Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
... Where did Medicine come from? Early ancestors who were curious how our bodies worked Early ancestors who were also curious about illness ...
... Where did Medicine come from? Early ancestors who were curious how our bodies worked Early ancestors who were also curious about illness ...
BIG Dissection Packet
... The frog's body is supported and protected by a bony framework called the skeleton The skull is flat, except for an expanded area that encases the small brain. Only nine vertebrae make up the frog's backbone, or vertebral column. The human backbone has 24 vertebrae. The frog has no ribs. The frog do ...
... The frog's body is supported and protected by a bony framework called the skeleton The skull is flat, except for an expanded area that encases the small brain. Only nine vertebrae make up the frog's backbone, or vertebral column. The human backbone has 24 vertebrae. The frog has no ribs. The frog do ...
School District of the Chathams
... COURSE/GRADE LEVEL(S): Anatomy & Physiology I. Course Overview This course is designed to explore the anatomy and physiology of the human body. In order to understand how the human body works, it must be broken down into systems that accomplish specific tasks. The course begins with a brief study of ...
... COURSE/GRADE LEVEL(S): Anatomy & Physiology I. Course Overview This course is designed to explore the anatomy and physiology of the human body. In order to understand how the human body works, it must be broken down into systems that accomplish specific tasks. The course begins with a brief study of ...
Name____________________________
... good for the circulatory system? Regular exercise strengthens the heart and lungs by making them work harder, which increases the amount of oxygen in the body. What do you think would happen if blood entering the heart mixed with blood leaving the heart? Blood carrying oxygen would mix with blood ca ...
... good for the circulatory system? Regular exercise strengthens the heart and lungs by making them work harder, which increases the amount of oxygen in the body. What do you think would happen if blood entering the heart mixed with blood leaving the heart? Blood carrying oxygen would mix with blood ca ...
directional term activity
... This lesson is designed to teach and reinforce the “language of anatomy”. In groups, label each other by anatomical direction. Then, students label drawings of themselves with anatomical directions. Keywords: superior, inferior, anterior, posterior, medial, lateral, intermediate, proximal, distal, s ...
... This lesson is designed to teach and reinforce the “language of anatomy”. In groups, label each other by anatomical direction. Then, students label drawings of themselves with anatomical directions. Keywords: superior, inferior, anterior, posterior, medial, lateral, intermediate, proximal, distal, s ...
Intro Invertebrates
... True body cavity (coelom). The organs of the digestive, nervous, and circulatory systems run the length of the body. Complex digestive and circulatory systems. Earthworms are hermaphrodites. Small brain located near the pharynx. A ventral nerve cord extends from the brain and runs the length of the ...
... True body cavity (coelom). The organs of the digestive, nervous, and circulatory systems run the length of the body. Complex digestive and circulatory systems. Earthworms are hermaphrodites. Small brain located near the pharynx. A ventral nerve cord extends from the brain and runs the length of the ...
Student Notes for Lab Quiz 2
... Circulation. Details noted below. It may also contain anything that was covered for Lab 3/4 Animal Diversity Lab (see study information for Lab Quiz #1). Note that for the Lab Practicum (on March 6) you will also need to know the functions of the structures. Types of questions: You will be shown a p ...
... Circulation. Details noted below. It may also contain anything that was covered for Lab 3/4 Animal Diversity Lab (see study information for Lab Quiz #1). Note that for the Lab Practicum (on March 6) you will also need to know the functions of the structures. Types of questions: You will be shown a p ...
The Human Body Intro
... and Respiratory systems for nutrients and oxygen but it is regulated by the hormones of the Endocrine system. ...
... and Respiratory systems for nutrients and oxygen but it is regulated by the hormones of the Endocrine system. ...
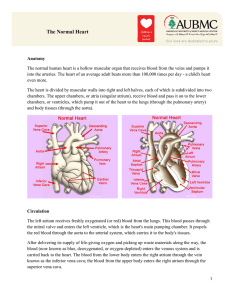
The Normal Heart
... The left atrium receives freshly oxygenated (or red) blood from the lungs. This blood passes through the mitral valve and enters the left ventricle, which is the heart's main pumping chamber. It propels the red blood through the aorta to the arterial system, which carries it to the body's tissues. A ...
... The left atrium receives freshly oxygenated (or red) blood from the lungs. This blood passes through the mitral valve and enters the left ventricle, which is the heart's main pumping chamber. It propels the red blood through the aorta to the arterial system, which carries it to the body's tissues. A ...
