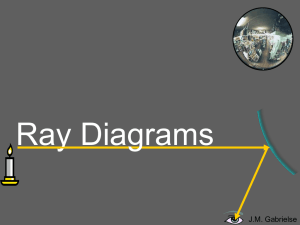
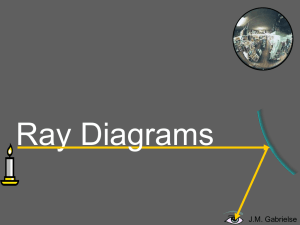
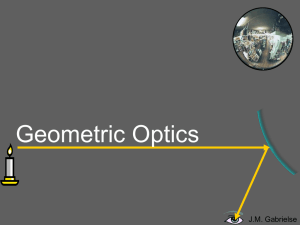
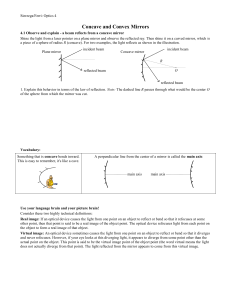
Drawing Ray Diagrams for Concave Mirrors
... which the reflecting surface is caved in Another name for the concave mirror is a CONVERGING MIRROR. ...
... which the reflecting surface is caved in Another name for the concave mirror is a CONVERGING MIRROR. ...
Document
... The first telescope, designed and built by Galileo, used lenses to focus light from faraway objects, into Galileo’s eye. His telescope consisted of a concave lens and a ...
... The first telescope, designed and built by Galileo, used lenses to focus light from faraway objects, into Galileo’s eye. His telescope consisted of a concave lens and a ...
LABORATORY TECHNIQUES
... 1. Before attaching the magnetic pinhole mount (PM) to the micrometer spindles, mount the appropriate microscope objective (MO) onto the spatial filter unit; then align the MO so that it is as close to the laser beam axis as possible. This will reduce aberrations, provide optimum light economy, and ...
... 1. Before attaching the magnetic pinhole mount (PM) to the micrometer spindles, mount the appropriate microscope objective (MO) onto the spatial filter unit; then align the MO so that it is as close to the laser beam axis as possible. This will reduce aberrations, provide optimum light economy, and ...
Gaurav Chetna Josan - Department of Electrical Engineering
... shortest events ever made by Man Ex: Sending infrared light into a crystal yielded this display of green light ...
... shortest events ever made by Man Ex: Sending infrared light into a crystal yielded this display of green light ...
Lecture Series: Building the Future of Optical Modeling and Design
... illumination, energy, medicine, manufacturing, green and bio technology. Optics and photonics gain momentum in all those applications and that causes an increasing interest in most recent developments of optical technology. We all experience fascinating progress in the development of new light sourc ...
... illumination, energy, medicine, manufacturing, green and bio technology. Optics and photonics gain momentum in all those applications and that causes an increasing interest in most recent developments of optical technology. We all experience fascinating progress in the development of new light sourc ...
Geometric Optics
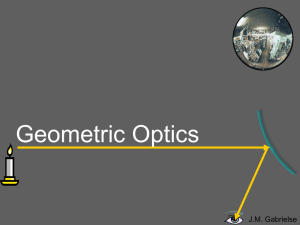
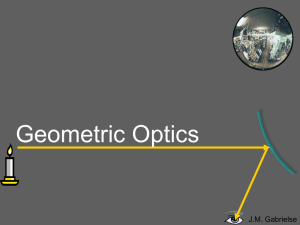
... The first ray comes in parallel to the optical axis and reflects through the focal point. The second ray comes through the focal point and reflects parallel to the optical axis. The light rays don’t converge, but the sight lines do. A virtual image forms where the sight lines converge. ...
... The first ray comes in parallel to the optical axis and reflects through the focal point. The second ray comes through the focal point and reflects parallel to the optical axis. The light rays don’t converge, but the sight lines do. A virtual image forms where the sight lines converge. ...
Geometric Optics
... The focal point is considered virtual since sight lines, not light rays, go through it. J.M. Gabrielse ...
... The focal point is considered virtual since sight lines, not light rays, go through it. J.M. Gabrielse ...
Geometric Optics - Mr. Gabrielse's Physics
... The focal point is considered virtual since sight lines, not light rays, go through it. J.M. Gabrielse ...
... The focal point is considered virtual since sight lines, not light rays, go through it. J.M. Gabrielse ...
Geometric Optics
... The focal point is considered virtual since sight lines, not light rays, go through it. J.M. Gabrielse ...
... The focal point is considered virtual since sight lines, not light rays, go through it. J.M. Gabrielse ...
The Absolute Sensitivity of Lens and Compound Eyes
... of h 1 , and for the big rhabdome (diameter ö = ( b / q ) d * ), located in the “ effective” focal plane. Comparing the moth eye with the human eye, the num bers in the Table show that for point-like objects the number q of quanta per receptor is smaller by a factor of 1000 than in the human eye (ra ...
... of h 1 , and for the big rhabdome (diameter ö = ( b / q ) d * ), located in the “ effective” focal plane. Comparing the moth eye with the human eye, the num bers in the Table show that for point-like objects the number q of quanta per receptor is smaller by a factor of 1000 than in the human eye (ra ...
