Chemistry with Physics Structure for Quiz
... How do you read a graduated cylinder? By reading the bottom of the meniscus at eye level. Read the volume using all certain digits and one uncertain digit. ...
... How do you read a graduated cylinder? By reading the bottom of the meniscus at eye level. Read the volume using all certain digits and one uncertain digit. ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... 2.3 × 1014 hertz. Using your graph, estimate the energy associated with this spectral line. [1] 68 Explain, in terms of subatomic particles and energy states, why light is emitted by the hydrogen gas. [1] 69 Identify one condition not mentioned in the passage, under which hydrogen gas behaves most l ...
... 2.3 × 1014 hertz. Using your graph, estimate the energy associated with this spectral line. [1] 68 Explain, in terms of subatomic particles and energy states, why light is emitted by the hydrogen gas. [1] 69 Identify one condition not mentioned in the passage, under which hydrogen gas behaves most l ...
Structure and Properties of Matter Jeopardy
... reactive metals are25% found __25% In group 1, the first column on the left In period 1, the first row across the top In group 13 through 16 near the right In periods 6 and 7 at the bottom ...
... reactive metals are25% found __25% In group 1, the first column on the left In period 1, the first row across the top In group 13 through 16 near the right In periods 6 and 7 at the bottom ...
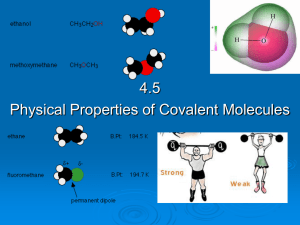
4.5 Physical properties of molecular covalent
... Simple covalent molecules tend to be gases, liquids or low melting point solids. A covalent molecule has an increasing tendency to become a solid as its molecular mass increases. This is because the strength of the van der waals forces increases, decreasing the distance between the molecules. E. ...
... Simple covalent molecules tend to be gases, liquids or low melting point solids. A covalent molecule has an increasing tendency to become a solid as its molecular mass increases. This is because the strength of the van der waals forces increases, decreasing the distance between the molecules. E. ...
H3AsO4 + 3 I- + 2 H3O+ H3AsO3 + I3- + H2O
... Bond strength and length is also affected by the number of shared electrons. Sharing of one pair of electrons produces a single bond; whereas the sharing of two or three pairs of electrons produces double or triple bonds, respectively. Multiple bonds are stronger and shorter than single bonds. The p ...
... Bond strength and length is also affected by the number of shared electrons. Sharing of one pair of electrons produces a single bond; whereas the sharing of two or three pairs of electrons produces double or triple bonds, respectively. Multiple bonds are stronger and shorter than single bonds. The p ...
6.1 Moles and Molar Masses
... Empirical formulas can be calculated from lab data, allowing us to identify unknown compounds: STEP 1: Assume mass percentages represent masses, in g: STEP 2: Divide each element's mass by their respective molar masses, turning them into moles. STEP 3: Divide all moles by the lowest number of moles ...
... Empirical formulas can be calculated from lab data, allowing us to identify unknown compounds: STEP 1: Assume mass percentages represent masses, in g: STEP 2: Divide each element's mass by their respective molar masses, turning them into moles. STEP 3: Divide all moles by the lowest number of moles ...
Slide 1
... • The formulas for compounds are determined by quantitative analysis. • If the numbers of moles obtained by quantitative analysis are fractional, they are transformed into whole numbers by dividing each fractional number by the smallest fractional value. This transformation produces the empirical fo ...
... • The formulas for compounds are determined by quantitative analysis. • If the numbers of moles obtained by quantitative analysis are fractional, they are transformed into whole numbers by dividing each fractional number by the smallest fractional value. This transformation produces the empirical fo ...
The Mole
... Converting With Moles Chemists often need to know about the quantitative relationships among the elements and compounds involved in a chemical reaction. These relationships may involve masses and or volumes. For Example, a chemist might want to know what volume of gas is produced when a certain mas ...
... Converting With Moles Chemists often need to know about the quantitative relationships among the elements and compounds involved in a chemical reaction. These relationships may involve masses and or volumes. For Example, a chemist might want to know what volume of gas is produced when a certain mas ...
