UB Chapter 3: Enzymes (Exercises 3.6) p.44
... c.i. Phase 1: The reaction rate rises as more substrate molecules collide with the enzyme. (Phase 2: The acceleration rate slows down (but the rate is still rising). At any one moment almost all the active sites are occupied by substrate.) Phase 3: The reaction rate stops to rise and the reaction go ...
... c.i. Phase 1: The reaction rate rises as more substrate molecules collide with the enzyme. (Phase 2: The acceleration rate slows down (but the rate is still rising). At any one moment almost all the active sites are occupied by substrate.) Phase 3: The reaction rate stops to rise and the reaction go ...
Purines and Pyrimidines
... The primary effect of deficiencies ADA and PNP is a form of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) due to accumulation of nucleosides that inhibit DNA synthesis, particularly in T-cells. Both are autosomal recessive disorders that present with severe infections. In ADA deficiency both cellular and ...
... The primary effect of deficiencies ADA and PNP is a form of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) due to accumulation of nucleosides that inhibit DNA synthesis, particularly in T-cells. Both are autosomal recessive disorders that present with severe infections. In ADA deficiency both cellular and ...
Control of metabolism
... • Pacemaker Enzymes – Regulation is accomplished by altering the activity of at least one pacemaker enzyme (or rate-determining step) of the pathway. ...
... • Pacemaker Enzymes – Regulation is accomplished by altering the activity of at least one pacemaker enzyme (or rate-determining step) of the pathway. ...
Mobile elements - people.vcu.edu
... Understanding Phylogeny and Predicting New Class III Inteins Mobile Elements ...
... Understanding Phylogeny and Predicting New Class III Inteins Mobile Elements ...
Proteins - Calderglen High School
... for supply of certain amino acids known as essential amino acids. Only eight amino acids are regarded as being essential for humans although a further two are required in childhood. Some amino acids have more than one amino group or more than one carboxyl group and these allow chains to form branche ...
... for supply of certain amino acids known as essential amino acids. Only eight amino acids are regarded as being essential for humans although a further two are required in childhood. Some amino acids have more than one amino group or more than one carboxyl group and these allow chains to form branche ...
Overlaps: Oomycete, fungal, bacteria pathogens
... Comments: Protease inhibitor activity (GO:0030414) currently resides ...
... Comments: Protease inhibitor activity (GO:0030414) currently resides ...
Enzyme
... • This will mean the enzyme will no longer be able to bind to its substrate • Denaturation is permanent. ...
... • This will mean the enzyme will no longer be able to bind to its substrate • Denaturation is permanent. ...
Chapter 3
... They help the reactants interact but are not used up in the reactions. May be used over and over again. Are usually highly specific for particular chemical reactions. They generally catalyze only one or a few types of reactions. – Can catalyze up to several million reactions per second. • As a resul ...
... They help the reactants interact but are not used up in the reactions. May be used over and over again. Are usually highly specific for particular chemical reactions. They generally catalyze only one or a few types of reactions. – Can catalyze up to several million reactions per second. • As a resul ...
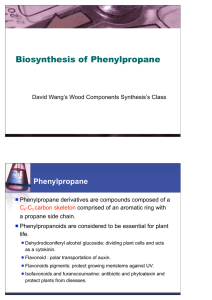
Biosynthesis of Phenylpropane
... enzymes and their abbreviations are as follows: CAD, (hydroxy)cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase; CCoAOMT, caffeoyl CoA Omethyltransferase; CCR, (hydroxy)cinnamoyl CoA reductase; C3H, p-coumaroyl shikimate/quinate 3-hydroxylase; C4H, cinnamate 4hydroxylase; 4CL, 4-coumarate CoA ligase; COMT, caffeic aci ...
... enzymes and their abbreviations are as follows: CAD, (hydroxy)cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase; CCoAOMT, caffeoyl CoA Omethyltransferase; CCR, (hydroxy)cinnamoyl CoA reductase; C3H, p-coumaroyl shikimate/quinate 3-hydroxylase; C4H, cinnamate 4hydroxylase; 4CL, 4-coumarate CoA ligase; COMT, caffeic aci ...
chapt 5
... Those that decrease the amount of an enzyme made are called gene-repressor proteins. Those that increase the amount of an enzyme made are ...
