Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
... organs, and vascular branches to the external carotid artery. The sympathetic trunk continues into the head as the internal carotid nerve, which enters the carotid canal and forms a plexus around the internal carotid artery to be distributed by its branches (Plates 124, 222; 8.24, 8.28A&B). Clean th ...
... organs, and vascular branches to the external carotid artery. The sympathetic trunk continues into the head as the internal carotid nerve, which enters the carotid canal and forms a plexus around the internal carotid artery to be distributed by its branches (Plates 124, 222; 8.24, 8.28A&B). Clean th ...
Analysis of force vectors and torques generated by rotator cuff
... plane (p<.05). The maximum muscle force may be estimated from the physiological cross-sectional area of each muscle (Ikai & Fukunaga, 1968). The subscapularis has the largest proportional physiological cross-sectional area among the cuff muscles and the decrease in the DSI of the subscapularis in th ...
... plane (p<.05). The maximum muscle force may be estimated from the physiological cross-sectional area of each muscle (Ikai & Fukunaga, 1968). The subscapularis has the largest proportional physiological cross-sectional area among the cuff muscles and the decrease in the DSI of the subscapularis in th ...
06 Radiological_Anatomy_of_Thorax_(2)[1]
... normal chest x-ray, such as when the patient cannot get out of bed. ...
... normal chest x-ray, such as when the patient cannot get out of bed. ...
Unit 17: Temporal and Infratemporal Fossa
... immediately below the temporomandibular joint and insertion of the lateral pterygoid muscle and cut through the ramus of the mandible immediately above the mandibular foramen without cutting the inferior alveolar nerve and vessels. Clean the vessels and nerves on the surface of the lateral and media ...
... immediately below the temporomandibular joint and insertion of the lateral pterygoid muscle and cut through the ramus of the mandible immediately above the mandibular foramen without cutting the inferior alveolar nerve and vessels. Clean the vessels and nerves on the surface of the lateral and media ...
The Wrist and Hand - Fisiokinesiterapia
... A. Superficial fascia (thick on palm, thin on dorsum) B. Flexor retinaculum • attaches to the pisiform and hamulus medially • attaches to the scaphoid and trapezium laterally • forms the carpal tunnel through which pass: ¾ (the tendon of flexor carpi radialis in its own separate compartment) ¾ the t ...
... A. Superficial fascia (thick on palm, thin on dorsum) B. Flexor retinaculum • attaches to the pisiform and hamulus medially • attaches to the scaphoid and trapezium laterally • forms the carpal tunnel through which pass: ¾ (the tendon of flexor carpi radialis in its own separate compartment) ¾ the t ...
Dissection Guidelines
... The dissection of animals is important for many reasons. It helps in the learning about the internal structures of animals. It also allows students to learn how organs and tissues are interrelated. Another purpose of dissection is to allow the comparison of organisms in terms of their organs and rel ...
... The dissection of animals is important for many reasons. It helps in the learning about the internal structures of animals. It also allows students to learn how organs and tissues are interrelated. Another purpose of dissection is to allow the comparison of organisms in terms of their organs and rel ...
Arterial, neural and muscular variations in the upper limb
... M — median nerve, Mc — musculocutaneous nerve, PCH — posterior circumflex humeral artery, RA — radial artery, SA — subscapular artery, SBA — superficial brachial artery, SUC — superior ulnar collateral artery, SH — short head of the biceps brachii muscle, UA — ulnar artery, * — first communicating b ...
... M — median nerve, Mc — musculocutaneous nerve, PCH — posterior circumflex humeral artery, RA — radial artery, SA — subscapular artery, SBA — superficial brachial artery, SUC — superior ulnar collateral artery, SH — short head of the biceps brachii muscle, UA — ulnar artery, * — first communicating b ...
Elbow-Radioulnar-Wrist Joints2008-11-19 04:201.4 MB
... articular disc of inf. radioulnar joint (above) so, head of ulna does not share in this joint. 2-scaphoid, lunate and triquetral bones (below). The joint cavity does not communicate with that of distal radioulnar j. or with cavities of intercarpal joints. ...
