Types of Nervous Systems
... thread like tubular structure on the lateral side of each kidney continues posteriorly beyond the kidney and enters the cloaca separately on its dorsal wall Urinary Bladder connected to the ventral wall of the cloaca which serves as storage of urine ...
... thread like tubular structure on the lateral side of each kidney continues posteriorly beyond the kidney and enters the cloaca separately on its dorsal wall Urinary Bladder connected to the ventral wall of the cloaca which serves as storage of urine ...
Abnormal anatomy of inferior orbital fissure and herniation of buccal
... fracture of the left orbital floor and comminuted fractures of the nasal bone. Initial diplopia settled but computed tomography (CT) showed entrapment of the inferior rectus muscle. He was counselled about late onset enophthalmus, and consented to an operation to explore and repair the orbital floor ...
... fracture of the left orbital floor and comminuted fractures of the nasal bone. Initial diplopia settled but computed tomography (CT) showed entrapment of the inferior rectus muscle. He was counselled about late onset enophthalmus, and consented to an operation to explore and repair the orbital floor ...
Body_Systems_Overview_T
... 3. What other systems are involved in a muscle contraction? Nervous 4. Muscles are made up of what organic molecule? Protein 5. Skeletal muscles generate force and produce movement by contracting, or pulling on body parts. Skeletal muscles are joined to bones by tough connective tissues called tendo ...
... 3. What other systems are involved in a muscle contraction? Nervous 4. Muscles are made up of what organic molecule? Protein 5. Skeletal muscles generate force and produce movement by contracting, or pulling on body parts. Skeletal muscles are joined to bones by tough connective tissues called tendo ...
PowerPoint 6: Cnidaria 1
... Contain gastrovascular cavity, not a true body cavity No head; no special body systems for circulation, gas exchange or excretion. Nervous system is a nerve net Have planula larvae ...
... Contain gastrovascular cavity, not a true body cavity No head; no special body systems for circulation, gas exchange or excretion. Nervous system is a nerve net Have planula larvae ...
Anatomical Study of the Fibularis Longus Muscle Motor Points and
... study was to determine the number and distribution of motor points of the FLM and relate them to observable parameters in the surface anatomy. Ten formalin-preserved limbs were used, and the lateral regions of the leg were dissected in detail. In all the cases, the muscle presented three fascicular ...
... study was to determine the number and distribution of motor points of the FLM and relate them to observable parameters in the surface anatomy. Ten formalin-preserved limbs were used, and the lateral regions of the leg were dissected in detail. In all the cases, the muscle presented three fascicular ...
Outline 18
... The primary bronchi are forks branching to the right and left from the ____________________ o The Lungs Each lung is somewhat conical with a concave base resting on the diaphragm and a blunt peak called the ____________ projecting above the clavicle The costal surface is the portion pressed ag ...
... The primary bronchi are forks branching to the right and left from the ____________________ o The Lungs Each lung is somewhat conical with a concave base resting on the diaphragm and a blunt peak called the ____________ projecting above the clavicle The costal surface is the portion pressed ag ...
Chapter 17 Special Senses
... • Ciliary body consists of ciliary processes and ciliary muscle • Iris ...
... • Ciliary body consists of ciliary processes and ciliary muscle • Iris ...
Axial Muscles of the Head, Neck, and Back
... OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0† ...
... OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0† ...
gcse mind maps 1 revision - Watford Grammar School for Boys Intranet
... arms and legs are moving at relatively constant speeds ...
... arms and legs are moving at relatively constant speeds ...
Anatomy Lecture 6 Stretch reflex: The doctor started by emphasizing
... 5- Positive Babinski sign 6- Absence of abdominal and cremasteric reflexes NOTE: - If the stroke’s damage was at the internal capsule, this damage is considered as extensive meaning that both upper and lower limbs are affected on one side of the body. ...
... 5- Positive Babinski sign 6- Absence of abdominal and cremasteric reflexes NOTE: - If the stroke’s damage was at the internal capsule, this damage is considered as extensive meaning that both upper and lower limbs are affected on one side of the body. ...
Phyla Annelida and Mollusca
... scissors extend the cut forward to the first segment. Be careful not to cut too deep. Starting at the first segment, cut the septa (thin membranes) that internally divide the segments, so the skin can be laid flat. Use additional pins to hold the integument open and expose the organs. Continue to la ...
... scissors extend the cut forward to the first segment. Be careful not to cut too deep. Starting at the first segment, cut the septa (thin membranes) that internally divide the segments, so the skin can be laid flat. Use additional pins to hold the integument open and expose the organs. Continue to la ...
BDS Ist YEAR EXAMINATION 2008-09
... 2. Please tick (√) correct one only. Cutting, overwriting or any other marking are not allowed. 3. For answering please use Ball- pen only. Q.1 ...
... 2. Please tick (√) correct one only. Cutting, overwriting or any other marking are not allowed. 3. For answering please use Ball- pen only. Q.1 ...
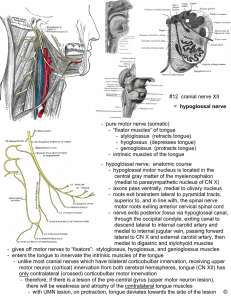
- pure motor nerve (somatic) - “fixator muscles” of tongue
... - styloglossus (retracts tongue) - hyoglossus (depresses tongue) - genioglossus (protracts tongue) - intrinsic muscles of the tongue - hypoglossal nerve: anatomic course - hypoglossal motor nucleus is located in the central gray matter of the myelencephalon (medial to parasympathetic nucleus of CN X ...
