physical and chemical change
... property is a quality or condition of a substance that can be observed or measured without changing the composition of the substance. Color is an example of a physical property. During a physical change, some properties of a sample of matter change, but the composition of the sample does not change. ...
... property is a quality or condition of a substance that can be observed or measured without changing the composition of the substance. Color is an example of a physical property. During a physical change, some properties of a sample of matter change, but the composition of the sample does not change. ...
calculations of mechanical work in 1, 2 and 3 dimensions
... Ask yourself: Is F constant with changing L? (What does the equationof-state say?) ...
... Ask yourself: Is F constant with changing L? (What does the equationof-state say?) ...
T.C UNIVERSITY of GAZIANTEP DEPARTMENT OF ENGINEERING
... values. The experiment is normally conducted using electrically neutral particles or atoms. This avoids the large deflection to the orbit of a charged particle moving through a magnetic field and allows spin-dependent effects to dominate. If the particle is treated as a classical spinning dipole, it ...
... values. The experiment is normally conducted using electrically neutral particles or atoms. This avoids the large deflection to the orbit of a charged particle moving through a magnetic field and allows spin-dependent effects to dominate. If the particle is treated as a classical spinning dipole, it ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... Introduce and analyze torque Understand the equilibrium dynamics of an extended object in response to forces Employ “conservation of angular momentum” concept ...
... Introduce and analyze torque Understand the equilibrium dynamics of an extended object in response to forces Employ “conservation of angular momentum” concept ...
- Philsci
... connected region of space and therefore cannot simultaneously pass through the two slits which are located in two separated regions of space. Therefore a classical particle emerging from the double slit apparatus can only have passed through one slit and cannot produce an interference pattern when d ...
... connected region of space and therefore cannot simultaneously pass through the two slits which are located in two separated regions of space. Therefore a classical particle emerging from the double slit apparatus can only have passed through one slit and cannot produce an interference pattern when d ...
DISTANCE EDUCATION M.Sc. (Physics) DEGREE EXAMINATION
... Explain the salient features of a single particle nuclear shell model. ...
... Explain the salient features of a single particle nuclear shell model. ...
Slide 1 - Electrical and Computer Engineering
... Pushing/pulling atoms using STM STM Lithography: • Atomic scale patterning technique • Manipulation of both single atoms or molecules • Can be used, for example, quantum data storage with extremely high storage density (one atom per bit). ...
... Pushing/pulling atoms using STM STM Lithography: • Atomic scale patterning technique • Manipulation of both single atoms or molecules • Can be used, for example, quantum data storage with extremely high storage density (one atom per bit). ...
Reduction and Emergence in Chemistry
... Admittedly the quantum mechanical theory of bonding that McLaughlin appeals to does, provide a more fundamental account of chemical bonding than the classical, or Lewis theory. Nevertheless, it does not permit one to predict in advance the behavior of elements or the properties that a compound might ...
... Admittedly the quantum mechanical theory of bonding that McLaughlin appeals to does, provide a more fundamental account of chemical bonding than the classical, or Lewis theory. Nevertheless, it does not permit one to predict in advance the behavior of elements or the properties that a compound might ...
Reduction and Emergence in Chemistry - Philsci
... Admittedly the quantum mechanical theory of bonding that McLaughlin appeals to does, provide a more fundamental account of chemical bonding that the classical, or Lewis theory. Nevertheless, it does not permit one to predict in advance the behavior of elements or the properties that a compound might ...
... Admittedly the quantum mechanical theory of bonding that McLaughlin appeals to does, provide a more fundamental account of chemical bonding that the classical, or Lewis theory. Nevertheless, it does not permit one to predict in advance the behavior of elements or the properties that a compound might ...
GROUP 13 ELEMENTS -THE BORON FAMILY -
... oxidation state. The melting point is 29.8º C and therefore melts by increasing room temperature by a little. Gallium is important because it forms gallium arsenide (GaAs), which can convert light directly into electricity. Also due to thermite reaction, aluminum can extract oxygen from water and hy ...
... oxidation state. The melting point is 29.8º C and therefore melts by increasing room temperature by a little. Gallium is important because it forms gallium arsenide (GaAs), which can convert light directly into electricity. Also due to thermite reaction, aluminum can extract oxygen from water and hy ...
Slides A - Department of Physics | Oregon State
... • Two “formal” lab reports (35%) are required. ...