KINGDOMS OF ORGANISMS
... Organs mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Function breaks down food to provide nutrients and removes solid wastes ...
... Organs mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Function breaks down food to provide nutrients and removes solid wastes ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Fredericksburg City Schools
... I.Overview of Anatomy and Physiology ____________________= the study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts and their relationships to one another…..large body structures---gross anatomy v.__________________anatomy(too small to be seen w/o a microscope) _______________________study of ...
... I.Overview of Anatomy and Physiology ____________________= the study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts and their relationships to one another…..large body structures---gross anatomy v.__________________anatomy(too small to be seen w/o a microscope) _______________________study of ...
What is anatomy?
... we want to thank all of the individuals who have helped move this project to completion. Beginning with early discussions between the authors, William Schmitt and Rebecca Gruliow helped in evaluating the need for this type of concise textbook and how quickly the project could be completed. These dis ...
... we want to thank all of the individuals who have helped move this project to completion. Beginning with early discussions between the authors, William Schmitt and Rebecca Gruliow helped in evaluating the need for this type of concise textbook and how quickly the project could be completed. These dis ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 12 Martini Lecture Outline
... Cross-Sectional Anatomy Cross-sectional views are important for understanding radiological techniques Standard method of viewing radiological images: View images from the feet toward the head (inferior views) The anterior aspect of the image is toward the top of the page The right side of the image ...
... Cross-Sectional Anatomy Cross-sectional views are important for understanding radiological techniques Standard method of viewing radiological images: View images from the feet toward the head (inferior views) The anterior aspect of the image is toward the top of the page The right side of the image ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 12 Martini Lecture Outline
... Cross-Sectional Anatomy Cross-sectional views are important for understanding radiological techniques Standard method of viewing radiological images: View images from the feet toward the head (inferior views) The anterior aspect of the image is toward the top of the page The right side of the image ...
... Cross-Sectional Anatomy Cross-sectional views are important for understanding radiological techniques Standard method of viewing radiological images: View images from the feet toward the head (inferior views) The anterior aspect of the image is toward the top of the page The right side of the image ...
U_5_Human_body_nove
... occur, permits development and birth of offspring, nourishes offspring, and produces sex hormones. ...
... occur, permits development and birth of offspring, nourishes offspring, and produces sex hormones. ...
Frog Dissection Pre-Lab
... Respiratory System 7. Unlike humans, frogs are also able to breath or exchange gas through their __________ 8. Air enters the mouth through the frog’s nostrils and passes through the ___________ down to the lungs. 9. Amphibians have two __________, which move oxygen into the blood and remove carbon ...
... Respiratory System 7. Unlike humans, frogs are also able to breath or exchange gas through their __________ 8. Air enters the mouth through the frog’s nostrils and passes through the ___________ down to the lungs. 9. Amphibians have two __________, which move oxygen into the blood and remove carbon ...
File
... 2. The main function of the human digestive system is to a) carry nutrients to all parts of the body b) exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs c) break down foods for absorption into the blood d) release energy from sugars within the cells 3. Running is an activity that causes the cells in ...
... 2. The main function of the human digestive system is to a) carry nutrients to all parts of the body b) exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs c) break down foods for absorption into the blood d) release energy from sugars within the cells 3. Running is an activity that causes the cells in ...
Vascular Anatomy of the upper limb
... ! Red : Important. ! Violet: Explanation. ! Gray: Additional Notes. ...
... ! Red : Important. ! Violet: Explanation. ! Gray: Additional Notes. ...
Lower Extremity Anatomy
... – Calcaneus – Largest tarsal, prominence of the heel, tuberosity which is insertion for ligaments and tendons (Achilles) • Sustentaculum Tali – medial surface which supports the talus • Sinus Tarsi – canal from articulation between talus and calcaneous ...
... – Calcaneus – Largest tarsal, prominence of the heel, tuberosity which is insertion for ligaments and tendons (Achilles) • Sustentaculum Tali – medial surface which supports the talus • Sinus Tarsi – canal from articulation between talus and calcaneous ...
History of anatomy

The history of anatomy extends from the earliest examinations of sacrificial victims to the sophisticated analyses of the body performed by modern scientists. It has been characterized, over time, by a continually developing understanding of the functions of organs and structures in the body. Human anatomy was the most prominent of the biological sciences of the 19th and early 20th centuries. Methods have also improved dramatically.