... articular disc of inf. radioulnar joint (above) so, head of ulna does not share in this joint. 2-scaphoid, lunate and triquetral bones (below). The joint cavity does not communicate with that of distal radioulnar j. or with cavities of intercarpal joints. ...
Short Report on the Muscle Length-Tension
... wrist is fully flexed, it is very hard for one to close their hand, let alone squeeze with force. It is natural, when squeezing hard, for the wrist to be neutral. It seems to yield the highest force. These results can be explained quite easily. When the wrist is flexed, the myosin is already in a co ...
... wrist is fully flexed, it is very hard for one to close their hand, let alone squeeze with force. It is natural, when squeezing hard, for the wrist to be neutral. It seems to yield the highest force. These results can be explained quite easily. When the wrist is flexed, the myosin is already in a co ...
Lab 23: Dissection: Frog
... of the anus and follow the same cutting pattern. You will find that it will be more difficult to cut along the midline up to the lower jaw because when you reach the fore legs, you must cut through the sternum (breastbone). Continue cutting, using the pattern for the skin, until you have cut away th ...
... of the anus and follow the same cutting pattern. You will find that it will be more difficult to cut along the midline up to the lower jaw because when you reach the fore legs, you must cut through the sternum (breastbone). Continue cutting, using the pattern for the skin, until you have cut away th ...
http://www.education.ed.ac.uk/cis/waterpolo/papers/rs.html
... Given that this action is somewhat unusual in everyday activities, the muscles may not naturally be well developed. The action of adducting the hip while the knee is extending means that inertia is great. Also, there is a large fluid resistance to rapid movement of the thigh, shank and foot against ...
... Given that this action is somewhat unusual in everyday activities, the muscles may not naturally be well developed. The action of adducting the hip while the knee is extending means that inertia is great. Also, there is a large fluid resistance to rapid movement of the thigh, shank and foot against ...
Trajectory of the main sensory and motor branches of the lumbar
... They were each systematically evaluated for evidence of previous retroperitoneal, abdominal, or spinal surgeries. Bilateral dissections of the abdominal wall, retroperitoneal cavity, and lumbar plexus were performed, yielding a total of 12 dissections. Dissections were performed at the University of ...
... They were each systematically evaluated for evidence of previous retroperitoneal, abdominal, or spinal surgeries. Bilateral dissections of the abdominal wall, retroperitoneal cavity, and lumbar plexus were performed, yielding a total of 12 dissections. Dissections were performed at the University of ...
Charles Neer - Fisiokinesiterapia
... Passage to the posterior one-third of the deltoid and an interval between infraspinatus and teres minor Structures at risk – Quadrangular space - posterior humeral circumflex artery and ...
... Passage to the posterior one-third of the deltoid and an interval between infraspinatus and teres minor Structures at risk – Quadrangular space - posterior humeral circumflex artery and ...
BONES OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
... ON YOURSELF AND/OR ANOTHER PERSON, LOCATE THE FOLLOWING: Spinous processes of thoracic and lumbar vertebrae Border between lumbar vertebrae and sacrum Sacrum and coccyx Notice the curvatures of the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral regions of the vertebral column This will require exposure of t ...
... ON YOURSELF AND/OR ANOTHER PERSON, LOCATE THE FOLLOWING: Spinous processes of thoracic and lumbar vertebrae Border between lumbar vertebrae and sacrum Sacrum and coccyx Notice the curvatures of the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral regions of the vertebral column This will require exposure of t ...
PARTS OF THE PHARYNX THE PHARYNX Skeleton THE
... Raising the larynx (helping to fold the epiglottis and seal off the airway) Pulling the pharynx up over the bolus Then circular/constrictor muscles contract and the longitudinal ones relax Carrying the bolus down Peristaltic contractions then take over ...
... Raising the larynx (helping to fold the epiglottis and seal off the airway) Pulling the pharynx up over the bolus Then circular/constrictor muscles contract and the longitudinal ones relax Carrying the bolus down Peristaltic contractions then take over ...
