Chapter 21 Lecture Outline
... Sacral Plexus: nerve fibers from 4th and 5th lumbar nerves and the first, second and third sacral nerves Tibial and common peroneal nerves emerge from the sacral plexus to form the sciatic nerve in the thigh o Blood Supply Arteries: Aorta divides into two common iliac arteries, divide and then ...
... Sacral Plexus: nerve fibers from 4th and 5th lumbar nerves and the first, second and third sacral nerves Tibial and common peroneal nerves emerge from the sacral plexus to form the sciatic nerve in the thigh o Blood Supply Arteries: Aorta divides into two common iliac arteries, divide and then ...
the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
... a. Cranial vault - forms the superior, lateral and posterior walls of the skull b. Cranial base - forms the interior aspect of the skull; there are 3 levels: anterior, middle, and posterior cranial cavities or fossae 2. Cranium: composed of eight bones a. Frontal Bone: anterior portion of the craniu ...
... a. Cranial vault - forms the superior, lateral and posterior walls of the skull b. Cranial base - forms the interior aspect of the skull; there are 3 levels: anterior, middle, and posterior cranial cavities or fossae 2. Cranium: composed of eight bones a. Frontal Bone: anterior portion of the craniu ...
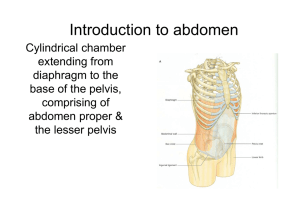
Introduction to abdoman
... Below umbilicus supply is from three suprficial branches of femoral artery Superficial epigastric Superficial external pudendal Superficial circumflex iliac ...
... Below umbilicus supply is from three suprficial branches of femoral artery Superficial epigastric Superficial external pudendal Superficial circumflex iliac ...
Human Body Systems Packet
... You have about one gallon of blood in your body. Plasma is the liquid part of the blood. Three main kinds of cells are found in plasma. Red blood cells are blood cells that carry oxygen to body cells and carbon dioxide away from body cells. White blood cells are blood cells that fight germs that cau ...
... You have about one gallon of blood in your body. Plasma is the liquid part of the blood. Three main kinds of cells are found in plasma. Red blood cells are blood cells that carry oxygen to body cells and carbon dioxide away from body cells. White blood cells are blood cells that fight germs that cau ...
Document
... The genial tubercles are located on the inner surface of the body of the mandible in the midline.These tubercles are the points of insertion of the genioglossus and geniohyoid muscles bilaterally to the upper and lower genial tubercles respectively. On a periapical radiograph, the genial tubercles a ...
... The genial tubercles are located on the inner surface of the body of the mandible in the midline.These tubercles are the points of insertion of the genioglossus and geniohyoid muscles bilaterally to the upper and lower genial tubercles respectively. On a periapical radiograph, the genial tubercles a ...
File
... Clinical note: When a thoracotomy is being performed, it is a convenient landmark from which the ribs can be counted along the lateral chest wall. Infraclavicular fossa- (or deltopectoral triangle) A small depression can be seen inferior to the clavicle at the junction of its convex medial and conca ...
... Clinical note: When a thoracotomy is being performed, it is a convenient landmark from which the ribs can be counted along the lateral chest wall. Infraclavicular fossa- (or deltopectoral triangle) A small depression can be seen inferior to the clavicle at the junction of its convex medial and conca ...
Internal Anatomy and Organization of the Heart
... Cardiac cells have specialized cell-to-cell junctions The sarcolemmae of two cardiac cells are bound together by desmosomes The intercalated discs bind the myofibrils of adjacent cells together Cardiac muscle cells are bound together by gap junctions Ions move directly from one cell to ano ...
... Cardiac cells have specialized cell-to-cell junctions The sarcolemmae of two cardiac cells are bound together by desmosomes The intercalated discs bind the myofibrils of adjacent cells together Cardiac muscle cells are bound together by gap junctions Ions move directly from one cell to ano ...
