The Body Systems – Final Exam Review Packet
... - Provides your body with support and shape - Many bones give your body the shape you are familiar with. The central part of your skeleton is your vertebral column, or spine. It is made up of 26 disc-shaped vertebrae. - Allows us to move - The skeletal and muscular systems rely on each other to allo ...
... - Provides your body with support and shape - Many bones give your body the shape you are familiar with. The central part of your skeleton is your vertebral column, or spine. It is made up of 26 disc-shaped vertebrae. - Allows us to move - The skeletal and muscular systems rely on each other to allo ...
TONGUE
... – somatic sensations: lingual nerve, a major branch of the mandibular nerve; also carries general sensation from areas of the oral mucosa and gingiva of the lower teeth. – taste sensation: facial nerve via the chorda tympani; also carries parasympathetic fibers from the facial nerve to the ...
... – somatic sensations: lingual nerve, a major branch of the mandibular nerve; also carries general sensation from areas of the oral mucosa and gingiva of the lower teeth. – taste sensation: facial nerve via the chorda tympani; also carries parasympathetic fibers from the facial nerve to the ...
Chapter 8
... exiting the articular cartilages due to the forces acting on the joint. – Acts as a shock absorber. ...
... exiting the articular cartilages due to the forces acting on the joint. – Acts as a shock absorber. ...
Endocrinology - You Can Do It!
... How can we know if the person has a flat foot? First we draw Feiss line, then we palpate the navicular bone, if the navicular bone is below the fesis line then this person has flat foot. In this case, the calcaneous is pushed backward and there is more stress in the metatarsals. ...
... How can we know if the person has a flat foot? First we draw Feiss line, then we palpate the navicular bone, if the navicular bone is below the fesis line then this person has flat foot. In this case, the calcaneous is pushed backward and there is more stress in the metatarsals. ...
practice quiz chapters7, 8,9
... help shift the trunk weight over the legs become accentuated as the toddler learns to walk accommodate the lumbar and cervical regions accommodate the thoracic and abdominopelvic viscera ...
... help shift the trunk weight over the legs become accentuated as the toddler learns to walk accommodate the lumbar and cervical regions accommodate the thoracic and abdominopelvic viscera ...
Right
... abdominal and pelvic cavities and cover the organs within these cavities Parietal peritoneum -lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities Visceral peritoneum -covers the organs Peritoneal cavity -the potential space between the parietal and visceral layer of peritoneum, in the male, is a cl ...
... abdominal and pelvic cavities and cover the organs within these cavities Parietal peritoneum -lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities Visceral peritoneum -covers the organs Peritoneal cavity -the potential space between the parietal and visceral layer of peritoneum, in the male, is a cl ...
urinary bladder - yeditepe anatomy fhs 121
... each of which divides into two or three minor calices. Each minor calyx is indented by a renal papilla, the apex of the renal pyramid, from which the urine is excreted. The pyramids and their associated cortex form the lobes of the kidney. ...
... each of which divides into two or three minor calices. Each minor calyx is indented by a renal papilla, the apex of the renal pyramid, from which the urine is excreted. The pyramids and their associated cortex form the lobes of the kidney. ...
Introduction to the Skeletal System
... Skull – protects brain Vertebrae – protect spinal chord ;also serves to keep skeleton upright Ribs – protect lungs and heart ; gives intercostal muscles a hard surface to move against for breathing ...
... Skull – protects brain Vertebrae – protect spinal chord ;also serves to keep skeleton upright Ribs – protect lungs and heart ; gives intercostal muscles a hard surface to move against for breathing ...
Biology 231
... Divisions of the Skeletal System (total 206 bones) Axial Skeleton (80 bones) – bones arranged around body’s longitudinal axis Skull – cranium and facial bones Spine (vertebral column) Thoracic cage – breastbone and ribs Hyoid and Auditory ossicles Appendicular Skeleton (126 bones) – upper and lower ...
... Divisions of the Skeletal System (total 206 bones) Axial Skeleton (80 bones) – bones arranged around body’s longitudinal axis Skull – cranium and facial bones Spine (vertebral column) Thoracic cage – breastbone and ribs Hyoid and Auditory ossicles Appendicular Skeleton (126 bones) – upper and lower ...
DeltaScience - Delta Education
... • Discuss the diagram of a pair of muscles. Tell students they can feel the muscle pairs contracting in their own arms. Have them wrap a hand around their upper arm, then bend and straighten their arm at the elbow. Tell them that a muscle feels firmer when it is contracted. Ask: Which muscle feels ...
... • Discuss the diagram of a pair of muscles. Tell students they can feel the muscle pairs contracting in their own arms. Have them wrap a hand around their upper arm, then bend and straighten their arm at the elbow. Tell them that a muscle feels firmer when it is contracted. Ask: Which muscle feels ...
No. 8
... descending in front of the inferior vena cava. (4) The floor of the epiploic foramen is limited by the upper border of the superior part of the duodenum. ...
... descending in front of the inferior vena cava. (4) The floor of the epiploic foramen is limited by the upper border of the superior part of the duodenum. ...
Unit 10 – Flatworm, Roundworm and Segmented Worms
... Ascaris is usually diagrammed to typify roundworm anatomy. Ascaris is a roundworm that is ___________________________. The entire life cycle can take place in the human body and the eggs can be passed out with feces. Eggs in food or water are _____________________ _____________________________, the ...
... Ascaris is usually diagrammed to typify roundworm anatomy. Ascaris is a roundworm that is ___________________________. The entire life cycle can take place in the human body and the eggs can be passed out with feces. Eggs in food or water are _____________________ _____________________________, the ...
