Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 03.January.2014 Friday
... Ulna does not reach and participate to the radiocarpal (wrist) joint! Head of the ulna ...
... Ulna does not reach and participate to the radiocarpal (wrist) joint! Head of the ulna ...
The infratemporal fossa
... indication : some dynamic movement is possible through the V3 branch of the trigeminal nerve .(also masseter muscle can be used in patient with facial paralysis ) . less common indication are for palate and maxillary reconstruction . TR AUMA TO THE TEMPORAL REGION : The bone of calvarium is thinnest ...
... indication : some dynamic movement is possible through the V3 branch of the trigeminal nerve .(also masseter muscle can be used in patient with facial paralysis ) . less common indication are for palate and maxillary reconstruction . TR AUMA TO THE TEMPORAL REGION : The bone of calvarium is thinnest ...
The Neck
... Nerves in the posterior ∆ Accessory nerve (spinal root): SCM & trapezius Cervical plexus: anterior rami of C2 to C4 (muscular branches – deep) phrenic nerve [C3 + C4 + C5]: ant. surface of ant. scalene nerves to rectus capitis anterior & lateralis, nerves to longus coli, longus capitis ...
... Nerves in the posterior ∆ Accessory nerve (spinal root): SCM & trapezius Cervical plexus: anterior rami of C2 to C4 (muscular branches – deep) phrenic nerve [C3 + C4 + C5]: ant. surface of ant. scalene nerves to rectus capitis anterior & lateralis, nerves to longus coli, longus capitis ...
Advanced Biomechanics Final Notes 10-14
... - Don’t just randomly throw orthotics in shoes, might fix one problem but cause another - Another issue is that the orthotics are too hard - Don’t want them too flimsy either Glut med controls valgosity of the knee Gait eval- want the knee to travel in a sagittal plane, patella should point straight ...
... - Don’t just randomly throw orthotics in shoes, might fix one problem but cause another - Another issue is that the orthotics are too hard - Don’t want them too flimsy either Glut med controls valgosity of the knee Gait eval- want the knee to travel in a sagittal plane, patella should point straight ...
Dissections of the upper limb I
... contribute to the formation of the medial muscular elevation. Mark their attachments in the dry bones. 14. In the living extend the elbow and feel the mass lateral to the cubital fossa between the thumb and fingers. Trace it above to the lateral epicondyle and lateral supra condylar ridge. Understan ...
... contribute to the formation of the medial muscular elevation. Mark their attachments in the dry bones. 14. In the living extend the elbow and feel the mass lateral to the cubital fossa between the thumb and fingers. Trace it above to the lateral epicondyle and lateral supra condylar ridge. Understan ...
Effective Treatments for the Neck
... A number of muscles of the neck remain major players in keeping an imbalance that over time multiplies compression to lead to disc degeneration. Professor Vladimir Janda, MD of Czechoslovakia, rehabilitation consultant for the World Health Organization was one of the first clinicians to bring this ...
... A number of muscles of the neck remain major players in keeping an imbalance that over time multiplies compression to lead to disc degeneration. Professor Vladimir Janda, MD of Czechoslovakia, rehabilitation consultant for the World Health Organization was one of the first clinicians to bring this ...
Animal Kingdom Test #2 - Parma City School District
... 18. What type of respiratory structure is present in the clam? a) lung b) visceral mass c) mantle d) gill e) book lung 19. What type of circulatory system do clams have? a) open b) closed c) no circulatory system is present d) diffusion e) osmosis 20. The tube shaped excretory structure in the clam ...
... 18. What type of respiratory structure is present in the clam? a) lung b) visceral mass c) mantle d) gill e) book lung 19. What type of circulatory system do clams have? a) open b) closed c) no circulatory system is present d) diffusion e) osmosis 20. The tube shaped excretory structure in the clam ...
1 - Parma City School District
... 18. What type of respiratory structure is present in the clam? a) lung b) visceral mass c) mantle d) gill e) book lung 19. What type of circulatory system do clams have? a) open b) closed c) no circulatory system is present d) diffusion e) osmosis 20. The tube shaped excretory structure in the clam ...