... - styloglossus (retracts tongue) - hyoglossus (depresses tongue) - genioglossus (protracts tongue) - intrinsic muscles of the tongue - hypoglossal nerve: anatomic course - hypoglossal motor nucleus is located in the central gray matter of the myelencephalon (medial to parasympathetic nucleus of CN X ...
Chapter 8
... The synovial membrane covers all surfaces within the joint capsule, except the areas the articular cartilage covers. It fills spaces and irregularities within the cavity. It secretes synovial fluid. It may store adipose tissue. It also reabsorbs the synovial fluid. 11. Explain the function of synov ...
... The synovial membrane covers all surfaces within the joint capsule, except the areas the articular cartilage covers. It fills spaces and irregularities within the cavity. It secretes synovial fluid. It may store adipose tissue. It also reabsorbs the synovial fluid. 11. Explain the function of synov ...
MUSCLES OF HAND MOVEMENTS OF THUMB PALMAR
... Fingers bend towards the palm and cannot be fully extended It is caused by underlying contractures of the palmar fascia The ring finger and little finger are commonly affected The middle finger may be affected in advanced cases, but the index finger and the thumb are nearly always spared. Progresses ...
... Fingers bend towards the palm and cannot be fully extended It is caused by underlying contractures of the palmar fascia The ring finger and little finger are commonly affected The middle finger may be affected in advanced cases, but the index finger and the thumb are nearly always spared. Progresses ...
Left inferior lobe
... – Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium – Goblet cells within epithelium – Underlying layer of lamina propria ...
... – Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium – Goblet cells within epithelium – Underlying layer of lamina propria ...
Ch22.Respiratory.System_1
... – Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium – Goblet cells within epithelium – Underlying layer of lamina propria ...
... – Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium – Goblet cells within epithelium – Underlying layer of lamina propria ...
Effective Treatments for the Neck and Head
... A number of muscles of the neck remain major players in keeping an imbalance that over time multiplies compression to lead to disc degeneration. Professor Vladimir Janda, MD of Czechoslovakia, rehabilitation consultant for the World Health Organization was one of the first clinicians to bring this ...
... A number of muscles of the neck remain major players in keeping an imbalance that over time multiplies compression to lead to disc degeneration. Professor Vladimir Janda, MD of Czechoslovakia, rehabilitation consultant for the World Health Organization was one of the first clinicians to bring this ...
D23-1 UNIT 23. DISSECTION: PHARYNX AND LARYNX
... 1. In this dissection, a considerable portion of the skull will be reflected forward with the cervical viscera (pharynx, esophagus, larynx, trachea, etc) to expose the pharynx from behind. In addition, you will be able to expose and study the origins and courses of certain cranial nerves, which have ...
... 1. In this dissection, a considerable portion of the skull will be reflected forward with the cervical viscera (pharynx, esophagus, larynx, trachea, etc) to expose the pharynx from behind. In addition, you will be able to expose and study the origins and courses of certain cranial nerves, which have ...
lesson assignment - Free
... systems and components. Anatomy is the study of these components and the systems that they comprise. Put another way, anatomy is the study of the structure of the body, and the spatial relationship of its parts. Radiographic anatomy is the study of body structures that can be satisfactorily recorded ...
... systems and components. Anatomy is the study of these components and the systems that they comprise. Put another way, anatomy is the study of the structure of the body, and the spatial relationship of its parts. Radiographic anatomy is the study of body structures that can be satisfactorily recorded ...
Structural Meso-Scale Bone Remodelling of the Pelvis
... a structural presence in similar areas but majority of thickness values were over or underestimates. The trabecular structure responded to different load cases but the lack of validation material has reduced the confidence of the trabecular validation. Within every model there are limitations which ...
... a structural presence in similar areas but majority of thickness values were over or underestimates. The trabecular structure responded to different load cases but the lack of validation material has reduced the confidence of the trabecular validation. Within every model there are limitations which ...
Available - Ggu.ac.in
... Coelom refers to a large fluid-filled space lying between the outer body wall and inner digestive tube. It arises as a secondary cavity between two layers of embryonic mesoderm and contains most of the visceral organs. A true coelom may be defined as “a secondary body cavity formed by splitting of m ...
... Coelom refers to a large fluid-filled space lying between the outer body wall and inner digestive tube. It arises as a secondary cavity between two layers of embryonic mesoderm and contains most of the visceral organs. A true coelom may be defined as “a secondary body cavity formed by splitting of m ...
RENZA, INC.
... Purpose Post Incident Analysis (PIA) • Who?, What?, How? • Used to prove good security procedures (or the lack thereof) • Used to reinstate C-TPAT status • Can be used as basis for penalty mitigation ...
... Purpose Post Incident Analysis (PIA) • Who?, What?, How? • Used to prove good security procedures (or the lack thereof) • Used to reinstate C-TPAT status • Can be used as basis for penalty mitigation ...
Regional Gross Anatomy “Pectoral Region”
... from upper trunk of the Brachial plexus) - long thoracic nerve (nerve roots from C5-6-7 of the Brachial plexus) ...
... from upper trunk of the Brachial plexus) - long thoracic nerve (nerve roots from C5-6-7 of the Brachial plexus) ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.