Sects. 6.5 through 6.9
... A particle is attached between two identical springs on a horizontal frictionless table. Both springs have spring constant k and are initially unstressed. (a) The particle is pulled a distance x along a direction perpendicular to the initial configuration of the springs. Show that the force exerted ...
... A particle is attached between two identical springs on a horizontal frictionless table. Both springs have spring constant k and are initially unstressed. (a) The particle is pulled a distance x along a direction perpendicular to the initial configuration of the springs. Show that the force exerted ...
Density Matrix
... In summary, by the term “state of a system” we will understand as a state of a micro or macroscopic system defined by its complete density matrix. With that understanding, not all states are characterized by a state vector. Only pure states for which ρ = |ψ >< ψ| are defined by a state vector. Energ ...
... In summary, by the term “state of a system” we will understand as a state of a micro or macroscopic system defined by its complete density matrix. With that understanding, not all states are characterized by a state vector. Only pure states for which ρ = |ψ >< ψ| are defined by a state vector. Energ ...
Light forces — Answers 1 Calculation of the mean force
... 4. Atoms confined in an optical lattice at a wavelength such that the main transition is unaffected (magic wavelength) are free from Doppler effect: the sidebands at ω0 ± ωz are well separated from the main line at ω0 , which has no Doppler broadening. This property is used in modern lattice clocks ...
... 4. Atoms confined in an optical lattice at a wavelength such that the main transition is unaffected (magic wavelength) are free from Doppler effect: the sidebands at ω0 ± ωz are well separated from the main line at ω0 , which has no Doppler broadening. This property is used in modern lattice clocks ...
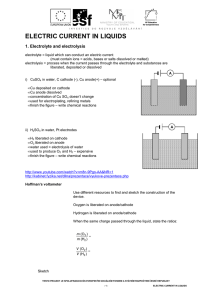
ELECTRIC CURRENT IN LIQUIDS
... passed through the solutions of H2SO4 and CuSO4. 4. A current passed through a solution of H2SO4 for 15 minutes and 10 mg of oxygen were liberated. Calculate a) the electrochemical equivalent of oxygen b) the value of the current. 5. Two identical vessels for electrolysis A and B contain the same vo ...
... passed through the solutions of H2SO4 and CuSO4. 4. A current passed through a solution of H2SO4 for 15 minutes and 10 mg of oxygen were liberated. Calculate a) the electrochemical equivalent of oxygen b) the value of the current. 5. Two identical vessels for electrolysis A and B contain the same vo ...
direct electron acceleration by chirped laser pulse in the regime of
... plane wave is not accelerated in average according to Lawson-Woodword theorem [1]. This is due to the fact that acceleration regions turn by deceleration ones. However this statement is not valid for special-limited fields, and also in the case of chirped pulse. Both conditions are realized for the ...
... plane wave is not accelerated in average according to Lawson-Woodword theorem [1]. This is due to the fact that acceleration regions turn by deceleration ones. However this statement is not valid for special-limited fields, and also in the case of chirped pulse. Both conditions are realized for the ...
Chapter 11
... have energy levels for electrons. Orbits are not circular. It can only tell us the probability of finding an electron a certain distance from the nucleus. ...
... have energy levels for electrons. Orbits are not circular. It can only tell us the probability of finding an electron a certain distance from the nucleus. ...
The Nature of Chemical Reactions
... mass of what you start with has to be equal to the mass of what you end with This is why equations must be balanced!!! A balanced equation says the number of atoms you started with has to be equal to the number of atoms you end with ...
... mass of what you start with has to be equal to the mass of what you end with This is why equations must be balanced!!! A balanced equation says the number of atoms you started with has to be equal to the number of atoms you end with ...
Physics Today
... stationary states, although bereft of electron orbits. Another was his assertion that an electron in the lowest-energy stationary state, the ground state (n = 1), does not emit radiation. That was contrary to classical electrodynamics, which would require an orbiting electron to continuously radiate ...
... stationary states, although bereft of electron orbits. Another was his assertion that an electron in the lowest-energy stationary state, the ground state (n = 1), does not emit radiation. That was contrary to classical electrodynamics, which would require an orbiting electron to continuously radiate ...
AQA Additional Sci C2 Revision Guide
... form positively charged ions. Non-metal atoms gain electrons to form negatively charged ions. Ions have the electronic structure of a noble gas i.e. they have full outer shells. Oppositely charged ions are strongly attracted to each other and are held together by ionic bonds. The diagram below shows ...
... form positively charged ions. Non-metal atoms gain electrons to form negatively charged ions. Ions have the electronic structure of a noble gas i.e. they have full outer shells. Oppositely charged ions are strongly attracted to each other and are held together by ionic bonds. The diagram below shows ...
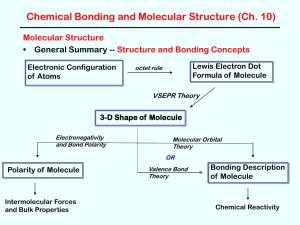
Chapter1011
... • Use valence bond theory to describe the bonding in the following (use clear 3-D pictures showing orbital overlap, etc) H2O NH3 CH4 PF3 --simple s bonds and lone pairs H2CNH --double bond like H2CCH2 ethene and H2CO formaldehyde) HCN --triple bond like HCCH ethyne and N2 nitrogen) ...
... • Use valence bond theory to describe the bonding in the following (use clear 3-D pictures showing orbital overlap, etc) H2O NH3 CH4 PF3 --simple s bonds and lone pairs H2CNH --double bond like H2CCH2 ethene and H2CO formaldehyde) HCN --triple bond like HCCH ethyne and N2 nitrogen) ...
Chapter9_4-7_FA05
... collision, you could use conservation of energy to convert the kinetic energy into potential energy, and find the height H. If you new the velocity of the block and bullet after collision, you could find the kinetic energy. You can use conservation of momentum to find the final velocity! ...
... collision, you could use conservation of energy to convert the kinetic energy into potential energy, and find the height H. If you new the velocity of the block and bullet after collision, you could find the kinetic energy. You can use conservation of momentum to find the final velocity! ...
EXAM 1
... conducting cylindrical pipe of inner radius ri and outer radius ro. The pipe is electrically neutral, while the wire carries a uniform charge, with linear charge density λ. (a) ...
... conducting cylindrical pipe of inner radius ri and outer radius ro. The pipe is electrically neutral, while the wire carries a uniform charge, with linear charge density λ. (a) ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.