Part I: Frog Dissection Questions
... 8. Is your frog a male or a female? How do you know? 9. List the parts of the Urogenital system in detail 10. What is the function of the Vasa Efferentia, Oviduct, and Ureter? The Brain (Optional Dissection- No questions) Part II: Analysis and Conclusion: (Use Textbook as Reference) 1. What is the d ...
... 8. Is your frog a male or a female? How do you know? 9. List the parts of the Urogenital system in detail 10. What is the function of the Vasa Efferentia, Oviduct, and Ureter? The Brain (Optional Dissection- No questions) Part II: Analysis and Conclusion: (Use Textbook as Reference) 1. What is the d ...
47772510efe1b13
... • The disc is avascular in the centre so ,the regenerative power is low. • The disc is composed of dense collagen fibers only in its centre but in posterior & anterior ends it contains elastic fibers • Synovial membrane has 3 types of cells :type A(fibroblast like cell) ,type B(macrophage like ) and ...
... • The disc is avascular in the centre so ,the regenerative power is low. • The disc is composed of dense collagen fibers only in its centre but in posterior & anterior ends it contains elastic fibers • Synovial membrane has 3 types of cells :type A(fibroblast like cell) ,type B(macrophage like ) and ...
Fall 231 2013 Supplemental package
... Identify abdominal quadrants and 9 abdominal regions and major organs found in each Be able to identify the superficial muscles on the muscle men ...
... Identify abdominal quadrants and 9 abdominal regions and major organs found in each Be able to identify the superficial muscles on the muscle men ...
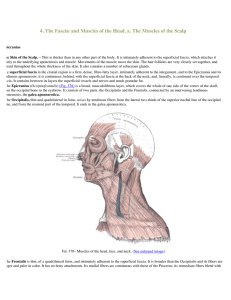
4. The Fascię and Muscles of the Head. a. The Muscles of the Scalp
... Relations.—The Buccinator is covered by the buccopharyngeal fascia, and is in relation by its superficial surface, behind, with a large mass of fat, which separates it from the ramus of the mandible, the Masseter, and a small portion of the Temporalis; this fat has been named the suctorial pad, beca ...
... Relations.—The Buccinator is covered by the buccopharyngeal fascia, and is in relation by its superficial surface, behind, with a large mass of fat, which separates it from the ramus of the mandible, the Masseter, and a small portion of the Temporalis; this fat has been named the suctorial pad, beca ...
241Supplement Bones
... 1. List the functions of the skeletal system. 2. Identify the two major types of bone. 3. Identify the anatomical areas of a longitudinally cut bone. 4. Identify major regions of an osteon (compact bone) and trabeculae (spongy bone) on histological specimens. 5. Explain the role of inorganic salts a ...
... 1. List the functions of the skeletal system. 2. Identify the two major types of bone. 3. Identify the anatomical areas of a longitudinally cut bone. 4. Identify major regions of an osteon (compact bone) and trabeculae (spongy bone) on histological specimens. 5. Explain the role of inorganic salts a ...
Human Torso Model Activity
... Use the torso model to complete the answers below. 1. List 2 organs from the anterior view that are part of the digestive system. 2. Is the nose superior or inferior to the diaphragm muscle which allows breathing to take place? 3. The heart is ___________________ to the lungs. The lungs are ________ ...
... Use the torso model to complete the answers below. 1. List 2 organs from the anterior view that are part of the digestive system. 2. Is the nose superior or inferior to the diaphragm muscle which allows breathing to take place? 3. The heart is ___________________ to the lungs. The lungs are ________ ...
241Supplement Bones
... 1. List the functions of the skeletal system. 2. Identify the two major types of bone. 3. Identify the anatomical areas of a longitudinally cut bone. 4. Identify major regions of an osteon (compact bone) and trabeculae (spongy bone) on histological specimens. 5. Explain the role of inorganic salts a ...
... 1. List the functions of the skeletal system. 2. Identify the two major types of bone. 3. Identify the anatomical areas of a longitudinally cut bone. 4. Identify major regions of an osteon (compact bone) and trabeculae (spongy bone) on histological specimens. 5. Explain the role of inorganic salts a ...
Sciatic Nerve
... Pay attention to the fact that the muscles of the thigh are designed To act on the knee joint For example, quadriceps femoris occupies the anterior compartment of the thigh but its Main action is to extend the knee joint The same should be considered for the muscles of the posterior compartment of ...
... Pay attention to the fact that the muscles of the thigh are designed To act on the knee joint For example, quadriceps femoris occupies the anterior compartment of the thigh but its Main action is to extend the knee joint The same should be considered for the muscles of the posterior compartment of ...
Limited posterior approach for internal fixation of a glenoid fracture
... of deltoid reattachment, a delay in rehabilitation, and weakness of arm extension [1]. Nowadays, the advocated posterior approaches are less invasive, since no infraspinatus detachment is necessary when using the interval between the teres minor and infraspinatus muscle [3, 5, 6, 7, 9]. The axillary ...
... of deltoid reattachment, a delay in rehabilitation, and weakness of arm extension [1]. Nowadays, the advocated posterior approaches are less invasive, since no infraspinatus detachment is necessary when using the interval between the teres minor and infraspinatus muscle [3, 5, 6, 7, 9]. The axillary ...
Physio pages use this.indd - Physiotherapy New Zealand
... In the physiotherapeutic literature scalenus anterior has been depicted as palpable and measurable by surface electromyography (EMG) within the posterior triangle of the neck, but without explaining in detail how this is achieved. The purpose of this study is to present the topographical anatomy of ...
... In the physiotherapeutic literature scalenus anterior has been depicted as palpable and measurable by surface electromyography (EMG) within the posterior triangle of the neck, but without explaining in detail how this is achieved. The purpose of this study is to present the topographical anatomy of ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.