Associate Professor Shien
... multiplexing (WDM) technologies can provide high speed and secure optical links that are immune to EM interference and that can transmit information to long distance without using electronic repeaters. Among them, erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) is the most commercial product to date. However, i ...
... multiplexing (WDM) technologies can provide high speed and secure optical links that are immune to EM interference and that can transmit information to long distance without using electronic repeaters. Among them, erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) is the most commercial product to date. However, i ...
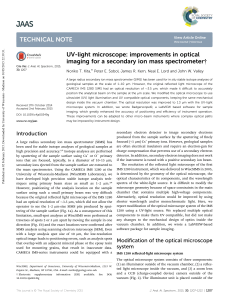
UV-light microscope: improvements in optical imaging for a
... components that did not transmit UV light were replaced with UV compatible versions, including the optical waveguide, the objective lens, the mirror and the transfer lens inside the vacuum chamber; as well as the condenser lens of the illuminator and the zoom lens below the CCD camera that are outsi ...
... components that did not transmit UV light were replaced with UV compatible versions, including the optical waveguide, the objective lens, the mirror and the transfer lens inside the vacuum chamber; as well as the condenser lens of the illuminator and the zoom lens below the CCD camera that are outsi ...
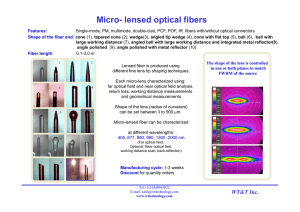
lensed fiber
... Shape of the fiber end: cone (1). tapered cone (2), wedge(3), angled tip wedge (4), cone with flat top (5), ball (6), ball with large working distance (7), angled ball with large working distance and integrated metal reflector(8), angle polished (9), angle polished with metal reflector (10) Fiber le ...
... Shape of the fiber end: cone (1). tapered cone (2), wedge(3), angled tip wedge (4), cone with flat top (5), ball (6), ball with large working distance (7), angled ball with large working distance and integrated metal reflector(8), angle polished (9), angle polished with metal reflector (10) Fiber le ...
Active imaging lens with real-time variable resolution and constant
... can increase the resolution in a given region by changing the magnification. However, it is also very different since it keeps the total field of view constant. Instead of increasing the resolution (in pixels/degree) by reducing the total field of view, it is achieved here by increasing it in a zone ...
... can increase the resolution in a given region by changing the magnification. However, it is also very different since it keeps the total field of view constant. Instead of increasing the resolution (in pixels/degree) by reducing the total field of view, it is achieved here by increasing it in a zone ...
10.2 Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
... Overview of the Infrared The highest frequency vibration is the H2 stretching motion which occurs at 4,400 cm-1. Although this transition is not infrared active (it is Raman active), ~4,000 cm-1 is usually taken to be the upper limit of the infrared. The lower limit is determined by instrumental co ...
... Overview of the Infrared The highest frequency vibration is the H2 stretching motion which occurs at 4,400 cm-1. Although this transition is not infrared active (it is Raman active), ~4,000 cm-1 is usually taken to be the upper limit of the infrared. The lower limit is determined by instrumental co ...
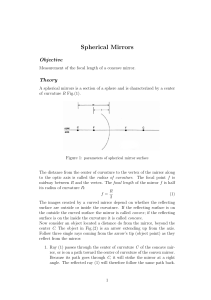
Spherical Mirrors
... Now consider an object located a distance do from the mirror, beyond the center C. The object in Fig.(2) is an arrow extending up from the axis. Follow three single rays coming from the arrow’s tip (object point) as they reflect from the mirror: 1. Ray (1) passes through the center of curvature C of ...
... Now consider an object located a distance do from the mirror, beyond the center C. The object in Fig.(2) is an arrow extending up from the axis. Follow three single rays coming from the arrow’s tip (object point) as they reflect from the mirror: 1. Ray (1) passes through the center of curvature C of ...
Part 4 - MZA Associates Corporation
... In wave optics simulation all optical effects, with the sole exception of optical propagation through vacuum or an ideal dielectric medium, are modeled as if they occurred at discrete planes. This is an approximation of course, since many important effects, such as the optical effects of atmospheric ...
... In wave optics simulation all optical effects, with the sole exception of optical propagation through vacuum or an ideal dielectric medium, are modeled as if they occurred at discrete planes. This is an approximation of course, since many important effects, such as the optical effects of atmospheric ...
Content
... ● aim is to enable the multiservice transport of packet based data and legacy traffic (Next generation SONET/SDH) ...
... ● aim is to enable the multiservice transport of packet based data and legacy traffic (Next generation SONET/SDH) ...
Shedding Light on Hybrid Optics: A Tutorial in
... devices are polarization sensitive. As a result, devices are needed that can either maintain or control polarization within an optical system. A wide variety of free-space optics are available to control polarization, or to manipulate light based on its polarization state. They include polarizers, w ...
... devices are polarization sensitive. As a result, devices are needed that can either maintain or control polarization within an optical system. A wide variety of free-space optics are available to control polarization, or to manipulate light based on its polarization state. They include polarizers, w ...
Concave Mirrors
... derivation and evaluate the outcome using limiting case analysis and your knowledge of how lenses form images of objects. AB is a bright object; A1B1 is the image of the object. (M, N, and C are points on the mirror, where rays hit it.) ...
... derivation and evaluate the outcome using limiting case analysis and your knowledge of how lenses form images of objects. AB is a bright object; A1B1 is the image of the object. (M, N, and C are points on the mirror, where rays hit it.) ...
Images and Plane Mirrors
... can be seen where backward extensions of reflected rays pass through one another. The object’s distance p from the mirror is related to the (apparent) image distance i from the mirror by (a) Object distance p is a positive quantity. Image distance i for a virtual image is a negative quantity. Only r ...
