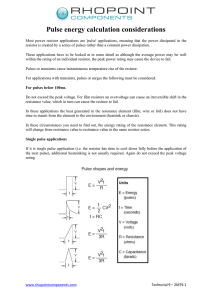
Unit Plan: Ohm`s Law – Current, voltage and resistance
... not. I can then explain that the ratio of the voltage to the current is resistance. Some materials have constant resistances in a given range and others do not. This can lead into a discussion of Ohm’s Law and the difference between Ohmic and non-Ohmic materials. I would then discuss the change in r ...
... not. I can then explain that the ratio of the voltage to the current is resistance. Some materials have constant resistances in a given range and others do not. This can lead into a discussion of Ohm’s Law and the difference between Ohmic and non-Ohmic materials. I would then discuss the change in r ...
Hands - Scioly.org
... 2a. Create a circuit with 2 LEDs, 2 AA batteries, and as many wires as you want in a way such that the LEDs are the brightest. Draw this circuit. b. Measure the voltage across each LED(Label on schematic diagram) c. Find the current across each LED LED1:________ LED2:_________ d. If each Led has re ...
... 2a. Create a circuit with 2 LEDs, 2 AA batteries, and as many wires as you want in a way such that the LEDs are the brightest. Draw this circuit. b. Measure the voltage across each LED(Label on schematic diagram) c. Find the current across each LED LED1:________ LED2:_________ d. If each Led has re ...
Ohmic devices - marineabudhabi
... 3. Electrical resistance: R of a conductor. Electrical resistance (R) of a conductor is expressed in ohms (Ω). The instrument to measure the electrical resistance of a conductor is called an ohmmeter. The ohmmeter is connected directly between the terminals of the conductor to measure the value of i ...
... 3. Electrical resistance: R of a conductor. Electrical resistance (R) of a conductor is expressed in ohms (Ω). The instrument to measure the electrical resistance of a conductor is called an ohmmeter. The ohmmeter is connected directly between the terminals of the conductor to measure the value of i ...
Series Parallel Circuits 9.1 Key
... What happens to the total resistance of a series circuit wUen another resistor is added? ...
... What happens to the total resistance of a series circuit wUen another resistor is added? ...
resistors old
... lower noise and are generally better for high frequency or radio frequency applications. Metal Oxide Resistors have better high surge current capability with a much higher temperature rating than the equivalent metal film resistors. Another type of film resistor commonly known as a Thick Film Resist ...
... lower noise and are generally better for high frequency or radio frequency applications. Metal Oxide Resistors have better high surge current capability with a much higher temperature rating than the equivalent metal film resistors. Another type of film resistor commonly known as a Thick Film Resist ...
Resistor

A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. Resistors act to reduce current flow, and, at the same time, act to lower voltage levels within circuits. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to limit current flow, to adjust signal levels, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity.Resistors are common elements of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in electronic equipment. Practical resistors as discrete components can be composed of various compounds and forms. Resistors are also implemented within integrated circuits.The electrical function of a resistor is specified by its resistance: common commercial resistors are manufactured over a range of more than nine orders of magnitude. The nominal value of the resistance will fall within a manufacturing tolerance.