... Those that decrease the amount of an enzyme made are called gene-repressor proteins. Those that increase the amount of an enzyme made are ...
The following Text was taken from the Student Lab Manual for
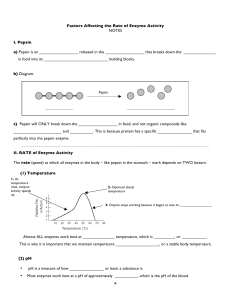
... greatly increasing the rate of this reaction. Although enzymes are absolutely essential for accelerating biochemical reactions, a number of conditions influence enzyme activity. Enzymes don’t always operate at their maximal rate, however. Most enzymes demonstrate temperature and pH optimums–a temper ...
... greatly increasing the rate of this reaction. Although enzymes are absolutely essential for accelerating biochemical reactions, a number of conditions influence enzyme activity. Enzymes don’t always operate at their maximal rate, however. Most enzymes demonstrate temperature and pH optimums–a temper ...
楔汴ꅥꝇꕑ닎떢껦䆺慲楢潮伭楬潧慳捣慨楲敤 佁 抦햸ºÞ澵쎻䆡 ¾Ü
... (300 g), we found that P. ostreatus production was significantly higher than the obtained with monocultures of P. citrinopileatus and higher than any other treatment. In all co-cultivation combinations yields were reduced being the mixed cultures (PO+PC) significantly lower (p≤ 0.05) than any other ...
... (300 g), we found that P. ostreatus production was significantly higher than the obtained with monocultures of P. citrinopileatus and higher than any other treatment. In all co-cultivation combinations yields were reduced being the mixed cultures (PO+PC) significantly lower (p≤ 0.05) than any other ...
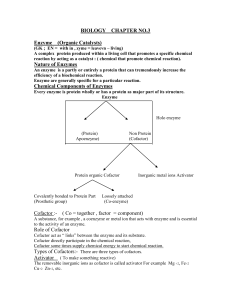
Nature of Enzymes
... Active site :- The part of an enzyme that react with the substrate ( the substance on which enzyme acts). Active site consisting of only a few amino acids (between 3-12 amino acids) Active site consist of two known regions Binding site :- It recognizes the specific substrate and form ES complex , it ...
... Active site :- The part of an enzyme that react with the substrate ( the substance on which enzyme acts). Active site consisting of only a few amino acids (between 3-12 amino acids) Active site consist of two known regions Binding site :- It recognizes the specific substrate and form ES complex , it ...
Inhibition of E. coli l-Asparaginase by Reaction with 2, 3
... der comparable conditions 1,2-cyclo hexanedione does not affect the activity o f L-asparaginase. ...
... der comparable conditions 1,2-cyclo hexanedione does not affect the activity o f L-asparaginase. ...
Slide 1
... fabrics to make sure the material is peroxide-free - to decompose the hydrogen peroxide which is used (in some cases) to disinfect the contact lens ...
... fabrics to make sure the material is peroxide-free - to decompose the hydrogen peroxide which is used (in some cases) to disinfect the contact lens ...
Table of Contents - Milan Area Schools
... Energy and Energy Conversions • If a chemical reaction increases entropy, its products are more disordered or random than its reactants are. • An example is the hydrolysis of a protein to its amino acids. Free energy is released, DG is negative, and DS is positive (entropy increases). • When protein ...
... Energy and Energy Conversions • If a chemical reaction increases entropy, its products are more disordered or random than its reactants are. • An example is the hydrolysis of a protein to its amino acids. Free energy is released, DG is negative, and DS is positive (entropy increases). • When protein ...
8 Factors Affecting the Rate of Enzyme Activity NOTES I. Pepsin a
... What data should be collected to support the hypothesis that enzyme C works best in an environment that is slightly basic? (1) the shape of enzyme C (2) the amount of substance W produced in five minutes at various pH levels (3) the shapes of substances X and Y after the reaction occurs ...
... What data should be collected to support the hypothesis that enzyme C works best in an environment that is slightly basic? (1) the shape of enzyme C (2) the amount of substance W produced in five minutes at various pH levels (3) the shapes of substances X and Y after the reaction occurs ...