HIGH-YIELD FACTS Ear, Nose, and Throat - McGraw-Hill
... nasal cavity transmits the nasopalatine nerve and branches of the sphenopalatine artery. ...
... nasal cavity transmits the nasopalatine nerve and branches of the sphenopalatine artery. ...
The ankle is a large joint made up of three bones: The shin bone
... High ankle sprain: The ligament joining the two bones of the lower leg (tibia and fibula), called the syndesmotic ligament, is injured. A high ankle sprain causes pain and swelling similar to a true ankle sprain, but can take longer to heal. Ankle fracture: A break in any of the three bones in the a ...
... High ankle sprain: The ligament joining the two bones of the lower leg (tibia and fibula), called the syndesmotic ligament, is injured. A high ankle sprain causes pain and swelling similar to a true ankle sprain, but can take longer to heal. Ankle fracture: A break in any of the three bones in the a ...
Muscles of the face
... nodes. A few buccal lymph nodes may be present along the course of these lymph vessels . the lateral parts of the eyelids , is drained by lymph vessels that end in the parotid lymph nodes. The central part of the lower lip and the skin of the chin are drained into the submental lymph nodes. ...
... nodes. A few buccal lymph nodes may be present along the course of these lymph vessels . the lateral parts of the eyelids , is drained by lymph vessels that end in the parotid lymph nodes. The central part of the lower lip and the skin of the chin are drained into the submental lymph nodes. ...
7. Development of digestive system I. Yolk sac. Primitive gut
... o anteriorly, there is an oral (oropharyngeal) membrane (breaks down before week 4) o posteriorly, there is a cloacal membrane (breaks down after month 3) − the primitive gut becomes divided into three parts: o the foregut, which develops into pharynx (extends from the oropharyngeal membrane to the ...
... o anteriorly, there is an oral (oropharyngeal) membrane (breaks down before week 4) o posteriorly, there is a cloacal membrane (breaks down after month 3) − the primitive gut becomes divided into three parts: o the foregut, which develops into pharynx (extends from the oropharyngeal membrane to the ...
as a pdf
... tissue is a bridge between the “deep” or lateral common iliac nodes and the presacral nodes. Without discussing the anatomical terminology of the different lymph node stations, the pelvic lymphadenectomy is complete when the vessels are totally free all around their circumference, the obturator nerv ...
... tissue is a bridge between the “deep” or lateral common iliac nodes and the presacral nodes. Without discussing the anatomical terminology of the different lymph node stations, the pelvic lymphadenectomy is complete when the vessels are totally free all around their circumference, the obturator nerv ...
Larynx
... oblique line (for attachment of Muscles). Muscles attaching to the oblique line include • Sternothyroid muscle (insertion) • Thyrohyoid muscle (origin) • Inferior constrictor muscle (origin) ...
... oblique line (for attachment of Muscles). Muscles attaching to the oblique line include • Sternothyroid muscle (insertion) • Thyrohyoid muscle (origin) • Inferior constrictor muscle (origin) ...
Skull part 2
... • Usually consists of 22 bones, all of which (except the lower jaw) are firmly interlocked along lines called “sutures”. – Cranium = 8 bones – Facial skeleton = 13 bones + lower jaw – Lower jaw bone is called the mandible, and is the only movable bone. ...
... • Usually consists of 22 bones, all of which (except the lower jaw) are firmly interlocked along lines called “sutures”. – Cranium = 8 bones – Facial skeleton = 13 bones + lower jaw – Lower jaw bone is called the mandible, and is the only movable bone. ...
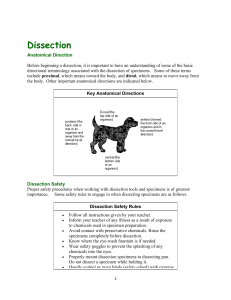
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.


![06 Radiological_Anatomy_of_Thorax_(2)[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000414327_1-04da754cadb08122653c700a0fc76def-300x300.png)