Chemistry Lesson Plans #07 - Chemical Reactions
... formula of a substance. Check each atom or polyatomic ion to be sure that the equation is balanced. Finally, make sure all the coefficients are in the lowest possible ratio that balances Sample Problems Hydrogen and oxygen react to form water. Write a balanced equation for this reaction. First, writ ...
... formula of a substance. Check each atom or polyatomic ion to be sure that the equation is balanced. Finally, make sure all the coefficients are in the lowest possible ratio that balances Sample Problems Hydrogen and oxygen react to form water. Write a balanced equation for this reaction. First, writ ...
Force and Motion -
... Pulling force (tension) in a thin and light rope: Two forces, one on each end, act along the rope direction. The two forces are of equal amplitude and in opposite directions because the rope is massless. It is also true for massless sticks. ...
... Pulling force (tension) in a thin and light rope: Two forces, one on each end, act along the rope direction. The two forces are of equal amplitude and in opposite directions because the rope is massless. It is also true for massless sticks. ...
Elementary Quantum Mechanics
... Quantum mechanics is a mathematical formalism, which, on the basis of knowledge of the state of a system, at a given time, allows the calculation of the state of the system at a later time, so that the result of experiments can be predicted. In quantum mechanics, the state of a particle is described ...
... Quantum mechanics is a mathematical formalism, which, on the basis of knowledge of the state of a system, at a given time, allows the calculation of the state of the system at a later time, so that the result of experiments can be predicted. In quantum mechanics, the state of a particle is described ...
PHY332 Atomic and Laser Physics AM FOX
... Atomic Physics is the subject that studies the inner workings of the atom. It remains one of the most important testing grounds for quantum theory, and is therefore a very area of active research, both for its contribution to fundamental physics and to technology. Furthermore, many other branches of ...
... Atomic Physics is the subject that studies the inner workings of the atom. It remains one of the most important testing grounds for quantum theory, and is therefore a very area of active research, both for its contribution to fundamental physics and to technology. Furthermore, many other branches of ...
Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
... balanced. The next step is to combine the two halfreactions to form an overall equation. 6) Multiply through each half-reactions by appropriate coefficients to match electrons in each half-reaction. (i.e. number of electrons lost by the oxidized species must equal the number gained by the reduced on ...
... balanced. The next step is to combine the two halfreactions to form an overall equation. 6) Multiply through each half-reactions by appropriate coefficients to match electrons in each half-reaction. (i.e. number of electrons lost by the oxidized species must equal the number gained by the reduced on ...
Day 72 TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... Release of energy as heat Release of energy as light Change in colour ...
... Release of energy as heat Release of energy as light Change in colour ...
Alkanes Chapter 1.1
... • Stereoisomers (sometimes called geometric isomers) are molecules that have the same chemical formula and structural backbone, but with a different arrangement of atoms in space • Cis isomer: a stereoisomer in which the groups of interest are located on the same side • Trans isomer: a stereoisomer ...
... • Stereoisomers (sometimes called geometric isomers) are molecules that have the same chemical formula and structural backbone, but with a different arrangement of atoms in space • Cis isomer: a stereoisomer in which the groups of interest are located on the same side • Trans isomer: a stereoisomer ...
5.3 Atomic Emission Spectra and the Quantum Mechanical Model
... • The energy absorbed by an electron for it to move from its current energy level to a higher energy level is identical to the energy of the light emitted by the electron as it drops back to its original energy level. • The wavelengths of the spectral lines are characteristic of the element, and the ...
... • The energy absorbed by an electron for it to move from its current energy level to a higher energy level is identical to the energy of the light emitted by the electron as it drops back to its original energy level. • The wavelengths of the spectral lines are characteristic of the element, and the ...
Hunting for Snarks in Quantum Mechanics
... outside the MaxEnt community. I include him because of his many profound contributions to probability theory and its applications in statistical mechanics and quantum theory.5 The central issue in the debate was famously articulated by EPR: Does quantum mechanics admit an experimentally accessible s ...
... outside the MaxEnt community. I include him because of his many profound contributions to probability theory and its applications in statistical mechanics and quantum theory.5 The central issue in the debate was famously articulated by EPR: Does quantum mechanics admit an experimentally accessible s ...