The present work gives recommendations for rational - Dimka
... Scheme assembling and achromat optimization results The analysis of different vendors’ microobjective series of a given class [9] gave the following default values of their basic optical characteristics: the back focal length f 3,7 mm; relative aperture – 1:2,4; field angle in object space – 2 ...
... Scheme assembling and achromat optimization results The analysis of different vendors’ microobjective series of a given class [9] gave the following default values of their basic optical characteristics: the back focal length f 3,7 mm; relative aperture – 1:2,4; field angle in object space – 2 ...
Michelson Lab Guide UTSA
... Exercise: What change might be made to the orientation the compensator plate that would still equalize the optical path for all wavelengths? Would there be any advantage to choosing the alternate orientation? ...
... Exercise: What change might be made to the orientation the compensator plate that would still equalize the optical path for all wavelengths? Would there be any advantage to choosing the alternate orientation? ...
OpticalPosterLax
... The “Q” value has been measured with the digital scope embedded software, specifically developed by Tektronix for eye-diagram analysis. This formula returns estimated values better than 10-13. Eye top 462.8 μW ...
... The “Q” value has been measured with the digital scope embedded software, specifically developed by Tektronix for eye-diagram analysis. This formula returns estimated values better than 10-13. Eye top 462.8 μW ...
Concave and Convex Mirrors
... After reflection, they all pass through the same point exactly in the middle between the mirror and the center of the sphere from which the mirror was cut. This point is called the focal point — the point through which rays parallel to the axis of the concave mirror pass after reflection from the mi ...
... After reflection, they all pass through the same point exactly in the middle between the mirror and the center of the sphere from which the mirror was cut. This point is called the focal point — the point through which rays parallel to the axis of the concave mirror pass after reflection from the mi ...
Diffractive Optical Elements
... HOLOEYE utilizes its steadily growing experience in the design and simulation of diffractive optical elements to offer its customers a competitive solution. Both in-house developed and commercially available state-of-the-art software tools are used for the DOE design process. ...
... HOLOEYE utilizes its steadily growing experience in the design and simulation of diffractive optical elements to offer its customers a competitive solution. Both in-house developed and commercially available state-of-the-art software tools are used for the DOE design process. ...
High-resolution retinal microscopy using MEMS
... any matrix of actuator deflections to a unique sensor matrix. This reconstructor was inverted using a singular value decomposition to provide a map from any sensor matrix to a best fit actuator deflection matrix. This constitutes a calibration step that is necessary only once, before beginning close ...
... any matrix of actuator deflections to a unique sensor matrix. This reconstructor was inverted using a singular value decomposition to provide a map from any sensor matrix to a best fit actuator deflection matrix. This constitutes a calibration step that is necessary only once, before beginning close ...
Chapter 3: Telescopes
... • Clouds, rain, and snow don’t interfere. • Observations at an entirely different frequency; get totally different information. ...
... • Clouds, rain, and snow don’t interfere. • Observations at an entirely different frequency; get totally different information. ...
Design technique for all-dielectric non
... nally difficult” [6]. However, for narrow spectral domains some solutions can be found that can help to reduce the degree of polarization to negligible values. Great results can be obtained by using anisotropic thin films, but the solution presented in this article had as imposing to use only isotro ...
... nally difficult” [6]. However, for narrow spectral domains some solutions can be found that can help to reduce the degree of polarization to negligible values. Great results can be obtained by using anisotropic thin films, but the solution presented in this article had as imposing to use only isotro ...
Reflector sight

A reflector sight or reflex sight is an optical device that allows the user to look through a partially reflecting glass element and see an illuminated projection of an aiming point or some other image superimposed on the field of view. These sights work on the simple optical principle that anything at the focus of a lens or curved mirror (such as an illuminated reticle) will look like it is sitting in front of the viewer at infinity. Reflector sights employ some sort of ""reflector"" to allow the viewer to see the infinity image and the field of view at the same time, either by bouncing the image created by lens off a slanted glass plate, or by using a mostly clear curved glass reflector that images the reticle while the viewer looks through the reflector. Since the reticle is at infinity it stays in alignment with the device the sight is attached to regardless of the viewer's eye position, removing most of the parallax and other sighting errors found in simple sighting devices.Since their invention in 1900, reflector sights have come to be used as gun sights on all kinds of weapons. They were used on fighter aircraft, in a limited capacity in World War I, widely used in World War II, and still used as the base component in many types of modern head-up displays. They have been used in other types of (usually large) weapons as well, such as anti-aircraft gun sights, anti tank gun sights, and any other role where the operator had to engage fast moving targets over a wide field of view, and the sight itself could be supplied with sufficient electrical power to function. There was some limited use of the sight on small arms after World War II but it came into widespread use after the late 70s with the invention of the red dot sight, with a red light-emitting diode (LED) as its reticle, making a dependable sight with durability and extremely long illumination run time.Reflector sights are also used in civilian applications such as sights on surveying equipment, optical telescope pointing aids, and camera viewfinders.