... • Two “formal” lab reports (35%) are required. ...
A mean-field approach to attractive few
... systems in order to investigate quantum effects. This means that they can effectively function as simulations of other quantum systems [7]. Over the past decades the field has made significant progress, with various experimental and theoretical techniques available for the study of these systems [8] ...
... systems in order to investigate quantum effects. This means that they can effectively function as simulations of other quantum systems [7]. Over the past decades the field has made significant progress, with various experimental and theoretical techniques available for the study of these systems [8] ...
Theoretical Errors in Contemporary Physics
... Relations between two physical theories can be deduced from an examination of their domain of validity. In particular, let DA and DB denote the domains of validity of theories A and B, respectively. Now, if DA ⊂ DB and DA 6= DB then one finds that theory B takes a higher hierarchical rank than theor ...
... Relations between two physical theories can be deduced from an examination of their domain of validity. In particular, let DA and DB denote the domains of validity of theories A and B, respectively. Now, if DA ⊂ DB and DA 6= DB then one finds that theory B takes a higher hierarchical rank than theor ...
Chapter 7 Goals
... Continued from the previous slide Finally, multiply empirical by n [C2H3As3Cu2O8] x 2 empirical formula ...
... Continued from the previous slide Finally, multiply empirical by n [C2H3As3Cu2O8] x 2 empirical formula ...
Degenerate Fermi Gases
... present for any value of the interaction also for small negative scattering length: COOPER PAIR FORMATION and BCS-superfluidity In 3D in vacuum an attractive potential has to be “attractive enough” to bound a pair of (red-blue) atoms. In 2D and 1D any attractive potential make it due to the differen ...
... present for any value of the interaction also for small negative scattering length: COOPER PAIR FORMATION and BCS-superfluidity In 3D in vacuum an attractive potential has to be “attractive enough” to bound a pair of (red-blue) atoms. In 2D and 1D any attractive potential make it due to the differen ...
CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 2: Organic
... If we look at the example of H 2 (g) one of the molecular orbitals is formed by adding the mathematical functions for the two 1s orbitals that come together to form this molecule. A molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the wave-like behaviour of an electron in a molecule. This fun ...
... If we look at the example of H 2 (g) one of the molecular orbitals is formed by adding the mathematical functions for the two 1s orbitals that come together to form this molecule. A molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the wave-like behaviour of an electron in a molecule. This fun ...
Chapter 3
... A. Explicitly teach an interpretation that aligns with student intuition, without discussing alternatives: Instructor A taught this course for engineering majors from a Realist/Statistical perspective (though he ...
... A. Explicitly teach an interpretation that aligns with student intuition, without discussing alternatives: Instructor A taught this course for engineering majors from a Realist/Statistical perspective (though he ...
Simultaneous optical trapping and detection of atoms by microdisk
... and negative 共attractive兲 for ⌬ ⬍ 0 共“red-detuned” light兲. Using the values of the parameter estimate of Sec. II B, we find that the force on an atom 100 nm away from the disk surface is about 70 K / nm. For later use in this paper, we now discuss the combined optical potential of two light fields ...
... and negative 共attractive兲 for ⌬ ⬍ 0 共“red-detuned” light兲. Using the values of the parameter estimate of Sec. II B, we find that the force on an atom 100 nm away from the disk surface is about 70 K / nm. For later use in this paper, we now discuss the combined optical potential of two light fields ...
CFD of an RCM
... configuration. It represents the probability that this configuration can be reached, from among all other configurations, by totally random means. For N particles arriving at a configuration in which there are n0 particles with energy 0, n1 with 1 etc, the statistical weight is: ...
... configuration. It represents the probability that this configuration can be reached, from among all other configurations, by totally random means. For N particles arriving at a configuration in which there are n0 particles with energy 0, n1 with 1 etc, the statistical weight is: ...
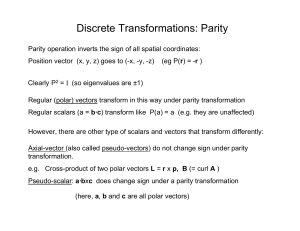
Discrete Transformations: Parity
... Survey of the literature by Lee and Yang showed there was little experimental evidence for parity conservation in weak decays ...
... Survey of the literature by Lee and Yang showed there was little experimental evidence for parity conservation in weak decays ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.