Enzyme inhibitor
... • The mechanism of partially competitive inhibition is similar to that of non-competitive, except that the EIS complex has catalytic activity, which may be lower or even higher (partially competitive activation) than that of the enzyme–substrate (ES) complex. This inhibition typically displays a low ...
... • The mechanism of partially competitive inhibition is similar to that of non-competitive, except that the EIS complex has catalytic activity, which may be lower or even higher (partially competitive activation) than that of the enzyme–substrate (ES) complex. This inhibition typically displays a low ...
Regeneration of Cofactors for Enzyme Biocatalysis
... reflects several important factors such as concentration and degradation of the cofactor over time, regioselectivity of regeneration, rate of catalysis, and time of reaction. Additionally, the availability of regenerative enzymes or reagents and their stability under process conditions is an importa ...
... reflects several important factors such as concentration and degradation of the cofactor over time, regioselectivity of regeneration, rate of catalysis, and time of reaction. Additionally, the availability of regenerative enzymes or reagents and their stability under process conditions is an importa ...
ENZYMES
... move, taste, and see. However, a bag of sugar can remain on the shelf for years without any obvious conversion to CO2 and H2O. Although this chemical process is thermodynamically favorable, it is very slow! Yet when sucrose is consumed by a human (or almost any other organism), it releases its chemi ...
... move, taste, and see. However, a bag of sugar can remain on the shelf for years without any obvious conversion to CO2 and H2O. Although this chemical process is thermodynamically favorable, it is very slow! Yet when sucrose is consumed by a human (or almost any other organism), it releases its chemi ...
“The only UNG useful in RT-PCR”
... control, is that the enzyme is sufficiently heat-labile to quickly inactivate at the temperatures used for reverse transcription. The easily heat-inactivated Cod UNG makes it possible to use contamination control also in RT-PCR, being able to remove more than 108 copies of contaminating DNA without ...
... control, is that the enzyme is sufficiently heat-labile to quickly inactivate at the temperatures used for reverse transcription. The easily heat-inactivated Cod UNG makes it possible to use contamination control also in RT-PCR, being able to remove more than 108 copies of contaminating DNA without ...
Probing the origins of glutathione biosynthesis through biochemical
... juncea) provided information about the active site architecture of a group 3 enzyme [16], but no functional studies examining the contributions of active-site residues for either these or any GCLs have been reported. Identification of amino acid residues that alter the kinetic properties of SynGCL i ...
... juncea) provided information about the active site architecture of a group 3 enzyme [16], but no functional studies examining the contributions of active-site residues for either these or any GCLs have been reported. Identification of amino acid residues that alter the kinetic properties of SynGCL i ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... motifs TENEP and ITENG, which contain the two glutamic acids (Glu-191 and Glu-406) involved in the general acid/base catalysis and the respective family 1 b-glucosidases nucleophiles (San-Aparicio et al. 1998). A part slot-like active site (Davies and Henrissat 1995) was formed by these residues nec ...
... motifs TENEP and ITENG, which contain the two glutamic acids (Glu-191 and Glu-406) involved in the general acid/base catalysis and the respective family 1 b-glucosidases nucleophiles (San-Aparicio et al. 1998). A part slot-like active site (Davies and Henrissat 1995) was formed by these residues nec ...
Effect of Alanine-293 Replacement on the Activity, ATP Binding, and
... encoding E. coli LeuRS, leuS, was subcloned from a λ15D7 clone of an E. coli genomic library by complementation of a leuS temperature-sensitive mutant KL231 in our laboratory ...
... encoding E. coli LeuRS, leuS, was subcloned from a λ15D7 clone of an E. coli genomic library by complementation of a leuS temperature-sensitive mutant KL231 in our laboratory ...
Exploration of binding site pattern in arachidonic
... interactions of AA and characterizing its binding sites in these enzymes therefore is crucial for developing enzyme specific and multi enzyme inhibitors for enhancing therapeutic efficacy and/or overcoming side effects. Results: AA binding sites in COXs and LOXs are identified and compared by the de ...
... interactions of AA and characterizing its binding sites in these enzymes therefore is crucial for developing enzyme specific and multi enzyme inhibitors for enhancing therapeutic efficacy and/or overcoming side effects. Results: AA binding sites in COXs and LOXs are identified and compared by the de ...
Phylogenomic Investigation of Phospholipid Synthesis in Archaea
... short- and long-chain enzymes, we carried out independent phylogenetic analyses for each one of the two paralogues, to which we will refer as short- or long-chain IPPS with regard to dominant functions of the characterized enzymes. However, as previously mentioned [39–41], substrate specificity exch ...
... short- and long-chain enzymes, we carried out independent phylogenetic analyses for each one of the two paralogues, to which we will refer as short- or long-chain IPPS with regard to dominant functions of the characterized enzymes. However, as previously mentioned [39–41], substrate specificity exch ...
Controlling reaction specificity in pyridoxal phosphate
... Claisen condensation, and others on substrates containing an amino group, most commonly α-amino acids. The wide variety of reactions catalyzed by PLP enzymes is enabled by the ability of the covalent aldimine intermediate formed between substrate and PLP to stabilize carbanionic intermediates at Cα ...
... Claisen condensation, and others on substrates containing an amino group, most commonly α-amino acids. The wide variety of reactions catalyzed by PLP enzymes is enabled by the ability of the covalent aldimine intermediate formed between substrate and PLP to stabilize carbanionic intermediates at Cα ...
