Chemistry Entrance Material for Grade 11 to 12 Answer Key
... 75. Define solubility. It is affixed amount of a solute dissolved in a saturated solution at constant temperature. T h e mean in g of th e w ord ‘solub le’ in ch emi stry 76. Which of the following is CORRECT concerning the terms 'soluble', 'slightly soluble', 'very slightly soluble' and 'negligible ...
... 75. Define solubility. It is affixed amount of a solute dissolved in a saturated solution at constant temperature. T h e mean in g of th e w ord ‘solub le’ in ch emi stry 76. Which of the following is CORRECT concerning the terms 'soluble', 'slightly soluble', 'very slightly soluble' and 'negligible ...
What is electricity?
... protons carry a charge. The amount of the charge is the same for each particle, but opposite in sign. Electrons carry a negative charge while protons carry positive charge. The objects around us contain billions and billions of atoms, and each atom contains many protons and electrons. The protons ar ...
... protons carry a charge. The amount of the charge is the same for each particle, but opposite in sign. Electrons carry a negative charge while protons carry positive charge. The objects around us contain billions and billions of atoms, and each atom contains many protons and electrons. The protons ar ...
Science24-UnitA-Section3.4
... Experiments like the one involving vinegar and baking soda are similar to the experiments Antoine Lavoisier performed. Lavoisier’s experiments led to the development of the Law of Conservation of Mass. In a chemical reaction the mass of the reactants is always equal to the mass of the products. Turn ...
... Experiments like the one involving vinegar and baking soda are similar to the experiments Antoine Lavoisier performed. Lavoisier’s experiments led to the development of the Law of Conservation of Mass. In a chemical reaction the mass of the reactants is always equal to the mass of the products. Turn ...
Maximal attainable boost and energy of elementary particles as a
... is not satisfied. Condition of asymptotic completeness is not trivial already in the framework of standard quantum field theory: if particles can form bound states, the structure of space of states is modified, and the S-matrix unitarity is restored only after bound states are accounted for in the u ...
... is not satisfied. Condition of asymptotic completeness is not trivial already in the framework of standard quantum field theory: if particles can form bound states, the structure of space of states is modified, and the S-matrix unitarity is restored only after bound states are accounted for in the u ...
Transient induced molecular negative ions formed in cold electron
... potential curve. In this case the electron will spend a considerable time at a radial distance close to rM. The electron can then be said to “orbit” about the centre of force (the polarized molecule). The angular motion speeds up as r decreases in order to conserve angular momentum, and a large numb ...
... potential curve. In this case the electron will spend a considerable time at a radial distance close to rM. The electron can then be said to “orbit” about the centre of force (the polarized molecule). The angular motion speeds up as r decreases in order to conserve angular momentum, and a large numb ...
Chemistry 2nd Semester Final Review
... CO2(g) + CaO(s). How many grams of calcium carbonate will I need to form 3.45 liters of carbon dioxide? 8. How many liters of water can be made from 55 grams of oxygen gas and an excess of hydrogen at a pressure of 12.4 atm and a temperature of 85C? 9. How many liters of water can be made from 34 g ...
... CO2(g) + CaO(s). How many grams of calcium carbonate will I need to form 3.45 liters of carbon dioxide? 8. How many liters of water can be made from 55 grams of oxygen gas and an excess of hydrogen at a pressure of 12.4 atm and a temperature of 85C? 9. How many liters of water can be made from 34 g ...
Presentation (PowerPoint File)
... Avoiding an exponential demand for physical resources requires a quantum computer to have a scalable tensor-product structure. This is a necessary, but not sufficient requirement for a scalable quantum computer. Are there other requirements? ...
... Avoiding an exponential demand for physical resources requires a quantum computer to have a scalable tensor-product structure. This is a necessary, but not sufficient requirement for a scalable quantum computer. Are there other requirements? ...
physical setting chemistry
... Calculate the average atomic mass of element X. • Show a correct numerical setup in the space provided in your answer booklet. • Record your answer. [1] • Express your answer to the correct number of significant figures. [1] ...
... Calculate the average atomic mass of element X. • Show a correct numerical setup in the space provided in your answer booklet. • Record your answer. [1] • Express your answer to the correct number of significant figures. [1] ...
