
Chapter 9 THE BODY AND ITS MOVEMENT
... It is made up of strong muscles . It produces a series of wave like movements that push the snails body forward . 3) The skeleton of a human body is inside the body. Such an skeleton is known as endoskeleton . Fish , amphibians , reptiles , birds and mammals have endoskeletons . Muscles that enables ...
... It is made up of strong muscles . It produces a series of wave like movements that push the snails body forward . 3) The skeleton of a human body is inside the body. Such an skeleton is known as endoskeleton . Fish , amphibians , reptiles , birds and mammals have endoskeletons . Muscles that enables ...
Lecture 1 – Anatomy Basics
... 1. What are the three main structural types of joints? Give an example of a specific location for each type in the body. 2. Describe and diagram the structure of a synovial joint. Label the components of the synovial joint and know the specific tissues that form each structure. 3. Know the general s ...
... 1. What are the three main structural types of joints? Give an example of a specific location for each type in the body. 2. Describe and diagram the structure of a synovial joint. Label the components of the synovial joint and know the specific tissues that form each structure. 3. Know the general s ...
Body Directions and Movement
... When the body is in anatomical position, it can be divided into three imaginary planes. These planes help clarify and specify movements. Sagittal Plane: Divides the body into right and left portions. Frontal (or coronal) Plane: Divides the body into front (anterior) and back (posterior) portio ...
... When the body is in anatomical position, it can be divided into three imaginary planes. These planes help clarify and specify movements. Sagittal Plane: Divides the body into right and left portions. Frontal (or coronal) Plane: Divides the body into front (anterior) and back (posterior) portio ...
Muscles of Shld/Shld Girdle
... There are several differences between the trunk and head, and other segments that you have studied this semester. To learn the muscles that cause and control movement of the trunk and head, you must first understand these differences. Unlike other segments and joints that you have already studied, m ...
... There are several differences between the trunk and head, and other segments that you have studied this semester. To learn the muscles that cause and control movement of the trunk and head, you must first understand these differences. Unlike other segments and joints that you have already studied, m ...
WebQuest: Planes, Directions, Terms
... a. Medial surface of the arm b. Lateral surface of the trunk c. Lateral surface of the arms d. Medial surface of the legs e. Anterior surface of the trunk f. Superior surface of the head Site #3: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objID=AP15605 ***For these questions, it may tell you th ...
... a. Medial surface of the arm b. Lateral surface of the trunk c. Lateral surface of the arms d. Medial surface of the legs e. Anterior surface of the trunk f. Superior surface of the head Site #3: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objID=AP15605 ***For these questions, it may tell you th ...
PowerPoint Sunusu
... internationally. Without anatomic terms, one cannot accurately discuss or record the abnormal functions of joints, the actions of muscles, the alteration of position of organs, or the exact location of swellings or tumors. ...
... internationally. Without anatomic terms, one cannot accurately discuss or record the abnormal functions of joints, the actions of muscles, the alteration of position of organs, or the exact location of swellings or tumors. ...
Musculoskeletal System
... œefine key terms • U œnderstand the most common pathologies affecting these organs • U œnderstand orthopedic surgeries and how they relate to pathologies • R œecognize common eponyms and acronyms • Iœ dentify when other sections of CPT® or ICD-9-CM should be accessed • œ Know when HCPCS Level II cod ...
... œefine key terms • U œnderstand the most common pathologies affecting these organs • U œnderstand orthopedic surgeries and how they relate to pathologies • R œecognize common eponyms and acronyms • Iœ dentify when other sections of CPT® or ICD-9-CM should be accessed • œ Know when HCPCS Level II cod ...
The sternum is an elongated, flattened bone, forming the middle
... after which it again widens a little to below the middle of the body, and then narrows to its lower extremity. Its average length in the adult is about 17 cm, and is rather greater in the male than in the female.Manubrium .—The manubrium is of a somewhat quadrangular form, broad and thick above, nar ...
... after which it again widens a little to below the middle of the body, and then narrows to its lower extremity. Its average length in the adult is about 17 cm, and is rather greater in the male than in the female.Manubrium .—The manubrium is of a somewhat quadrangular form, broad and thick above, nar ...
L5-MUSCLES OF BACK2013
... At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Distinguish between the different groups of back muscles. Compare between groups of back muscles as regard their nerve supply and action. List the back muscles of each group. Describe the attachments of each muscle of the superficial gro ...
... At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Distinguish between the different groups of back muscles. Compare between groups of back muscles as regard their nerve supply and action. List the back muscles of each group. Describe the attachments of each muscle of the superficial gro ...
Answers to Review Questions
... blood cells in marrow; supports body; protects organs; helps with movement; stores minerals. Muscular—helps with movement; generates heat. ...
... blood cells in marrow; supports body; protects organs; helps with movement; stores minerals. Muscular—helps with movement; generates heat. ...
Animals - SandersBiologyStuff
... Complex animals tend to have high levels of cell __________________. Other characteristics of complex animals: 1. _______________ ________________ –have __________________________________ sides that are the same. 2. ___________________________- have a front end or head with a concentration of ______ ...
... Complex animals tend to have high levels of cell __________________. Other characteristics of complex animals: 1. _______________ ________________ –have __________________________________ sides that are the same. 2. ___________________________- have a front end or head with a concentration of ______ ...
