Section 1 Forming New Substances Chapter 9
... Chemical formulas of reactants are listed on the lefthand side of the equation. Products are listed on the righthand side of the equation. Reactants and products are separated by putting an arrow between them to show the direction of the reaction. Reactions at equilibrium will have arrows facing bot ...
... Chemical formulas of reactants are listed on the lefthand side of the equation. Products are listed on the righthand side of the equation. Reactants and products are separated by putting an arrow between them to show the direction of the reaction. Reactions at equilibrium will have arrows facing bot ...
Computational Prototyping Tools and Techniques—J.K. White, L. Daniel, A. Megretski, J. Peraire, B. Tidor, K. Willcox
... contrast, integrated circuit designers do not need such a high level of specialization. Instead, they rely on a coordinated suite of synthesis and verification tools that makes it possible to design an application-specific circuit with high confidence of first-pass success, even without becoming an ...
... contrast, integrated circuit designers do not need such a high level of specialization. Instead, they rely on a coordinated suite of synthesis and verification tools that makes it possible to design an application-specific circuit with high confidence of first-pass success, even without becoming an ...
Introduction to Stoichiometry
... What is Stoichiometry? The proportional relationship between two or more substances during a chemical reaction. In other words, using dimensional analysis to convert one substance to another There are many different types, but they are all similar. So, let’s start small. How small? ...
... What is Stoichiometry? The proportional relationship between two or more substances during a chemical reaction. In other words, using dimensional analysis to convert one substance to another There are many different types, but they are all similar. So, let’s start small. How small? ...
1 • Introduction The Scientific Method (1 of 20) 1
... PE = the potential to do work which is due to an object’s position in a field. For example, if I hold a book 0.5 m above a student’s head it can do some damage... 1.0 m above her/his head, more work can be done. Important ideas: Objects tend to change from high PE to low PE (downhill). High PE is le ...
... PE = the potential to do work which is due to an object’s position in a field. For example, if I hold a book 0.5 m above a student’s head it can do some damage... 1.0 m above her/his head, more work can be done. Important ideas: Objects tend to change from high PE to low PE (downhill). High PE is le ...
Example
... Example: A hydrate of magnesium iodide has the formula MgI2 ∙ X H2O. To determine the value of X, a student heats a sample of the hydrate until all the water is gone. A 1.628 g sample of hydrate is heated to constant mass of 1.072 g. What is the value of X? ...
... Example: A hydrate of magnesium iodide has the formula MgI2 ∙ X H2O. To determine the value of X, a student heats a sample of the hydrate until all the water is gone. A 1.628 g sample of hydrate is heated to constant mass of 1.072 g. What is the value of X? ...
Chemistry II
... horizontally by the number of protons in the atom’s nucleus and places those with similar chemical properties in columns. The repeating patterns of this table reflect patterns of outer electron states. (HS-PS1-1) (Note: This Disciplinary Core Idea is also addressed by HS-PS1-1.) • A stable molecule ...
... horizontally by the number of protons in the atom’s nucleus and places those with similar chemical properties in columns. The repeating patterns of this table reflect patterns of outer electron states. (HS-PS1-1) (Note: This Disciplinary Core Idea is also addressed by HS-PS1-1.) • A stable molecule ...
Alcohol responsive 2D coordination network of 3
... One of the most important objectives in the field of coordination networks or metal organic frameworks is the engineering of porous structures with a well defined chemical environment [1–2]. This is however very difficult to achieve in 3D structures due to catenation and interpenetration. Thus in re ...
... One of the most important objectives in the field of coordination networks or metal organic frameworks is the engineering of porous structures with a well defined chemical environment [1–2]. This is however very difficult to achieve in 3D structures due to catenation and interpenetration. Thus in re ...
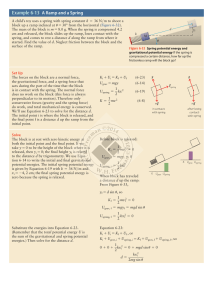
Example 6-13 A Ramp and a Spring
... the spring. That’s consistent with our result: The block moves 81 cm up the ramp, much greater than the 4.2-cm distance by which the spring was originally compressed. Our solution shows that the net effect of the block’s motion is to convert spring potential energy at the initial position to gravita ...
... the spring. That’s consistent with our result: The block moves 81 cm up the ramp, much greater than the 4.2-cm distance by which the spring was originally compressed. Our solution shows that the net effect of the block’s motion is to convert spring potential energy at the initial position to gravita ...
Chemkin-Pro
... combustion system design. Because this condition Accurate emissions prediction with chemistry is dictated by real chemistry and fluid dynamics, Combustor design simulation requires resolution of complex geometry, turbulent flow patterns, heat the reduced chemistry intrinsic to most CFD tools cannot ...
... combustion system design. Because this condition Accurate emissions prediction with chemistry is dictated by real chemistry and fluid dynamics, Combustor design simulation requires resolution of complex geometry, turbulent flow patterns, heat the reduced chemistry intrinsic to most CFD tools cannot ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... questions on this separate answer sheet. Record your answers for the questions in Part B–2 and Part C in your separate answer booklet. Be sure to fill in the heading on the front of your answer booklet. All answers in your answer booklet should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, whic ...