Electron orbital radius distance in the hydrogen atom, and the
... relativity conditions and ignoring relativity. I found that under relativity conditions, all electron orbitals appear to overlap in each individual atom, not just in the hydrogen atom. This explains why we can observe the physical world and solid matter, even though matter is mostly empty space. Und ...
... relativity conditions and ignoring relativity. I found that under relativity conditions, all electron orbitals appear to overlap in each individual atom, not just in the hydrogen atom. This explains why we can observe the physical world and solid matter, even though matter is mostly empty space. Und ...
From Last Time… Today Particle in a box or a
... • Superposition: quantum mechanics says wavefunction can be in two very different configurations, both at the same time. • Measurements: The act of measuring a quantum system can change its quantum state • Quantum Tunneling: particles can sometimes escape the quantum boxes they are in • Entanglement ...
... • Superposition: quantum mechanics says wavefunction can be in two very different configurations, both at the same time. • Measurements: The act of measuring a quantum system can change its quantum state • Quantum Tunneling: particles can sometimes escape the quantum boxes they are in • Entanglement ...
Circumstellar and Interstellar Molecules
... component of the angular momentum vector of each electron along the internuclear axis can only take values ml = l, (l − 1), (l − 2), . . . , −l. The variable, λ, is the absolute value of ml , where λ = 0, 1, 2, . . . , correspond to σ, π, δ, . . . , analagous to atomic s, p, d, . . . , orbitals. For ...
... component of the angular momentum vector of each electron along the internuclear axis can only take values ml = l, (l − 1), (l − 2), . . . , −l. The variable, λ, is the absolute value of ml , where λ = 0, 1, 2, . . . , correspond to σ, π, δ, . . . , analagous to atomic s, p, d, . . . , orbitals. For ...
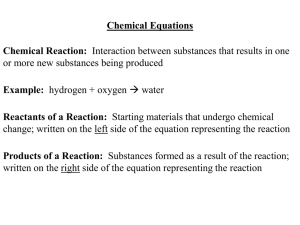
Chemical Equations Chemical Reaction: Interaction between
... the uptake of serotonin by the brain. What is the molar mass of ...
... the uptake of serotonin by the brain. What is the molar mass of ...
Semester II Exam Review Questions
... 16. A container of Yummygum is sitting at a pressure of 45 atm and temperature of 100 oC. What will happen as the temperature is increased 400 oC? 17. A container of Yummygum is sitting at a temperature of 100 oC and 1 atm of pressure. What phase change will occur if the pressure is increased to 90 ...
... 16. A container of Yummygum is sitting at a pressure of 45 atm and temperature of 100 oC. What will happen as the temperature is increased 400 oC? 17. A container of Yummygum is sitting at a temperature of 100 oC and 1 atm of pressure. What phase change will occur if the pressure is increased to 90 ...
Chapter 7: The Mole and Chemical Composition
... symbol on the periodic table). Here is how it is done. Let’s say you have 0.50 moles of Carbon. How many grams is that? 12.01 grams Carbon 0.50 mol Carbon X --------------------------- = 6.0 grams of Carbon 1 mol Carbon This method only works if you label the units of the numbers you are working wit ...
... symbol on the periodic table). Here is how it is done. Let’s say you have 0.50 moles of Carbon. How many grams is that? 12.01 grams Carbon 0.50 mol Carbon X --------------------------- = 6.0 grams of Carbon 1 mol Carbon This method only works if you label the units of the numbers you are working wit ...
Note
... atom(s) so that the atoms become charged ions C. metallic ions are positively charged and non-metallic ions are negatively charged D. because the ions are oppositely charged, they attract each other negatively charged ions are attracted to nearby ions of the opposite charge so that individual molecu ...
... atom(s) so that the atoms become charged ions C. metallic ions are positively charged and non-metallic ions are negatively charged D. because the ions are oppositely charged, they attract each other negatively charged ions are attracted to nearby ions of the opposite charge so that individual molecu ...
chemistry - My Study materials – Kumar
... Antoine L. Lavoisier, a French scientist, established the theory of Law of Conservation of Mass. The law of conservation of mass states, “Mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction”. All matters in the universe exist in three states. There are two ways of classification of matt ...
... Antoine L. Lavoisier, a French scientist, established the theory of Law of Conservation of Mass. The law of conservation of mass states, “Mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction”. All matters in the universe exist in three states. There are two ways of classification of matt ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.