Concept-Development Practice Page
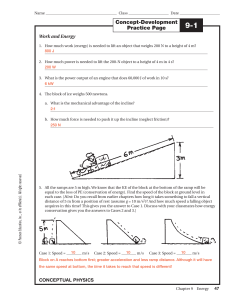
... Match each form of hidden kinetic energy with its description. ...
... Match each form of hidden kinetic energy with its description. ...
Syllabus for Semesters I to VI For Physics (Hons.) for 2011-2014
... transformation and diagonalization of real symmetric matrices with non-degenerate eigenvalues. Study of orthogonal, Hermitian and unitary systems. Study of Hermitian eigensystems, function spaces, inner product, operators as linear transformations, Hermiticity. The nature of ortho-normalization in f ...
... transformation and diagonalization of real symmetric matrices with non-degenerate eigenvalues. Study of orthogonal, Hermitian and unitary systems. Study of Hermitian eigensystems, function spaces, inner product, operators as linear transformations, Hermiticity. The nature of ortho-normalization in f ...
Polarized excitons in nanorings and the optical Aharonov
... Our discussion implies the conservation of angular momentum in a QR which can be, in principle, destroyed by defects. However, as mentioned already, recent experiments on optical and electronic properties of QR’s give strong evidence of coherent motion of electrons in these selfassembled nanostructu ...
... Our discussion implies the conservation of angular momentum in a QR which can be, in principle, destroyed by defects. However, as mentioned already, recent experiments on optical and electronic properties of QR’s give strong evidence of coherent motion of electrons in these selfassembled nanostructu ...
Optical control of the spin state of two Mn atoms... L. Besombes, C. L. Cao, S. Jamet,
... of the scattering of carriers to an excited state of the QD by the carrier-Mn coupling acting as a perturbation on the exciton wave function.30 This second-order perturbation is not included in the spin effective Hamiltonian Eq. (1) and should be taken into account in a more detailed modeling. It is ...
... of the scattering of carriers to an excited state of the QD by the carrier-Mn coupling acting as a perturbation on the exciton wave function.30 This second-order perturbation is not included in the spin effective Hamiltonian Eq. (1) and should be taken into account in a more detailed modeling. It is ...
2006 Practice Final Exam - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State
... calculator, and your University ID Card. If you have notes with you, place them in a sealed backpack and place the backpack OUT OF SIGHT or place the notes directly on the table at the front of the room. Fill in the front page of the Scantron answer sheet with your test form number (listed above), l ...
... calculator, and your University ID Card. If you have notes with you, place them in a sealed backpack and place the backpack OUT OF SIGHT or place the notes directly on the table at the front of the room. Fill in the front page of the Scantron answer sheet with your test form number (listed above), l ...
The Negative Gravitational Mass - Introduction to Nature Sciences
... have a positive or negative mass. Dirac interpreted these negative mass states as antiparticles that he hid away in the 'Dirac Sea.' While this outdated interpretation still lives on in old-textbooks and new-age books on quantum mechanics, we now know that this picture is wrong. Anti-particles have ...
... have a positive or negative mass. Dirac interpreted these negative mass states as antiparticles that he hid away in the 'Dirac Sea.' While this outdated interpretation still lives on in old-textbooks and new-age books on quantum mechanics, we now know that this picture is wrong. Anti-particles have ...
Statistical Physics (PHY831), Part 2-Exact results and solvable models
... which is the same as the chemical potential found in the classical ideal gas (see Eq. (15)) of the lecture notes for Part 2. Note that the chemical potential is large and negative at high temperature, so the fugacity approaches zero. The fugacity is always positive as it is an exponential of real nu ...
... which is the same as the chemical potential found in the classical ideal gas (see Eq. (15)) of the lecture notes for Part 2. Note that the chemical potential is large and negative at high temperature, so the fugacity approaches zero. The fugacity is always positive as it is an exponential of real nu ...