Anatomical Guide - Introduction To Mortuary Sciences
... • Close to center of circulation • Close to center of venous drainage • Has no branches except its terminal branches • Supplies fluid directly to the head • Accompanied by a very large vein that can be used for drainage. • Arterial coagula are pushed away from the head. ...
... • Close to center of circulation • Close to center of venous drainage • Has no branches except its terminal branches • Supplies fluid directly to the head • Accompanied by a very large vein that can be used for drainage. • Arterial coagula are pushed away from the head. ...
pnoble1
... and Myology) were photographed. Morpho-Imaging and its content was produced using Adobe programs. It was hosted on the RVC1 multimedia platform and linked to the educational Philips iSiteTM Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) of the VUB5. Results: Morpho-Imaging consists of three major ...
... and Myology) were photographed. Morpho-Imaging and its content was produced using Adobe programs. It was hosted on the RVC1 multimedia platform and linked to the educational Philips iSiteTM Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) of the VUB5. Results: Morpho-Imaging consists of three major ...
A Framework for Push-grasping in Clutter
... d. calculate the action volume of the plan e. determine the penetrated objects if none then return the plan f. update the NGR and avoidVol g. recursive call of reconfigure of the next object on the list if done add the recursive plan before plan if fail then search again ----if all actions tried the ...
... d. calculate the action volume of the plan e. determine the penetrated objects if none then return the plan f. update the NGR and avoidVol g. recursive call of reconfigure of the next object on the list if done add the recursive plan before plan if fail then search again ----if all actions tried the ...
large intestines of the horse
... a long U-shaped loop consisting of two parallel limbs and a terminal flexure. The U-shaped loop is folded on itself forming a double horseshoe-shaped loop. In situ, the two horseshoe-shaped loops lie more or less on top of each other. The ventral loop is called the ventral colon, and the dorsal loop ...
... a long U-shaped loop consisting of two parallel limbs and a terminal flexure. The U-shaped loop is folded on itself forming a double horseshoe-shaped loop. In situ, the two horseshoe-shaped loops lie more or less on top of each other. The ventral loop is called the ventral colon, and the dorsal loop ...
AXIAL SKELETON The skeleton can be divided into two parts: the
... a. Cranial vault - forms the superior, lateral and posterior walls of the skull b. Cranial base - forms the interior aspect of the skull; there are 3 levels: anterior, middle, and posterior cranial cavities or fossae 2. Cranium: composed of eight bones a. Frontal Bone: anterior portion of the craniu ...
... a. Cranial vault - forms the superior, lateral and posterior walls of the skull b. Cranial base - forms the interior aspect of the skull; there are 3 levels: anterior, middle, and posterior cranial cavities or fossae 2. Cranium: composed of eight bones a. Frontal Bone: anterior portion of the craniu ...
Document
... of sweat production (cooling the body). The sweat glands do not produce sweat in response to an increase in sodium chloride in the blood and are not, therefore, organs of ...
... of sweat production (cooling the body). The sweat glands do not produce sweat in response to an increase in sodium chloride in the blood and are not, therefore, organs of ...
FULL TEXT - An International Journal of Experimental
... directed superiorly into the head and inferiorly into the body. Injection was done at a moderate/high pressure and a slow flow rate (~6-8 oz. per min). The embalming solution consisted of: 1 L formaldehyde, 1 L of methanol, 2.5 L of isopropyl Alcohol, 0.5 L of glycerin and enough water to make 12 L ...
... directed superiorly into the head and inferiorly into the body. Injection was done at a moderate/high pressure and a slow flow rate (~6-8 oz. per min). The embalming solution consisted of: 1 L formaldehyde, 1 L of methanol, 2.5 L of isopropyl Alcohol, 0.5 L of glycerin and enough water to make 12 L ...
Joints of Upper limb
... the margins of the olecranon fossa of the humerus and below to the upper margin and sides of the olecranon process of the ulna and to the anular ligament. ...
... the margins of the olecranon fossa of the humerus and below to the upper margin and sides of the olecranon process of the ulna and to the anular ligament. ...