Chapter 3
... Consider the combustion of carbon monoxide (CO) in oxygen gas: 2CO(g) + O2(g) 2CO2(g) Starting with 3.60 moles of CO, calculate the number of moles of CO2 produced if there is enough oxygen gas to react with all of the CO. A) 7.20 mol B) 44.0 mol C) 3.60 mol D) 1.80 mol Nitrous oxide (N2O) is also c ...
... Consider the combustion of carbon monoxide (CO) in oxygen gas: 2CO(g) + O2(g) 2CO2(g) Starting with 3.60 moles of CO, calculate the number of moles of CO2 produced if there is enough oxygen gas to react with all of the CO. A) 7.20 mol B) 44.0 mol C) 3.60 mol D) 1.80 mol Nitrous oxide (N2O) is also c ...
Subject Area Assessment Guides
... holding the material together are opposed by the internal energy of particle motion, which tends to break the substance apart. In a solid, internal agitation is insufficient to overcome intermolecular or inter-atomic forces. When enough energy is added to the solid, the kinetic energy of the atoms a ...
... holding the material together are opposed by the internal energy of particle motion, which tends to break the substance apart. In a solid, internal agitation is insufficient to overcome intermolecular or inter-atomic forces. When enough energy is added to the solid, the kinetic energy of the atoms a ...
LONG-RANGE SCATTERING AT LOW ENERGIES We shall give an
... We shall give an account on various recent results [DS2] on the quantum mechanical scattering theory in the low-energy regime for a class of negative slowly decaying potentials including the attractive Coulombic. This includes the construction of wave operators of Isozaki–Kitada type diagonalizing t ...
... We shall give an account on various recent results [DS2] on the quantum mechanical scattering theory in the low-energy regime for a class of negative slowly decaying potentials including the attractive Coulombic. This includes the construction of wave operators of Isozaki–Kitada type diagonalizing t ...
Term 1 and 2 Powerpoints
... deteriorated, and what percent of our atmosphere is made up harmful pollutants? Well when fossil fuels are burned, or maybe even things like wood or who knows, scientists most likely calculate the molecules given off so they can come up with these statistics. Well maybe they deal with moles or liter ...
... deteriorated, and what percent of our atmosphere is made up harmful pollutants? Well when fossil fuels are burned, or maybe even things like wood or who knows, scientists most likely calculate the molecules given off so they can come up with these statistics. Well maybe they deal with moles or liter ...
Topic 1 Assignment File
... Calculate the percent yields in each of the following cases: a. Theoretical yield 50.0 g of product; actual yield 41.9 g b. Theoretical yield is 290 kg of product; actual yield is 270 kg c. Theoret ...
... Calculate the percent yields in each of the following cases: a. Theoretical yield 50.0 g of product; actual yield 41.9 g b. Theoretical yield is 290 kg of product; actual yield is 270 kg c. Theoret ...
The Mole
... A hydrate is an ionic compound that has crystallized from a water solution and has water molecules incorporated into their crystal structure. Hydrates have a specific number of water molecules chemically bonded to each formula unit. Compounds that have no water molecules incorporated into them are c ...
... A hydrate is an ionic compound that has crystallized from a water solution and has water molecules incorporated into their crystal structure. Hydrates have a specific number of water molecules chemically bonded to each formula unit. Compounds that have no water molecules incorporated into them are c ...
AP Chemistry Second Semester Notes
... 3. compounds are groups of atoms in fixed ratio b. subatomic structure 2. precision = consistent (even if incorrect) is 1. J. J. Thomson (1897): measure charge-tomeasured by percent deviation (N trials): mass ratio of electrons with cathode rays % = 100 |trial – mean|/N(mean) 2. Millikan (1909): ...
... 3. compounds are groups of atoms in fixed ratio b. subatomic structure 2. precision = consistent (even if incorrect) is 1. J. J. Thomson (1897): measure charge-tomeasured by percent deviation (N trials): mass ratio of electrons with cathode rays % = 100 |trial – mean|/N(mean) 2. Millikan (1909): ...
