AP® BIOLOGY 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
... with good descriptions of those terms. A total of 6 points were earned from the description of how a plasmid can be modified. The first point was earned for providing the definition of the plasmid. The next 3 points were earned for the description of the cutting of the DNA: the plasmid and the gene ...
... with good descriptions of those terms. A total of 6 points were earned from the description of how a plasmid can be modified. The first point was earned for providing the definition of the plasmid. The next 3 points were earned for the description of the cutting of the DNA: the plasmid and the gene ...
Homeostasis Invertase
... level of the protein (e.g. enzyme). In fact, there is coordination across these levels to maintain homeostasis of critical factors such as body temperature, ionic concentrations (like protons and calcium), and "building blocks" like amino acids and nucleic acids. From an evolutionary perspective, th ...
... level of the protein (e.g. enzyme). In fact, there is coordination across these levels to maintain homeostasis of critical factors such as body temperature, ionic concentrations (like protons and calcium), and "building blocks" like amino acids and nucleic acids. From an evolutionary perspective, th ...
Enzymes - Dr. Hamad Ali Yaseen
... of another enzyme. This generally arises due to similar but different genes encoding these enzymes and frequently is tissue-type specific or dependent on the growth or developmental status of an organism. ...
... of another enzyme. This generally arises due to similar but different genes encoding these enzymes and frequently is tissue-type specific or dependent on the growth or developmental status of an organism. ...
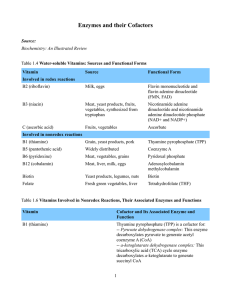
Enzymes and their Cofactors Source: Biochemistry: An Illustrated
... -- Methionine synthase/homocysteine methyltransferase: This enzyme transfers a methyl group from 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (N5-methylTHF) onto homocysteine to form methionine. Methionine reacts with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to generate S-adenosyl methionine (SAM), the latter of which regenerates ...
... -- Methionine synthase/homocysteine methyltransferase: This enzyme transfers a methyl group from 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (N5-methylTHF) onto homocysteine to form methionine. Methionine reacts with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to generate S-adenosyl methionine (SAM), the latter of which regenerates ...
Nucleic Acids Research
... mRNA (ref. 19 for a general review). For example, proline is coded by 5'-CCN-3' and alanine by 5'-GCN-3'. In other cases the pattern may be more complex, such as for isoleucine, which is coded by 5'-AT(T, C or A)-3'. Note that certain amino acids (e.g. serine) may be coded by two distinct groups of ...
... mRNA (ref. 19 for a general review). For example, proline is coded by 5'-CCN-3' and alanine by 5'-GCN-3'. In other cases the pattern may be more complex, such as for isoleucine, which is coded by 5'-AT(T, C or A)-3'. Note that certain amino acids (e.g. serine) may be coded by two distinct groups of ...
Multiple roles for ATP hydrolysis in nucleic acid modifying enzymes
... four-way junction in the DNA. RecA can promote strand exchange over a distance of around 3 kbp even in the presence of non-hydrolysable ATP analogues such as ATP-g-S (Menetski et al., 1990). The obvious conclusion from this observation is that ATP hydrolysis is not required for the strand exchange p ...
... four-way junction in the DNA. RecA can promote strand exchange over a distance of around 3 kbp even in the presence of non-hydrolysable ATP analogues such as ATP-g-S (Menetski et al., 1990). The obvious conclusion from this observation is that ATP hydrolysis is not required for the strand exchange p ...
enzymes - UniMAP Portal
... • In a series of experiments at the University of Berlin, he found that the sugar was fermented even when there were no living yeast cells in the mixture. • He named the enzyme that brought about the fermentation of sucrose "zymase". • In 1907 he received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his bioche ...
... • In a series of experiments at the University of Berlin, he found that the sugar was fermented even when there were no living yeast cells in the mixture. • He named the enzyme that brought about the fermentation of sucrose "zymase". • In 1907 he received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his bioche ...
ENZYMES AND PROTEINS
... feature of enzyme-catalysed reaction is that it occurs within the confines of a pocket on the enzyme called the active site. The molecule that is bound by the active site and acted upon by the enzyme is called as substrate. The enzyme substrate complex is central to the action of enzyme. Quality con ...
... feature of enzyme-catalysed reaction is that it occurs within the confines of a pocket on the enzyme called the active site. The molecule that is bound by the active site and acted upon by the enzyme is called as substrate. The enzyme substrate complex is central to the action of enzyme. Quality con ...
Enzymes, ATP and Bioenergetics
... Note – Coenzymes in their reduced form (NADH + H+ and FADH2) have a higher energy potential than they do when in their oxidized form (NAD and FAD). 3. Constitutive Vs repressible Vs inducible enzymes - Enzymes can be categorized as constitutive, repressible or inducible on the basis of regulatory m ...
... Note – Coenzymes in their reduced form (NADH + H+ and FADH2) have a higher energy potential than they do when in their oxidized form (NAD and FAD). 3. Constitutive Vs repressible Vs inducible enzymes - Enzymes can be categorized as constitutive, repressible or inducible on the basis of regulatory m ...
Biochemical studies in FRUIT DEVELOPMENT
... large proportion of the needed energy is made available in the process of respiration, during which hexose sugar is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water. The enzymes mediating a portion of this process are associated with sub-cellular Application of plant analysis to particles termed mitochondria, a ...
... large proportion of the needed energy is made available in the process of respiration, during which hexose sugar is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water. The enzymes mediating a portion of this process are associated with sub-cellular Application of plant analysis to particles termed mitochondria, a ...
Nomenclature for incompletely specified bases in nucleic acid
... R is the symbol previously recommended [1]. 3.3 Pyrimidine (thymine or cytosine): Y Y is the symbol previously recommended [1]. 3.4 Adenine or thymine: W Although several diverse symbols have been used for this pair, (and for the reciprocal pair G + C), only two symbols have a rational basis, L and ...
... R is the symbol previously recommended [1]. 3.3 Pyrimidine (thymine or cytosine): Y Y is the symbol previously recommended [1]. 3.4 Adenine or thymine: W Although several diverse symbols have been used for this pair, (and for the reciprocal pair G + C), only two symbols have a rational basis, L and ...
IR L Pre» Limited, Oxford, England. 3021
... Fig. 1. Origin of the 3ymbols M and K. The four bases are drawn so as to show the relationship between adenine and cytosine on the one hand, which both have aMino groups at the ring position most distant from the point of attachment to the sugar, and between guanine and thymine on the other, which b ...
... Fig. 1. Origin of the 3ymbols M and K. The four bases are drawn so as to show the relationship between adenine and cytosine on the one hand, which both have aMino groups at the ring position most distant from the point of attachment to the sugar, and between guanine and thymine on the other, which b ...