Enzymes
... There are two fundamental conditions for life. One, the living entity must be able to self-replicate (a topic considered in Part IV of this book); two, the organism must be able to catalyze chemical reactions efficiently and selectively. The central importance of catalysis may surprise some beginnin ...
... There are two fundamental conditions for life. One, the living entity must be able to self-replicate (a topic considered in Part IV of this book); two, the organism must be able to catalyze chemical reactions efficiently and selectively. The central importance of catalysis may surprise some beginnin ...
Role of NAD+-Dependent Malate Dehydrogenase in the Metabolism
... the three domains of life. It plays crucial roles in many metabolic pathways, including the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, energy generation and the formation of metabolites for biosynthesis. Aerobic bacteria utilizing methane as a sole source of carbon and energy (methanotrophs) belong to the Alph ...
... the three domains of life. It plays crucial roles in many metabolic pathways, including the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, energy generation and the formation of metabolites for biosynthesis. Aerobic bacteria utilizing methane as a sole source of carbon and energy (methanotrophs) belong to the Alph ...
please refer to anzfa`s guide to applications and proposals for a
... Proposal P86 – Development of a Standard to Regulate the Use of Processing Aids, which reviewed the toxicity of processing aids. This Standard was gazetted in the former Australian Food Standards Code in April 1996. Standard 1.3.3 – Processing Aids was established as a result of Proposal P188 – Revi ...
... Proposal P86 – Development of a Standard to Regulate the Use of Processing Aids, which reviewed the toxicity of processing aids. This Standard was gazetted in the former Australian Food Standards Code in April 1996. Standard 1.3.3 – Processing Aids was established as a result of Proposal P188 – Revi ...
The sequence of human serum albumin cDNA and its expression in
... An additional cDNA clone extending even farther 5' was obtained by similar oligodeoxynucleotide primed cDNA synthesis (from a primer corresponding to amino acid codons no. 175-179). Although not employed in the construction of the mature HSA expression plasmid, this cDNA clone (P-14) allowed determi ...
... An additional cDNA clone extending even farther 5' was obtained by similar oligodeoxynucleotide primed cDNA synthesis (from a primer corresponding to amino acid codons no. 175-179). Although not employed in the construction of the mature HSA expression plasmid, this cDNA clone (P-14) allowed determi ...
Enzymes:The Catalysts of Life I
... are these specific amino acids brought together to form the active site (Figure 6-2b). Of the 20 different amino acids that make up proteins, only a few are actually involved in the active sites of the many proteins that have been studied. Often, these are cysteine, histidine, serine, aspartate, glu ...
... are these specific amino acids brought together to form the active site (Figure 6-2b). Of the 20 different amino acids that make up proteins, only a few are actually involved in the active sites of the many proteins that have been studied. Often, these are cysteine, histidine, serine, aspartate, glu ...
Nucleotide sequence and structural organization of
... and carbon dioxide is important because of their contribution to flavour and eye-hole formation in Dutch-type cheeses. Like other lactic acid bacteria, many Leuconostoc species harbour one or more natural plasmids of various sizcs. To date, phenotypes such as lactose utilization ...
... and carbon dioxide is important because of their contribution to flavour and eye-hole formation in Dutch-type cheeses. Like other lactic acid bacteria, many Leuconostoc species harbour one or more natural plasmids of various sizcs. To date, phenotypes such as lactose utilization ...
Chemical Modifications and Kinetic Study of Ribonuclease Sa Active
... According to Takahashi (1968) phenylglyoxal, a specific reagent for arginine, inactivates ribonuclease Ti. He found that phenylglyoxal blocks Arg 77 which binds the anionic phosphate group of the substrate (Takahashi 1970). In contrary to RNase Ti, the activity of ribonuclease Sa is not affected by ...
... According to Takahashi (1968) phenylglyoxal, a specific reagent for arginine, inactivates ribonuclease Ti. He found that phenylglyoxal blocks Arg 77 which binds the anionic phosphate group of the substrate (Takahashi 1970). In contrary to RNase Ti, the activity of ribonuclease Sa is not affected by ...
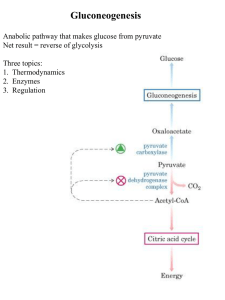
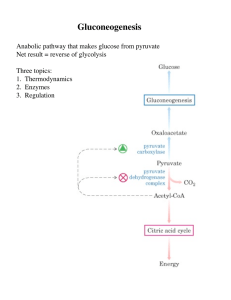
Gluconeogenesis - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... Formed by phosphorylation of F6-P, catalyzed by PFK-2 Broken down by FBPase-2 PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to signal low ...
... Formed by phosphorylation of F6-P, catalyzed by PFK-2 Broken down by FBPase-2 PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to signal low ...
Broad-Spectrum Peptide Inhibitors of Aminoglycoside Antibiotic
... one class of modifying enzyme would therefore be highly desirable and would allow the rescue of aminoglycoside antibiotic activity, analogous to the employment of -lactamase inhibitors to overcome penicillin resistance [3]. The three-dimensional structures of representative members of all three cla ...
... one class of modifying enzyme would therefore be highly desirable and would allow the rescue of aminoglycoside antibiotic activity, analogous to the employment of -lactamase inhibitors to overcome penicillin resistance [3]. The three-dimensional structures of representative members of all three cla ...