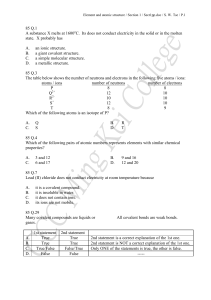
85 Q.1 A substance X melts at 1600oC. Its does
... At room temperature and pressure, iodine exists as (1) molecules held together by covalent bonds. (2) ions is a lattice. (3) molecules held together by van der Waals’ forces. A. C. ...
... At room temperature and pressure, iodine exists as (1) molecules held together by covalent bonds. (2) ions is a lattice. (3) molecules held together by van der Waals’ forces. A. C. ...
Optically polarized atoms_Atomic_Transitions
... D. DeMille, D. Budker, N. Derr, and E. Deveney, How we know that photons are bosons: experimental tests of spin-statistics for photons, in: Proceedings of the International Conference on SpinStatistics Connection and Commutation Relations: Experimental Tests and Theoretical Implications, Anacapri, I ...
... D. DeMille, D. Budker, N. Derr, and E. Deveney, How we know that photons are bosons: experimental tests of spin-statistics for photons, in: Proceedings of the International Conference on SpinStatistics Connection and Commutation Relations: Experimental Tests and Theoretical Implications, Anacapri, I ...
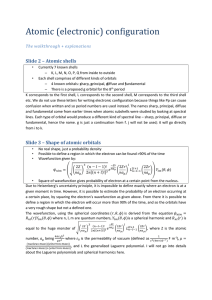
Atomic configuration guide
... orbital for the latter 3 orbitals, while the first one is unique, making a total of 7 f orbitals. Pauli’s exclusion principle states that no 2 fermions can occupy the same quantum state. To put it into simpler terms in this context, no 2 electrons can be at the same place, having the same momentum a ...
... orbital for the latter 3 orbitals, while the first one is unique, making a total of 7 f orbitals. Pauli’s exclusion principle states that no 2 fermions can occupy the same quantum state. To put it into simpler terms in this context, no 2 electrons can be at the same place, having the same momentum a ...
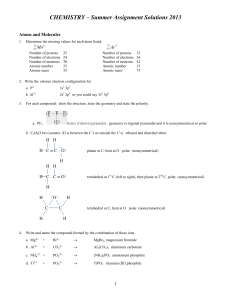
CHEMISTRY – Summer Assignment Solutions 2013
... Wrote the 1st periodic table based on increasing atomic mass and similar properties. Left gaps where necessary in order to line-up families with similar properties. Predicted products of missing elements that, when discovered, would fill-in the gaps ...
... Wrote the 1st periodic table based on increasing atomic mass and similar properties. Left gaps where necessary in order to line-up families with similar properties. Predicted products of missing elements that, when discovered, would fill-in the gaps ...
FINAL EXAM, CHE 101, SUMMER 2007 (200 PTS)
... Problem Solving: Chapters 7 and 10 20. We learned the concept of acid strength. We said that acids are classified as strong or weak. Strong acids dissociate nearly completely in water whereas weak acids dissociate only slightly. We said that the acid dissociation constant, Ka, is a measure of acid s ...
... Problem Solving: Chapters 7 and 10 20. We learned the concept of acid strength. We said that acids are classified as strong or weak. Strong acids dissociate nearly completely in water whereas weak acids dissociate only slightly. We said that the acid dissociation constant, Ka, is a measure of acid s ...
lecture slides file
... Chemical properties describe the ability of the substance to form new substances, either by decomposition or reaction with other substances (corrosiveness, flammability, acidity, toxicity, etc.). No two substances have identical physical and chemical properties. Physical changes are reversible chang ...
... Chemical properties describe the ability of the substance to form new substances, either by decomposition or reaction with other substances (corrosiveness, flammability, acidity, toxicity, etc.). No two substances have identical physical and chemical properties. Physical changes are reversible chang ...
1.5. Angular momentum operators
... with µB being the so called Bohr magneton, a constant. What does this mean? According to the equation above, the energy of the hydrogen atom in magnetic field will depend on the quantum number m: if m is positive, it will grow; if m is negative, it will decrease; and it is not changing for m = 0. Si ...
... with µB being the so called Bohr magneton, a constant. What does this mean? According to the equation above, the energy of the hydrogen atom in magnetic field will depend on the quantum number m: if m is positive, it will grow; if m is negative, it will decrease; and it is not changing for m = 0. Si ...
Electron Notes
... - there is a maximum of seven energy levels in an atom. - e- on the energy level closest to the nucleus have the lowest energy. The 7th energy level has the highest energy. - an e- requires one ‘quanta’ of energy to jump to the next energy level. • e- at their lowest energy level are considered to b ...