Energy in SHM - Ryerson Department of Physics
... 1. Attach the spring to a horizontal rod connected to the vertical stand and hang the mass from the spring as shown in Figure 1. Securely fasten the 200 g mass to the spring and the spring to the rod, using twist ties so the mass cannot fall. 2. Connect the Motion Detector to the DIG/SONIC 1 channel ...
... 1. Attach the spring to a horizontal rod connected to the vertical stand and hang the mass from the spring as shown in Figure 1. Securely fasten the 200 g mass to the spring and the spring to the rod, using twist ties so the mass cannot fall. 2. Connect the Motion Detector to the DIG/SONIC 1 channel ...
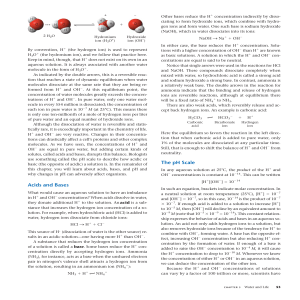
Acids and Bases The pH Scale
... use something called the pH scale to describe how acidic or basic (the opposite of acidic) a solution is. In the remainder of this chapter, you will learn about acids, bases, and pH and why changes in pH can adversely affect organisms. ...
... use something called the pH scale to describe how acidic or basic (the opposite of acidic) a solution is. In the remainder of this chapter, you will learn about acids, bases, and pH and why changes in pH can adversely affect organisms. ...
molecular interactions 01
... This dipole can polarize another molecule and induce in it an instantaneous dipole moment m2. Although the first dipole will go on to change the size and direction of its dipole (≈ 10-16 s) the second dipole will follow it; the two dipoles are correlated in direction, with the positive charge on one ...
... This dipole can polarize another molecule and induce in it an instantaneous dipole moment m2. Although the first dipole will go on to change the size and direction of its dipole (≈ 10-16 s) the second dipole will follow it; the two dipoles are correlated in direction, with the positive charge on one ...
Challenge Problems
... for these elements today are very different from their accepted atomic masses at the time Döbereiner made his observations. Döbereiner also observed that strontium, calcium, and barium showed a gradual gradation in their properties, with the values of some of strontium’s properties being about midwa ...
... for these elements today are very different from their accepted atomic masses at the time Döbereiner made his observations. Döbereiner also observed that strontium, calcium, and barium showed a gradual gradation in their properties, with the values of some of strontium’s properties being about midwa ...
Wave Function of the Universe
... sensible value for a closed universe. And solving it is just like looking for an eigenstate of any other Hamiltonian. Folks who have studied quantum mechanics have probably solved the "time-independent Schrodinger equation" in order to find the bound states of a hydrogen atom. It looks like this: H ...
... sensible value for a closed universe. And solving it is just like looking for an eigenstate of any other Hamiltonian. Folks who have studied quantum mechanics have probably solved the "time-independent Schrodinger equation" in order to find the bound states of a hydrogen atom. It looks like this: H ...
Chapter 3 Approximation Methods in QM
... degenerate PT, we need to use these |nlml sms i to diagonalize the perturbation operator V̂LS and to obtain the zero-order wavefunction and first-order energy correction. We have already done so in the previous chapter. The zeroth-order wavefunction are angular momentum states |nlsjmi which are eige ...
... degenerate PT, we need to use these |nlml sms i to diagonalize the perturbation operator V̂LS and to obtain the zero-order wavefunction and first-order energy correction. We have already done so in the previous chapter. The zeroth-order wavefunction are angular momentum states |nlsjmi which are eige ...
The concept of mass (mass, energy, relativity)
... Despite the unusual appearance of Eq. (7.3) from the point of view of Newtonian mechanics (we should say, rather, precisely because of this unusual appearance), this equation correctly describes the motion of relativistic particles. From the beginning of the century it was frequently submitted to ex ...
... Despite the unusual appearance of Eq. (7.3) from the point of view of Newtonian mechanics (we should say, rather, precisely because of this unusual appearance), this equation correctly describes the motion of relativistic particles. From the beginning of the century it was frequently submitted to ex ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.