... can be seen where backward extensions of reflected rays pass through one another. The object’s distance p from the mirror is related to the (apparent) image distance i from the mirror by (a) Object distance p is a positive quantity. Image distance i for a virtual image is a negative quantity. Only r ...
Convex Mirrors
... concave or a convex mirror? Determine the focal length of the mirror Archimedes might have used to burn ships that were 150 m away. Justify your answer. 5.12 Regular problem You wish to order a mirror from a scientific supply company. You want to use the mirror while shaving or applying makeup. The ...
... concave or a convex mirror? Determine the focal length of the mirror Archimedes might have used to burn ships that were 150 m away. Justify your answer. 5.12 Regular problem You wish to order a mirror from a scientific supply company. You want to use the mirror while shaving or applying makeup. The ...
Chapter 12 - GEOCITIES.ws
... Note that the visual angles are usually small so tan sin and tan sin . ...
... Note that the visual angles are usually small so tan sin and tan sin . ...
Designing an Experimental Prototype to Support Geometric Optics
... with materials of different refractive index. In this research only centered spherical surfaces with an imaginary axis (optical axis) joining the vertices of the surfaces in a straight line were considered. A spherical optical system commonly used might be lenses, transparent objects (usually glass) ...
... with materials of different refractive index. In this research only centered spherical surfaces with an imaginary axis (optical axis) joining the vertices of the surfaces in a straight line were considered. A spherical optical system commonly used might be lenses, transparent objects (usually glass) ...
Stops, Pupils, Field Optics and Cameras
... Chief Ray – any ray that passes through the center of the aperture stop. It will also pass through the center of the entrance and exit pupils. Different chief rays will correspond to different object and image ...
... Chief Ray – any ray that passes through the center of the aperture stop. It will also pass through the center of the entrance and exit pupils. Different chief rays will correspond to different object and image ...
Lab Writeup Michelson(New)
... The image of M1 appears in line with M2 and may be either in front of or behind M2 (see Fig. 2). The complete theory, which must take into account the fact that the source is an extended source, shows that when M2, and the image of M1 are parallel, then monochromatic light produces an interference p ...
... The image of M1 appears in line with M2 and may be either in front of or behind M2 (see Fig. 2). The complete theory, which must take into account the fact that the source is an extended source, shows that when M2, and the image of M1 are parallel, then monochromatic light produces an interference p ...
Cloaking at Optical Frequencies - Cornell ECE
... The cloaking device is composed of a spatially varying density of sub-wavelength 50 nm diameter silicon posts embedded in an SiO2 medium, and the reflective surface consists of a distributed Bragg reflector (DBR). The distribution of posts induces a variation of the effective index of refraction ac ...
... The cloaking device is composed of a spatially varying density of sub-wavelength 50 nm diameter silicon posts embedded in an SiO2 medium, and the reflective surface consists of a distributed Bragg reflector (DBR). The distribution of posts induces a variation of the effective index of refraction ac ...
document
... • A light placed at the focal point is reflected in a beam. • Car headlights, flashlights, lighthouses, spotlights, and other devices use concave mirrors in this way to create concentrated light beams of nearly parallel rays. ...
... • A light placed at the focal point is reflected in a beam. • Car headlights, flashlights, lighthouses, spotlights, and other devices use concave mirrors in this way to create concentrated light beams of nearly parallel rays. ...
Test - Wave Optics
... Light is an electromagnetic wave phenomenon described by the same theoretical principles that govern all forms of electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation propagates in the form of two mutually coupled vector waves, an electric-field wave and a magnetic-field wave. Nevertheless, it is po ...
... Light is an electromagnetic wave phenomenon described by the same theoretical principles that govern all forms of electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation propagates in the form of two mutually coupled vector waves, an electric-field wave and a magnetic-field wave. Nevertheless, it is po ...
Integrated Optics
... • Integrated optics is a system of light-controlling components combined into a single device. The ultimate aim is to create miniature optical circuits similar to the silicon chips that have revolutionized the electronics industry. The advantage of the optical approach however is that data can be pr ...
... • Integrated optics is a system of light-controlling components combined into a single device. The ultimate aim is to create miniature optical circuits similar to the silicon chips that have revolutionized the electronics industry. The advantage of the optical approach however is that data can be pr ...
Reflector sight

A reflector sight or reflex sight is an optical device that allows the user to look through a partially reflecting glass element and see an illuminated projection of an aiming point or some other image superimposed on the field of view. These sights work on the simple optical principle that anything at the focus of a lens or curved mirror (such as an illuminated reticle) will look like it is sitting in front of the viewer at infinity. Reflector sights employ some sort of ""reflector"" to allow the viewer to see the infinity image and the field of view at the same time, either by bouncing the image created by lens off a slanted glass plate, or by using a mostly clear curved glass reflector that images the reticle while the viewer looks through the reflector. Since the reticle is at infinity it stays in alignment with the device the sight is attached to regardless of the viewer's eye position, removing most of the parallax and other sighting errors found in simple sighting devices.Since their invention in 1900, reflector sights have come to be used as gun sights on all kinds of weapons. They were used on fighter aircraft, in a limited capacity in World War I, widely used in World War II, and still used as the base component in many types of modern head-up displays. They have been used in other types of (usually large) weapons as well, such as anti-aircraft gun sights, anti tank gun sights, and any other role where the operator had to engage fast moving targets over a wide field of view, and the sight itself could be supplied with sufficient electrical power to function. There was some limited use of the sight on small arms after World War II but it came into widespread use after the late 70s with the invention of the red dot sight, with a red light-emitting diode (LED) as its reticle, making a dependable sight with durability and extremely long illumination run time.Reflector sights are also used in civilian applications such as sights on surveying equipment, optical telescope pointing aids, and camera viewfinders.