... - there is a maximum of seven energy levels in an atom. - e- on the energy level closest to the nucleus have the lowest energy. The 7th energy level has the highest energy. - an e- requires one ‘quanta’ of energy to jump to the next energy level. • e- at their lowest energy level are considered to b ...
chapt 2
... Because bases are negatively charged, they will react with a positively charged hydrogen in solution. The strength of an acid or base is determined by how completely it will dissociate in water. ...
... Because bases are negatively charged, they will react with a positively charged hydrogen in solution. The strength of an acid or base is determined by how completely it will dissociate in water. ...
this PDF file - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... racket. This probability is so low it may as well be 0; this matches with what would be expected from theory. Discussion From the probability above, it is shown that although theoretically still possible, the chance of a tennis ball quantum tunnelling through a racket is effectively nil. In this pap ...
... racket. This probability is so low it may as well be 0; this matches with what would be expected from theory. Discussion From the probability above, it is shown that although theoretically still possible, the chance of a tennis ball quantum tunnelling through a racket is effectively nil. In this pap ...
a new insight into the quantization of energy
... emanated from the elements within the flame of their Bunsen burner. 2 Johann Balmer produced an empirical equation that described this spectrum in the late 1800’s. 3 Johannes Rydberg extended Baumer’s formulation to the spectra of all of the elements.4 These discoveries allowed astronomers to determ ...
... emanated from the elements within the flame of their Bunsen burner. 2 Johann Balmer produced an empirical equation that described this spectrum in the late 1800’s. 3 Johannes Rydberg extended Baumer’s formulation to the spectra of all of the elements.4 These discoveries allowed astronomers to determ ...
Chapter 3 Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical
... 19. A 25.5-g sample of ammonium carbonate contains _______ mol of ammonium ions. (a). 0.468 (b). 0.288 (c). 0.531 (d). 2.00 Explanation: Realize that the formula for ammonium carbonate is (NH4)2CO3 and calculate the molar mass (96.0856 g/mol). Convert grams to moles and then using the stoichiometric ...
... 19. A 25.5-g sample of ammonium carbonate contains _______ mol of ammonium ions. (a). 0.468 (b). 0.288 (c). 0.531 (d). 2.00 Explanation: Realize that the formula for ammonium carbonate is (NH4)2CO3 and calculate the molar mass (96.0856 g/mol). Convert grams to moles and then using the stoichiometric ...
Lenz vector operations on spherical hydrogen atom
... the quantum mechanical Lenz vector operator. The derivation is performed using formalism no more sophisticated than that used to derive the properties of the angular momentum ladder operators in undergraduate quantum mechanics courses. The properties of these Lenz vector operators illustrate the acc ...
... the quantum mechanical Lenz vector operator. The derivation is performed using formalism no more sophisticated than that used to derive the properties of the angular momentum ladder operators in undergraduate quantum mechanics courses. The properties of these Lenz vector operators illustrate the acc ...
Nuclear Physics - Thierry Karsenti
... are also used to explain some observables in the atomic nucleus. As most of the information available about the atomic nucleus is obtained from its emission spectrum and the interaction of the radiation with matter, it is essential to study the atomic nucleus starting from its properties. ...
... are also used to explain some observables in the atomic nucleus. As most of the information available about the atomic nucleus is obtained from its emission spectrum and the interaction of the radiation with matter, it is essential to study the atomic nucleus starting from its properties. ...
Snímek 1 - Fordham University Computer and Information Sciences
... In large scale electrical circuits, current is measured as an average of large number of collisions of electrons in the wires. This measure only works if there are enough electrons to define an average that is unchanging. In extremely small wires, the electron no longer “bounce” around in the wire b ...
... In large scale electrical circuits, current is measured as an average of large number of collisions of electrons in the wires. This measure only works if there are enough electrons to define an average that is unchanging. In extremely small wires, the electron no longer “bounce” around in the wire b ...
AP* Chemistry ATOMIC STRUCTURE velocity = λ υ
... • emission spectrum—the spectrum of bright lines, bands, or continuous radiation that is provided by a specific emitting substance as it loses energy and returns to its ground state OR the collection of frequencies of light given off by an "excited" electron • absorption spectrum—a graph or display ...
... • emission spectrum—the spectrum of bright lines, bands, or continuous radiation that is provided by a specific emitting substance as it loses energy and returns to its ground state OR the collection of frequencies of light given off by an "excited" electron • absorption spectrum—a graph or display ...
Pauli`s exclusion principle in spinor coordinate space
... any case, once it is known that the electrons are separate at some particular time, no solution will allow them to overlap and develop a some common volume. They must have always been separated. In practice, any electron can be removed from the assembled system by electromagnetic forces. Apparently, ...
... any case, once it is known that the electrons are separate at some particular time, no solution will allow them to overlap and develop a some common volume. They must have always been separated. In practice, any electron can be removed from the assembled system by electromagnetic forces. Apparently, ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.