... 18. What type of respiratory structure is present in the clam? a) lung b) visceral mass c) mantle d) gill e) book lung 19. What type of circulatory system do clams have? a) open b) closed c) no circulatory system is present d) diffusion e) osmosis 20. The tube shaped excretory structure in the clam ...
The Lymphatic System
... 2. Monitoring body fluids provided by lymphocytes and macrophages. **Lymphocytes attack viruses, bacteria, and other parasitic cells within the lymph nodes. ...
... 2. Monitoring body fluids provided by lymphocytes and macrophages. **Lymphocytes attack viruses, bacteria, and other parasitic cells within the lymph nodes. ...
The hand
... The sole bone of the thigh is the femur, the largest and strongest bone in the body. It articulates proximally with the hip and distally with the tibia and fibula. Major markings include the head, fovea capitis, greater and lesser trochanters, gluteal tuberosity, lateral and medial condyles and epic ...
... The sole bone of the thigh is the femur, the largest and strongest bone in the body. It articulates proximally with the hip and distally with the tibia and fibula. Major markings include the head, fovea capitis, greater and lesser trochanters, gluteal tuberosity, lateral and medial condyles and epic ...
21 Surface Anatomy of upper and lower limbs
... may be felt slightly distal to the ulnar head when the hand is supinated. The olecranon and posterior border of the ulna lie subcutaneously and can be palpated easily. When the elbow joint is extended, the tip of the olecranon process, the medial and the lateral epicondyles lie in a straight line. W ...
... may be felt slightly distal to the ulnar head when the hand is supinated. The olecranon and posterior border of the ulna lie subcutaneously and can be palpated easily. When the elbow joint is extended, the tip of the olecranon process, the medial and the lateral epicondyles lie in a straight line. W ...
Unit 23: Deep Face, Infratemporal Fossa Dissection Instructions
... alveolar nerve into the mandible. With the autopsy saw cut through the neck of the mandible immediately below the temporomandibular joint and insertion of the lateral pterygoid muscle. Next cut through the ramus of the mandible immediately above the mandibular foramen without cutting the inferior al ...
... alveolar nerve into the mandible. With the autopsy saw cut through the neck of the mandible immediately below the temporomandibular joint and insertion of the lateral pterygoid muscle. Next cut through the ramus of the mandible immediately above the mandibular foramen without cutting the inferior al ...
Anterior and Medial Thigh
... b. inserts along the entire back of the shaft of the femur down to the adductor tubercle that is on the medial supracondylar line c. the adductor magnus is divided into two parts (1) the upper fibers are horizontal - from pubic ramus (a) adducts, medially rotates and assists in flexing the thigh (b) ...
... b. inserts along the entire back of the shaft of the femur down to the adductor tubercle that is on the medial supracondylar line c. the adductor magnus is divided into two parts (1) the upper fibers are horizontal - from pubic ramus (a) adducts, medially rotates and assists in flexing the thigh (b) ...
凌树才_Anterolateral Abdominal Wall
... -four-layered fold of peritoneum, the anterior two layers descend from the greater curvature of stomach and superior part of duodenum and hangs down like an apron in front of coils of small intestine, and then turns upward and attaches to the transverse colon. If an infection occurs in the intestine ...
... -four-layered fold of peritoneum, the anterior two layers descend from the greater curvature of stomach and superior part of duodenum and hangs down like an apron in front of coils of small intestine, and then turns upward and attaches to the transverse colon. If an infection occurs in the intestine ...
Frog Dissection
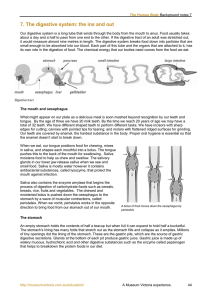
... lower eyelids. Locate the nictitating membrane that is a transparent covering that sweeps upward over the eyes. Identify the tympanic membrane or the eardrum located on each side of the head. Observe the frontal organ or brow spot found between and anterior to the two eyes. The frontal organ is the ...
