An introduction to enzyme structure and function
... A more recent explanation to the fitting of enzymes is the induced-fit hypothesis. This hypothesis still states that one substrate fits one active site, this is scientific fact. But this hypothesis suggests that the enzyme molecule slightly changes shape when it collides with substrate, making the a ...
... A more recent explanation to the fitting of enzymes is the induced-fit hypothesis. This hypothesis still states that one substrate fits one active site, this is scientific fact. But this hypothesis suggests that the enzyme molecule slightly changes shape when it collides with substrate, making the a ...
1. Vmax, the maximum velocity, of an enzyme-catalyzed
... d. irreversible inhibitor. 4. Diisopropyl fluorophosphate (DIFP) inactivates chymotrypsin by covalently modifying serine-195. This occurs because a. ...
... d. irreversible inhibitor. 4. Diisopropyl fluorophosphate (DIFP) inactivates chymotrypsin by covalently modifying serine-195. This occurs because a. ...
mature green papaya: (pawpaw)
... 7. In scientific studies using papain as a digestant, it has been established that proteins are actually chemically transformed into all the various amino acids that are so vital to human nutrition. Papain has the property to transform albumanoids into peptones in either an acid, alkaline or neutral ...
... 7. In scientific studies using papain as a digestant, it has been established that proteins are actually chemically transformed into all the various amino acids that are so vital to human nutrition. Papain has the property to transform albumanoids into peptones in either an acid, alkaline or neutral ...
RuBISCO WS - St Paul`s School Intranet
... atoms of atmospheric carbon dioxide are made available to organisms in the form of energy-rich molecules such as sucrose. While RuBisCO is the most abundant enzyme in the world, it is also one of the least efficient. RuBisCO is so slow that it can "capture" only a few carbon dioxide molecules each s ...
... atoms of atmospheric carbon dioxide are made available to organisms in the form of energy-rich molecules such as sucrose. While RuBisCO is the most abundant enzyme in the world, it is also one of the least efficient. RuBisCO is so slow that it can "capture" only a few carbon dioxide molecules each s ...
Enzymes 1. All cells in multicellular organisms contain thousands of
... Although it is also true that cells can only function within a specific pH range, this fact cannot be inferred from the given information. 7. As the graph shows, pepsin only remains active up to a pH of about 4.8. If the pH is any higher than this, the pepsin's folds will become so distorted that it ...
... Although it is also true that cells can only function within a specific pH range, this fact cannot be inferred from the given information. 7. As the graph shows, pepsin only remains active up to a pH of about 4.8. If the pH is any higher than this, the pepsin's folds will become so distorted that it ...
K m - kois.sk
... - block the enzyme but they do not usually destroy it Irreversible inhibitors: Combine irreversibly with the functional groups of the amino acids in the active site, e.g. nerve gases and pesticides, containing organophosphorus, combine with serine residues in the acetylcholine esterase. ...
... - block the enzyme but they do not usually destroy it Irreversible inhibitors: Combine irreversibly with the functional groups of the amino acids in the active site, e.g. nerve gases and pesticides, containing organophosphorus, combine with serine residues in the acetylcholine esterase. ...
5.1 Activity and temperature – Further questions and answers Q1. Bk
... Irreversible inhibition of enzymes occurs for several reasons, for example when a chemical substance binds permanently to the active site of an enzyme. Sulfanilamide is an antibiotic that inhibits enzyme activity in bacteria. The antibiotic is used to combat infection by permanently binding to the a ...
... Irreversible inhibition of enzymes occurs for several reasons, for example when a chemical substance binds permanently to the active site of an enzyme. Sulfanilamide is an antibiotic that inhibits enzyme activity in bacteria. The antibiotic is used to combat infection by permanently binding to the a ...
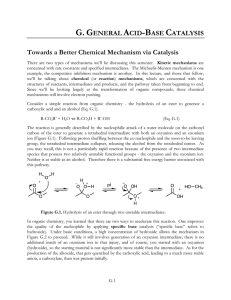
G.GENERAL ACID-BASE CATALYSIS Towards a Better Chemical
... acid), the enzyme reaches maximum activity. But, activity diminishes again at higher pH as the general acid is deprotonated, leaving the enzyme without one of its key catalytic groups. An alternate visualization of the data employs a logarithmic axis for the rate data, and the pKa’s of the conjugat ...