Liver Segmental Anatomy Robin Smithuis Liver anatomy can be
... Three dimensional liver imaging is of most practical value if a resection of one or more segments or sectors is considered, especially in the right hemiliver. In these cases, 3D liver imaging can demonstrate the precise location of the scissuras t o the surgeon pre-operatively. The 8 anatomical poin ...
... Three dimensional liver imaging is of most practical value if a resection of one or more segments or sectors is considered, especially in the right hemiliver. In these cases, 3D liver imaging can demonstrate the precise location of the scissuras t o the surgeon pre-operatively. The 8 anatomical poin ...
File
... • Phalanges (toe bones) • Metatarsals (long foot bones) • Tarsals (small bones near ankle) ...
... • Phalanges (toe bones) • Metatarsals (long foot bones) • Tarsals (small bones near ankle) ...
HIP Joint
... • At the front of the joint, the strong iliofemoral ligament attaches from the pelvis to femur. This Y-shaped ligament is also known as the ligament of Bigelow. This ligament seeks to resist excessive extension of the hip joint. It is often considered to be the strongest ligament in the human body. ...
... • At the front of the joint, the strong iliofemoral ligament attaches from the pelvis to femur. This Y-shaped ligament is also known as the ligament of Bigelow. This ligament seeks to resist excessive extension of the hip joint. It is often considered to be the strongest ligament in the human body. ...
The Anatomy of the Hyoid Region of Molossus Molossus and its
... the hyoid structures of bats of the genera Rhinopoma, Emballonura, Nycteris, Megaderma, Rhinolophus, Pteronotus, Phyllostomus, and Eptesicus, which were previously described by my sponsor Gri'tfiths and associates. In Molossus, the geniohyoid and sternohyoid insertions, as well as the hyoglossus ori ...
... the hyoid structures of bats of the genera Rhinopoma, Emballonura, Nycteris, Megaderma, Rhinolophus, Pteronotus, Phyllostomus, and Eptesicus, which were previously described by my sponsor Gri'tfiths and associates. In Molossus, the geniohyoid and sternohyoid insertions, as well as the hyoglossus ori ...
Frog Dissection
... As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid and fertilized in water. On the outside of the frog’s head are two external nares, or nostrils; two tympani, or eardrums; and two eyes, each of which has thre ...
... As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid and fertilized in water. On the outside of the frog’s head are two external nares, or nostrils; two tympani, or eardrums; and two eyes, each of which has thre ...
The Upper Extremity
... The Lateral Cord gives : • .Lat. Root of median nerve • .Lat.pectoral nerve • Musculocutaneous : –Course: branches to arm, distal to elbow becomes cutaneous :sensory to skin of lateral side of forearm . –Motor : • Biceps brachii, brachialis, coracobrachialis ...
... The Lateral Cord gives : • .Lat. Root of median nerve • .Lat.pectoral nerve • Musculocutaneous : –Course: branches to arm, distal to elbow becomes cutaneous :sensory to skin of lateral side of forearm . –Motor : • Biceps brachii, brachialis, coracobrachialis ...
Retroperitoneal Space (lec.2) ھ دي ن .د
... It passes upward and medially along the medial margin of the deep inguinal ring and enters the rectus sheath behind the rectus abdominis muscle. The deep circumflex iliac artery arises close to the inferior epigastric artery . It ascends laterally to the anterior superior iliac spine and the iliac c ...
... It passes upward and medially along the medial margin of the deep inguinal ring and enters the rectus sheath behind the rectus abdominis muscle. The deep circumflex iliac artery arises close to the inferior epigastric artery . It ascends laterally to the anterior superior iliac spine and the iliac c ...
Chapter
... symphysis as it has no synovial tissue or fluid, and contains a fibrocartilaginous disc The bone surfaces of this joint are covered with hyaline cartilage, but are kept apart by the presence of the disc ...
... symphysis as it has no synovial tissue or fluid, and contains a fibrocartilaginous disc The bone surfaces of this joint are covered with hyaline cartilage, but are kept apart by the presence of the disc ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.