... questions on this separate answer sheet. Record your answers for the questions in Part B–2 and Part C in your separate answer booklet. Be sure to fill in the heading on the front of your answer booklet. All answers in your answer booklet should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, whic ...
chemistry
... same number (6.023 10 ) of molecules therefore, they occupy same volume under similar conditions of temperature and pressure. The volume occupied by one mole molecules of a gaseous substance is called Molar volume. One mole molecules of all gases occupy 22.4 litres at 273 K and 760 mm pressure (S. ...
... same number (6.023 10 ) of molecules therefore, they occupy same volume under similar conditions of temperature and pressure. The volume occupied by one mole molecules of a gaseous substance is called Molar volume. One mole molecules of all gases occupy 22.4 litres at 273 K and 760 mm pressure (S. ...
Chemical Formulas and Chemical Compounds
... a. What is the mass in grams of 3.00 mol of butane? ...
... a. What is the mass in grams of 3.00 mol of butane? ...
Molecular Modeling Activity for Carbohydrates
... In order to join the molecules, remove an OH end from one molecule and an -H end from another. 7. Does removing the -H and OH ends allow the molecules to fit easily together? ___________________ 8. The -H and OH ends that were removed can also fit together with each other to form a molecule. Thi ...
... In order to join the molecules, remove an OH end from one molecule and an -H end from another. 7. Does removing the -H and OH ends allow the molecules to fit easily together? ___________________ 8. The -H and OH ends that were removed can also fit together with each other to form a molecule. Thi ...
2.5 THE NAMES AND FORMULAS OF COMPOUNDS
... explain many of the properties of ionic compounds, but they aren’t sufficient to explain the physical state of molecular compounds. If covalent bonds were the only forces at work, molecular compounds would all be gases, as there would be no attraction between the molecules strong enough to order the ...
... explain many of the properties of ionic compounds, but they aren’t sufficient to explain the physical state of molecular compounds. If covalent bonds were the only forces at work, molecular compounds would all be gases, as there would be no attraction between the molecules strong enough to order the ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... 1. Write the most common guidelines to determine significant figures (digits) with an example? 2. Use factor labeling method to convert the following: a. 200 meters = ___ miles. b. 650 in = ____ meters c. 4 years= _____ seconds. d. 200 liters = _____ ml 3. Classify each of the following as units of ...
... 1. Write the most common guidelines to determine significant figures (digits) with an example? 2. Use factor labeling method to convert the following: a. 200 meters = ___ miles. b. 650 in = ____ meters c. 4 years= _____ seconds. d. 200 liters = _____ ml 3. Classify each of the following as units of ...
Practical Difficulty and Techniques in Matrix-Product-State
... Computational difficulty of MPS simulation of quantum computing (Josza’s theorem) and practical difficulty Structure dependence of computational cost (From an empirical point of view) Accumulation of numerical error and workaround by using multiple-precision computing Other techniques in developing ...
... Computational difficulty of MPS simulation of quantum computing (Josza’s theorem) and practical difficulty Structure dependence of computational cost (From an empirical point of view) Accumulation of numerical error and workaround by using multiple-precision computing Other techniques in developing ...
3.1 Atomic Mass - Pace University Webspace
... occur and what we get is the actual yield. This is yield is less than the theoretical yield and happens because of the fact that many reactions are reversible and are not produced 100 percent from left to right. ...
... occur and what we get is the actual yield. This is yield is less than the theoretical yield and happens because of the fact that many reactions are reversible and are not produced 100 percent from left to right. ...
Chapter 2
... Atomic Number and Atomic Mass • Atoms of the various elements differ in number of subatomic particles • An element’s atomic number is the number of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be appro ...
... Atomic Number and Atomic Mass • Atoms of the various elements differ in number of subatomic particles • An element’s atomic number is the number of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be appro ...
Outline Fast Multipole Methods CMSC 858M/AMSC 698R Lecture(s) 3(4)
... For |y-x*|< r*, the sum of the series is a continuous and infinitely differentiable function of y. ...
... For |y-x*|< r*, the sum of the series is a continuous and infinitely differentiable function of y. ...
Review 1
... made of silver but does not want it damaged during the analysis. The chemist decides to determine the density, knowing that silver has a density of 10.5 g/ml. The figurine is put into a graduated cylinder that contains 32.6 ml of water. The reading while the figurine is in the water is 60.1 ml. The ...
... made of silver but does not want it damaged during the analysis. The chemist decides to determine the density, knowing that silver has a density of 10.5 g/ml. The figurine is put into a graduated cylinder that contains 32.6 ml of water. The reading while the figurine is in the water is 60.1 ml. The ...
Chapter 1: The Nature of Analytical Chemistry
... composition of samples. – 4. Spectroscopic methods based on interaction of electromagnetic radiation with analyte atoms & molecules, or on the production of radiation by ...
... composition of samples. – 4. Spectroscopic methods based on interaction of electromagnetic radiation with analyte atoms & molecules, or on the production of radiation by ...
Topic 1: Quantitative Chemistry
... Solid –particles closely packed in fixed positions; forces between particles strong enough to restrict movement; have fixed shape Liquid –particles closely packed but not in fixed position; forces between particles weak enough to allow movement but fix the volume; no fixed shape Gas –forces betwe ...
... Solid –particles closely packed in fixed positions; forces between particles strong enough to restrict movement; have fixed shape Liquid –particles closely packed but not in fixed position; forces between particles weak enough to allow movement but fix the volume; no fixed shape Gas –forces betwe ...