... acid), the enzyme reaches maximum activity. But, activity diminishes again at higher pH as the general acid is deprotonated, leaving the enzyme without one of its key catalytic groups. An alternate visualization of the data employs a logarithmic axis for the rate data, and the pKa’s of the conjugat ...
Learning Outcome Check List
... State what is meant by catabolism and anabolism and given examples of each State that the metabolism is the total set of reactions in a cell Explain the importance of reversible and irreversible steps in pathways Explain the importance of alternative steps in metabolic pathways Explain why ...
... State what is meant by catabolism and anabolism and given examples of each State that the metabolism is the total set of reactions in a cell Explain the importance of reversible and irreversible steps in pathways Explain the importance of alternative steps in metabolic pathways Explain why ...
FOR ENZYMES THE LIMITS FOR LIFE DEFINE THE LIMITS
... spontaneously, from various types of chemical damage, and from radiation damage which is largely due to ultraviolet rays. Such damage may occur to almost any molecule in the cell, but has long term results mainly when it involves DNA. Therefore, at least a subset of enzymes, with the responsibility ...
... spontaneously, from various types of chemical damage, and from radiation damage which is largely due to ultraviolet rays. Such damage may occur to almost any molecule in the cell, but has long term results mainly when it involves DNA. Therefore, at least a subset of enzymes, with the responsibility ...
19 Micro lab
... the ODC well, it is the SUBSTRATE. The product here is putricine, which is also a product of putrefaction and has that death smell. It is more alkaline (basic), so phenol red turns red. Therefore, in tubes 2, 3, and 4, we are looking for red as a positive result. CIT: citrate (a salt of citric acid) ...
... the ODC well, it is the SUBSTRATE. The product here is putricine, which is also a product of putrefaction and has that death smell. It is more alkaline (basic), so phenol red turns red. Therefore, in tubes 2, 3, and 4, we are looking for red as a positive result. CIT: citrate (a salt of citric acid) ...
Extra slides (lecture Wed. 11/4)
... the transition state free energy • articulated by Linus Pauling • recall that providing something that binds a molecule tightly effectively lowers its free energy If the enzymes binding site is most complementary to the transition state (and so lowers the energy of the transition state more than the ...
... the transition state free energy • articulated by Linus Pauling • recall that providing something that binds a molecule tightly effectively lowers its free energy If the enzymes binding site is most complementary to the transition state (and so lowers the energy of the transition state more than the ...
Enzyme Inhibition
... enzymic reactions The are usually specific and they work at low concentrations They block the enzyme but they do not usually destroy it Many drugs and poisons are inhibitors of enzymes in the nervous system ...
... enzymic reactions The are usually specific and they work at low concentrations They block the enzyme but they do not usually destroy it Many drugs and poisons are inhibitors of enzymes in the nervous system ...
Lesson 23. Clinical enzymology
... of influx is determined by the rate of release from damaged cells and altered rate of enzyme synthesis. 23.2.2 Localization of Damage Enzymes used to measure tissue damage are present in nearly all cells with varying concentration. So the measurement may indicate an abnormality, but the specific dia ...
... of influx is determined by the rate of release from damaged cells and altered rate of enzyme synthesis. 23.2.2 Localization of Damage Enzymes used to measure tissue damage are present in nearly all cells with varying concentration. So the measurement may indicate an abnormality, but the specific dia ...
Enzymes - fblocks
... Km (Michaelis Constant) of an enzyme is numerically equal to the substrate concentration at which the velocity of reaction is equal to 1/2 Vmax Km is the substrate concentration at which 1/2 maximal velocity is reached If Km is small, the substrate concentration required for the reaction to reach 1/ ...
... Km (Michaelis Constant) of an enzyme is numerically equal to the substrate concentration at which the velocity of reaction is equal to 1/2 Vmax Km is the substrate concentration at which 1/2 maximal velocity is reached If Km is small, the substrate concentration required for the reaction to reach 1/ ...
The Estimation of Kinetic Parameters in Systems - Beilstein
... Systems Biology Standard Markup Language (SMBL) [20] was chosen as the file format standard to communicate between the various applications and modules. The user has the opportunity to choose retrieved sequence, structural and kinetic data from the various sources and in the end to review his choice ...