Which notation represents an atom of sodium
... temperature is 20.°C. The direction of heat flow is heat travels from source a) from the person to the ice, only to sink (high to low) b) from the person to the ice and air, and from the air to the ice c) from the ice to the person, only d) from the ice to the person and air, and from the air to ...
... temperature is 20.°C. The direction of heat flow is heat travels from source a) from the person to the ice, only to sink (high to low) b) from the person to the ice and air, and from the air to the ice c) from the ice to the person, only d) from the ice to the person and air, and from the air to ...
Week 8 - Day 3 (End of Chapter 6)
... Lewis theory generally predicts trends in properties, but it does not give good numerical predictions. ...
... Lewis theory generally predicts trends in properties, but it does not give good numerical predictions. ...
Chemistry
... 6. Distinguish ionic and covalent compounds in terms of physical and chemical properties including electron distribution between bonded atoms. 7. Describe the basic electronic structure of molecules in terms of Valence Bond Theory and Molecular Orbital Theory. 8. Determine the geometry of and electr ...
... 6. Distinguish ionic and covalent compounds in terms of physical and chemical properties including electron distribution between bonded atoms. 7. Describe the basic electronic structure of molecules in terms of Valence Bond Theory and Molecular Orbital Theory. 8. Determine the geometry of and electr ...
9791/02 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL
... (d) When a bromine molecule adds across a C=C double bond the two bromine atoms bond to opposite faces of the molecule. Draw all different possible products when one molecule of cyclohexa-1,4-diene reacts with two molecules of bromine. Show the six-membered carbon ring as a hexagon in the plane of t ...
... (d) When a bromine molecule adds across a C=C double bond the two bromine atoms bond to opposite faces of the molecule. Draw all different possible products when one molecule of cyclohexa-1,4-diene reacts with two molecules of bromine. Show the six-membered carbon ring as a hexagon in the plane of t ...
Ch 11 Review - mvhs
... (d) Acetone molecules are attracted to each other by van der Waals attraction and dipole-dipole attraction. 1-propanol molecules show these two types of attraction. However, 1-propanol can also undergo hydrogen bonding. This distinguishing feature results in the higher boiling point of 1-propanol. 2 ...
... (d) Acetone molecules are attracted to each other by van der Waals attraction and dipole-dipole attraction. 1-propanol molecules show these two types of attraction. However, 1-propanol can also undergo hydrogen bonding. This distinguishing feature results in the higher boiling point of 1-propanol. 2 ...
Your views are welcomed upon the theme of
... outer shell or an octet of electrons in the outer shell. Helium has the former, but not the latter. Argon has the latter, but not a full outer shell. Only the atom of neon has both.) Discrete atoms that do not have this type of outer shell structure are seldom found in nature: so single atoms of car ...
... outer shell or an octet of electrons in the outer shell. Helium has the former, but not the latter. Argon has the latter, but not a full outer shell. Only the atom of neon has both.) Discrete atoms that do not have this type of outer shell structure are seldom found in nature: so single atoms of car ...
The Motion of a Pair of Charged Particles
... for Xc the position closest to D/2 in a given trajectory – that’s what led to ∆T = .0005 [? ]. While it is clear from Figure 4 that the four cases we have considered have quantitatively different values for T ∗ , we are not claiming particularly high accuracy for T ∗ . The accuracy is, however, goo ...
... for Xc the position closest to D/2 in a given trajectory – that’s what led to ∆T = .0005 [? ]. While it is clear from Figure 4 that the four cases we have considered have quantitatively different values for T ∗ , we are not claiming particularly high accuracy for T ∗ . The accuracy is, however, goo ...
Chemistry Answers - Heathcote School and Science College
... In a titration between potassium hydroxide solution and nitric acid 25.0 cm3 of 0.25 mol/dm3 potassium hydroxide solution is neutralised by 0.2 mol/dm3 nitric acid. Use the information to calculate the volume of nitric acid needed to exactly neutralise the potassium hydroxide solution. Give your ans ...
... In a titration between potassium hydroxide solution and nitric acid 25.0 cm3 of 0.25 mol/dm3 potassium hydroxide solution is neutralised by 0.2 mol/dm3 nitric acid. Use the information to calculate the volume of nitric acid needed to exactly neutralise the potassium hydroxide solution. Give your ans ...