On the Theory of Quanta Louis-Victor de Broglie (1892-1987) P ARIS
... The 20th century: Relativity and quantum theory. Nevertheless, a few imperfections remained. Lord K ELVIN brought attention to two dark clouds on the horizon. One resulted from the then unsolvable problems of interpreting M ICHELSON’s and M OR LEY ’s experiment. The other pertained to methods of sta ...
... The 20th century: Relativity and quantum theory. Nevertheless, a few imperfections remained. Lord K ELVIN brought attention to two dark clouds on the horizon. One resulted from the then unsolvable problems of interpreting M ICHELSON’s and M OR LEY ’s experiment. The other pertained to methods of sta ...
Producing Squeezed Input States for an Atomic Clock Using an Optical Cavity.
... squeezing has been studied experimentally for over a decade, with demonstrations of squeezing by absorption of squeezed light [3], by entangling operations performed on a few ions [4], or by exploiting repulsive interactions in a BEC in a multiwell potential [5]. Squeezing within the Zeeman manifold ...
... squeezing has been studied experimentally for over a decade, with demonstrations of squeezing by absorption of squeezed light [3], by entangling operations performed on a few ions [4], or by exploiting repulsive interactions in a BEC in a multiwell potential [5]. Squeezing within the Zeeman manifold ...
1b-Redox FIB notes and practice
... 3. The oxidation number of hydrogen in most of its compound is +1. The exception is when hydrogen bonds to metals to make a metal hydride. Ie. In NaH, H would be have an oxidation number of ____. This is because hydrogen attracts electrons more strongly than does the metal atom. Ex) HBr(aq) + NaOH(a ...
... 3. The oxidation number of hydrogen in most of its compound is +1. The exception is when hydrogen bonds to metals to make a metal hydride. Ie. In NaH, H would be have an oxidation number of ____. This is because hydrogen attracts electrons more strongly than does the metal atom. Ex) HBr(aq) + NaOH(a ...
SSP Chapter 23
... the quantum-mechanical gas will follow a new type of statistical distribution known as the Fermi-Dirac distribution (Supplement 23-2 at the end of this chapter). This in turn will affect the way the electron gas can absorb energy from an external source, such as a heat source, and the way it respond ...
... the quantum-mechanical gas will follow a new type of statistical distribution known as the Fermi-Dirac distribution (Supplement 23-2 at the end of this chapter). This in turn will affect the way the electron gas can absorb energy from an external source, such as a heat source, and the way it respond ...
Intensities of analogous Rydberg series in CF3Cl, CF3Br and in
... analogies in the valence structure and expected electronic behaviour of the presently studied molecules. Finally, we have compared the oscillator strengths for analogous transitions in the two molecular species and their isolated halogen atoms, given their analogies in the electronic structure of th ...
... analogies in the valence structure and expected electronic behaviour of the presently studied molecules. Finally, we have compared the oscillator strengths for analogous transitions in the two molecular species and their isolated halogen atoms, given their analogies in the electronic structure of th ...
Paper
... in a 15 G bias field. The spin domains were typically 100 200 mm long. Second, the condensates were placed in a metastable state by applying a magnetic field gradient B0 in the opposite direction of that used to initially separate the components [4]. This metastable state corresponds to that shown i ...
... in a 15 G bias field. The spin domains were typically 100 200 mm long. Second, the condensates were placed in a metastable state by applying a magnetic field gradient B0 in the opposite direction of that used to initially separate the components [4]. This metastable state corresponds to that shown i ...
Classical statistical distributions can violate Bell`s - Philsci
... of the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen arguments [2] on the incompleteness of quantum mechanics. The core of the theorem takes the form of inequalities involving average values of two-particle observables. Bell showed that these inequalities must be satisfied by any theory containing additional local hidden ...
... of the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen arguments [2] on the incompleteness of quantum mechanics. The core of the theorem takes the form of inequalities involving average values of two-particle observables. Bell showed that these inequalities must be satisfied by any theory containing additional local hidden ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.