... Systems Biology Standard Markup Language (SMBL) [20] was chosen as the file format standard to communicate between the various applications and modules. The user has the opportunity to choose retrieved sequence, structural and kinetic data from the various sources and in the end to review his choice ...
The overlooked value of viruses by Dr. David L. (“Woody
... has now emerged that some bacteriophages have hijacked the idea and developed a similar mechanism, one that is targeted against their bacterial hosts. In particular, it was found that bacteriophages which infect cholera-causing bacteria have acquired the technology to re-target the degrading enzyme ...
... has now emerged that some bacteriophages have hijacked the idea and developed a similar mechanism, one that is targeted against their bacterial hosts. In particular, it was found that bacteriophages which infect cholera-causing bacteria have acquired the technology to re-target the degrading enzyme ...
Beta-oxidation of docosahexaenoic acid and tetracosahexaenoic
... to one beta-oxidation cycle. In order to study this process, isolated human fibroblasts and rat hepatocytes were incubated with [I -'4C]docosahexaenoic acid and [2-14C]tetracosahexaenoicacid. Both docosahexaenoic acid and tetracosahexaenoic acid were beta-oxidized by control human fibroblasts and is ...
... to one beta-oxidation cycle. In order to study this process, isolated human fibroblasts and rat hepatocytes were incubated with [I -'4C]docosahexaenoic acid and [2-14C]tetracosahexaenoicacid. Both docosahexaenoic acid and tetracosahexaenoic acid were beta-oxidized by control human fibroblasts and is ...
a-Amylase from barley malt (A2771)
... α-Amylase isolated from barley has a molecular weight of 45 kDa (gel filtration).1 A molecular weight of 41 kDa has also been reported.2 Barley has two amylase isozymes, type B with pI 5.9-6.6 and type A with pI 4.6-5.2.3 The pH range for activity of α-amylase isolated from barley is 5.5 to 8.0, wit ...
... α-Amylase isolated from barley has a molecular weight of 45 kDa (gel filtration).1 A molecular weight of 41 kDa has also been reported.2 Barley has two amylase isozymes, type B with pI 5.9-6.6 and type A with pI 4.6-5.2.3 The pH range for activity of α-amylase isolated from barley is 5.5 to 8.0, wit ...
1. Explain how monomers are related to polymers. 2. Why would
... 1. Describe with as much detail the function of hemoglobin 2. List 3 enzymes, and brief description of their function. ...
... 1. Describe with as much detail the function of hemoglobin 2. List 3 enzymes, and brief description of their function. ...
ENZYMES
... assumption that the enzyme maintains its shape after the substrate(s) binds to it (similar to how a lock maintains its shape). - it is now known that the active site undergoes a slight change in shape to accommodate the substrate(s) more effectively – known as the induced-fit model. ...
... assumption that the enzyme maintains its shape after the substrate(s) binds to it (similar to how a lock maintains its shape). - it is now known that the active site undergoes a slight change in shape to accommodate the substrate(s) more effectively – known as the induced-fit model. ...
14-7-SA-V1-S1__enzym..
... a. Triose phosphate isomerase is referred to as a “perfect enzyme” because product is formed as soon as enzyme and substrate collide. b. Phosphoglucose isomerase converts the glucose ring to a fructose ring. c. Domains of phosphoglycerate kinase clamp down on the substrate so as to exclude water fro ...
... a. Triose phosphate isomerase is referred to as a “perfect enzyme” because product is formed as soon as enzyme and substrate collide. b. Phosphoglucose isomerase converts the glucose ring to a fructose ring. c. Domains of phosphoglycerate kinase clamp down on the substrate so as to exclude water fro ...
Beta-lactamase

Beta-lactamases are enzymes (EC 3.5.2.6) produced by some bacteria that provide resistance to β-lactam antibiotics like penicillins, cephamycins, and carbapenems (ertapenem), although carbapenems are relatively resistant to beta-lactamase. Beta-lactamase provides antibiotic resistance by breaking the antibiotics' structure. These antibiotics all have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a β-lactam. Through hydrolysis, the lactamase enzyme breaks the β-lactam ring open, deactivating the molecule's antibacterial properties.Beta-lactam antibiotics are typically used to treat a broad spectrum of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.Beta-lactamases produced by Gram-negative organisms are usually secreted, especially when antibiotics are present in the environment.