... lower eyelids. Locate the nictitating membrane that is a transparent covering that sweeps upward over the eyes. Identify the tympanic membrane or the eardrum located on each side of the head. Observe the frontal organ or brow spot found between and anterior to the two eyes. The frontal organ is the ...
ACR-517-Handout-13 - Acupuncture Massage College
... • Several different systems: Jiao, Zhu, Yamamoto (YNSA), etc ...
... • Several different systems: Jiao, Zhu, Yamamoto (YNSA), etc ...
Upper Respiratory Organs
... Muscles of Inspiration Diaphragm- Located between abdominal and thoracic cavity. - Origin, Xiphoid process , costal cartilages of last six ribs - Insertion, Central tendon - Pulls down on central tendon, increases vertical length of thorax ...
... Muscles of Inspiration Diaphragm- Located between abdominal and thoracic cavity. - Origin, Xiphoid process , costal cartilages of last six ribs - Insertion, Central tendon - Pulls down on central tendon, increases vertical length of thorax ...
Lecture (1) Parts: 1. Thoracic cage. 2. Thoracic wall. 3. Thoracic cavity.
... Foramen, circular. Transverse process has facet to articulate with the rib of the same number. Spine, long and oblique. Body 2 Superior facets, for inferior facet of the same Rib number. ...
... Foramen, circular. Transverse process has facet to articulate with the rib of the same number. Spine, long and oblique. Body 2 Superior facets, for inferior facet of the same Rib number. ...
BIO 2125 - Animal Form and Function Midterm
... 3.24 The outermost body covering of a nematode is called this.____________________ Cuticle 3.25 This opening is found on the annelid's pygidium.________________________ Anus ...
... 3.24 The outermost body covering of a nematode is called this.____________________ Cuticle 3.25 This opening is found on the annelid's pygidium.________________________ Anus ...
Shoulder Injuries
... supraspinatus tendon, subacromial bursa, long head of biceps tendon (all are under the coracoacromial arch) ...
... supraspinatus tendon, subacromial bursa, long head of biceps tendon (all are under the coracoacromial arch) ...
Vertebral Column
... As you get older, the H2O content decreases and the nucleus becomes more fibrocartilaginous, therefore less easily deformable and more easily damaged ...
... As you get older, the H2O content decreases and the nucleus becomes more fibrocartilaginous, therefore less easily deformable and more easily damaged ...
The Human Body - Background Notes 7-9
... work together for precision and strength. The skeletal system Our skeleton is the body's supporting framework. When muscles pull on the skeleton, movements are made. A skeleton has bones, joints and cartilage and makes up 20% of our body weight. Joints are the meeting point of adjoining bones that c ...
... work together for precision and strength. The skeletal system Our skeleton is the body's supporting framework. When muscles pull on the skeleton, movements are made. A skeleton has bones, joints and cartilage and makes up 20% of our body weight. Joints are the meeting point of adjoining bones that c ...
2-Bones of Lower Limb-20152014-12-01 21:352.4 MB
... •Which one of the following bones forms the heel of foot? a. Talus. b. Calcaneum. c. Cuboid. d. Navicular. The medial bone of the leg is : ...
... •Which one of the following bones forms the heel of foot? a. Talus. b. Calcaneum. c. Cuboid. d. Navicular. The medial bone of the leg is : ...
anatomy
... 1. Flexion - decrease in joint angle, if thigh or shoulder it means bringing it anteriorly a. lateral flexion - bending of a joint, decrease of a joint angle 2. Extension - increase in joint angle In anatomic position most joints are in extension 3. Abduction - away from the main axis 4. Adduction - ...
... 1. Flexion - decrease in joint angle, if thigh or shoulder it means bringing it anteriorly a. lateral flexion - bending of a joint, decrease of a joint angle 2. Extension - increase in joint angle In anatomic position most joints are in extension 3. Abduction - away from the main axis 4. Adduction - ...
name of joint
... cushion the movement of one body part over another b. located between skin and bone (where skin rubs over bone), and between muscle, tendons, ligaments and bone. ...
... cushion the movement of one body part over another b. located between skin and bone (where skin rubs over bone), and between muscle, tendons, ligaments and bone. ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.