GRAS - Chemistry PAS Task Group_Raw
... nearly so) of the observed activity in an enzyme assay is derived from a single enzyme then the enzyme preparation is considered enzymatically pure, even if it lacks mass purity. 10. For micro-organisms, the name should be provided in accordance with the International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteri ...
... nearly so) of the observed activity in an enzyme assay is derived from a single enzyme then the enzyme preparation is considered enzymatically pure, even if it lacks mass purity. 10. For micro-organisms, the name should be provided in accordance with the International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteri ...
pancreatic secretion
... and liver are accessory digestive organs]. • Pancreas is elongated gland lies behind and below the stomach. • It has exocrine and endocrine secretions. • Exocrine Pancreas secretes pancreatic juice. ...
... and liver are accessory digestive organs]. • Pancreas is elongated gland lies behind and below the stomach. • It has exocrine and endocrine secretions. • Exocrine Pancreas secretes pancreatic juice. ...
Metabolizma - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... in a pathway. • Control coefficient determined for each enzyme. = D activity / D enzyme concentration. • Enzymes with large control coefficients impt to overall regulation. • Recent finding suggest that the control of most pathways is shared by multiple pathwayt enzymes ...
... in a pathway. • Control coefficient determined for each enzyme. = D activity / D enzyme concentration. • Enzymes with large control coefficients impt to overall regulation. • Recent finding suggest that the control of most pathways is shared by multiple pathwayt enzymes ...
metalloenzyme_1
... Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase is a zinc metalloenzyme containing four g atoms zinc per molecular weight of 89,0003. As with alcohol dehyrogenase, each of the two identical subunits contains two zinc atoms, one at the active site and one at another site. In addition, the enzyme, when isolated ...
... Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase is a zinc metalloenzyme containing four g atoms zinc per molecular weight of 89,0003. As with alcohol dehyrogenase, each of the two identical subunits contains two zinc atoms, one at the active site and one at another site. In addition, the enzyme, when isolated ...
File
... Uric Acid and Urea, Respectively Purine nucleotides are degraded by a pathway in which they lose their phosphate through the action of 5-Nucleotidase . Adenylate yields adenosine, which is deaminated to inosine by adenosine deaminase, and inosine is hydrolyzed to hypoxanthine (its purine base) and D ...
... Uric Acid and Urea, Respectively Purine nucleotides are degraded by a pathway in which they lose their phosphate through the action of 5-Nucleotidase . Adenylate yields adenosine, which is deaminated to inosine by adenosine deaminase, and inosine is hydrolyzed to hypoxanthine (its purine base) and D ...
Disaccharides - Home - KSU Faculty Member websites
... pressure. It swells in water to produce a viscous, colloidal solution. It is used to increase the viscosity and to stabilize lotions, suspensions, pastes, and ointments. In ophthalmic preparations as protectant. It is also used bulk laxative in chronic constipation and in treatment of obesity ...
... pressure. It swells in water to produce a viscous, colloidal solution. It is used to increase the viscosity and to stabilize lotions, suspensions, pastes, and ointments. In ophthalmic preparations as protectant. It is also used bulk laxative in chronic constipation and in treatment of obesity ...
Datasheet - Sigma
... pH homeostasis, calcification, and bone resorption. There are at least five distinct CA families (α, β, γ, δ, and ε). These families have no significant amino acid sequence similarity and, in most cases, are thought to be an example of convergent evolution. The α-CAs are found in humans. At least 14 ...
... pH homeostasis, calcification, and bone resorption. There are at least five distinct CA families (α, β, γ, δ, and ε). These families have no significant amino acid sequence similarity and, in most cases, are thought to be an example of convergent evolution. The α-CAs are found in humans. At least 14 ...
Beta-lactamase

Beta-lactamases are enzymes (EC 3.5.2.6) produced by some bacteria that provide resistance to β-lactam antibiotics like penicillins, cephamycins, and carbapenems (ertapenem), although carbapenems are relatively resistant to beta-lactamase. Beta-lactamase provides antibiotic resistance by breaking the antibiotics' structure. These antibiotics all have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a β-lactam. Through hydrolysis, the lactamase enzyme breaks the β-lactam ring open, deactivating the molecule's antibacterial properties.Beta-lactam antibiotics are typically used to treat a broad spectrum of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.Beta-lactamases produced by Gram-negative organisms are usually secreted, especially when antibiotics are present in the environment.