GCSE PE TEST – Circulatory System, Respiratory System +Energy
... b.) Give two places in the body where the pulse can be measured. (2) ...
... b.) Give two places in the body where the pulse can be measured. (2) ...
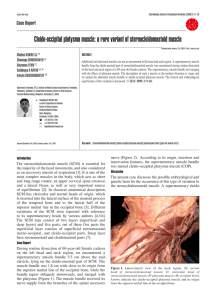
Cleido-occipital platysma muscle: a rare variant of
... the majority of the head movements, and also considered as an accessory muscle of respiration [1]. It is one of the most complex muscles in the body, which acts as short and long range rotator, an upper cervical spine extensor, and a lateral flexor, as well as very important source of equilibrium [2 ...
... the majority of the head movements, and also considered as an accessory muscle of respiration [1]. It is one of the most complex muscles in the body, which acts as short and long range rotator, an upper cervical spine extensor, and a lateral flexor, as well as very important source of equilibrium [2 ...
Ch 5 - whsanatomy
... * The ________ has no part in forming the _________ * The distal end has the lateral malleolus, forming the _______________________________________ The foot a. Calcaneus (_________) b. Tarsus (_________) c. Metatarsals (_________) d. Phalanges (_________) • Supports our body weight and serves as a l ...
... * The ________ has no part in forming the _________ * The distal end has the lateral malleolus, forming the _______________________________________ The foot a. Calcaneus (_________) b. Tarsus (_________) c. Metatarsals (_________) d. Phalanges (_________) • Supports our body weight and serves as a l ...
Analogous structures They appear similar but are from different
... • They have evolved geographically isolated from each other, but because their environments are similar they have functional and structural similarities. ...
... • They have evolved geographically isolated from each other, but because their environments are similar they have functional and structural similarities. ...
The Appendicular Skeleton
... The 5 metacarpals form the palm if the hand. These long bones are not named, but are numbered 1 to 5 from the thumb to the little finger. The heads of these bones form your knuckles when you clench your fist. Metacarpal #1 is associated with your thumb and has the most flexibility and even a differe ...
... The 5 metacarpals form the palm if the hand. These long bones are not named, but are numbered 1 to 5 from the thumb to the little finger. The heads of these bones form your knuckles when you clench your fist. Metacarpal #1 is associated with your thumb and has the most flexibility and even a differe ...
MBBS first Prof. Syllabus, uploaded on 2014-05-17
... Bony landmarks of upper limb, head & neck, trunk and lower limb. Surface marking: Region wise UPPER LIMB Anterior and posterior axillary folds, armpit, anatomical snuff box, breast, tendon of biceps, triceps, flexor carpi ulnaris, palmaris longus, flexon carpi radialis, extensor pollicis longus, ext ...
... Bony landmarks of upper limb, head & neck, trunk and lower limb. Surface marking: Region wise UPPER LIMB Anterior and posterior axillary folds, armpit, anatomical snuff box, breast, tendon of biceps, triceps, flexor carpi ulnaris, palmaris longus, flexon carpi radialis, extensor pollicis longus, ext ...
Bony Thorax - Northwest ISD Moodle
... almost entirely surrounded by bone and forms a deep “bowl” containing the pelvic organs Pelvic Inlet: pelvic brim; widest dimension is along the frontal plane Pelvic Outlet: inferior margin of the true pelvis; bounded anteriorly by the pubic arch, laterally by the ischia, and posteriorly by the sacr ...
... almost entirely surrounded by bone and forms a deep “bowl” containing the pelvic organs Pelvic Inlet: pelvic brim; widest dimension is along the frontal plane Pelvic Outlet: inferior margin of the true pelvis; bounded anteriorly by the pubic arch, laterally by the ischia, and posteriorly by the sacr ...
Muscles of the back
... At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Distinguish between the different groups of back muscles. Compare between groups of back muscles as regard their nerve supply and action. List the back muscles of each group. Describe the attachments of each muscle of the superficial gro ...
... At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Distinguish between the different groups of back muscles. Compare between groups of back muscles as regard their nerve supply and action. List the back muscles of each group. Describe the attachments of each muscle of the superficial gro ...
ANSWER KEY for Study Guide for Human Body Systems
... digestive track without conscience effort (thinking about it). Voluntary muscles are controlled by will and are usually skeletal muscles. Throwing a dodgeball is an example of using voluntary muscles. You will your arm to move. 5. What is the difference between the axial and appendicular skeletons? ...
... digestive track without conscience effort (thinking about it). Voluntary muscles are controlled by will and are usually skeletal muscles. Throwing a dodgeball is an example of using voluntary muscles. You will your arm to move. 5. What is the difference between the axial and appendicular skeletons? ...
General Body and Directional Terms
... g. Transverse plane 1. A horizontal (cross-section) plane, parallel to the ground and through the waistline 2. Divides the body into upper and lower halves Ventral 1. Anterior 2. Refers to the front of the body Dorsal 1. Posterior 2. Refers to the back of the body Cephalad 1. Above the waistline 2. ...
... g. Transverse plane 1. A horizontal (cross-section) plane, parallel to the ground and through the waistline 2. Divides the body into upper and lower halves Ventral 1. Anterior 2. Refers to the front of the body Dorsal 1. Posterior 2. Refers to the back of the body Cephalad 1. Above the waistline 2. ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.