PS_CHEM7_ch4 - WordPress.com
... such as Ca2+ and Fe3+ by replacing them with enough Na+ ions to maintain the same number of positive charges in the solution. If 1.0 103 L of “hard” water is 0.015 M Ca2 and 0.0010 M Fe3 , how many moles of Na+ are needed to replace these ions? ...
... such as Ca2+ and Fe3+ by replacing them with enough Na+ ions to maintain the same number of positive charges in the solution. If 1.0 103 L of “hard” water is 0.015 M Ca2 and 0.0010 M Fe3 , how many moles of Na+ are needed to replace these ions? ...
Stoichiometry
... just as a dozen is used to indicate a number of eggs. Converting from moles to atoms is done the same as converting dozens to items. 1.5 doz = (1.5 doz)(12 items.doz-1) = 18 items and 1.5 mol = (1.5 mol)( 6.0x1023 atoms.mol-1) = 9.0x1023 atoms. The mole is used simply because it is much easier to di ...
... just as a dozen is used to indicate a number of eggs. Converting from moles to atoms is done the same as converting dozens to items. 1.5 doz = (1.5 doz)(12 items.doz-1) = 18 items and 1.5 mol = (1.5 mol)( 6.0x1023 atoms.mol-1) = 9.0x1023 atoms. The mole is used simply because it is much easier to di ...
Step 2
... number to each element wherever it appears in the equation. If the reaction is a redox reaction, identify the element that undergoes an increase in oxidation number and the elements the undergoes a decrease. Find the numerical values of the increase and decrease. Determine the smallest whole-number ...
... number to each element wherever it appears in the equation. If the reaction is a redox reaction, identify the element that undergoes an increase in oxidation number and the elements the undergoes a decrease. Find the numerical values of the increase and decrease. Determine the smallest whole-number ...
Stoichiometry, Lab Basics, Reactions
... hydrogen gas. The H2 produced was then collected by water displacement at 27C (where the vapor pressure of water is 21 torr) and a barometric pressure of 757 torr. If 0.555 L of gas is collected, the partial pressure of hydrogen gas is: A) 0.555 x (273+27) B) 0.555 x 757 C) 757 – 27 D) 757 – 21 E) ...
... hydrogen gas. The H2 produced was then collected by water displacement at 27C (where the vapor pressure of water is 21 torr) and a barometric pressure of 757 torr. If 0.555 L of gas is collected, the partial pressure of hydrogen gas is: A) 0.555 x (273+27) B) 0.555 x 757 C) 757 – 27 D) 757 – 21 E) ...
Notebook - Science
... molecule: group of atoms bonded together, representing the smallest fundamental unit of a chemical compound that can take part in a chemical reaction compound: substance consisting of atoms or ions of two or more different elements in definite proportions joined by chemical bonds isomer: different a ...
... molecule: group of atoms bonded together, representing the smallest fundamental unit of a chemical compound that can take part in a chemical reaction compound: substance consisting of atoms or ions of two or more different elements in definite proportions joined by chemical bonds isomer: different a ...
chem A exercise package C
... regions, such as for oxygen, will result in the gain of two electrons. This process of overlapping atoms is called covalent bonding. The substance that results from covalent bonding is called a covalent substance. The process of overlapping atoms will keep occurring for a particular atom until it ha ...
... regions, such as for oxygen, will result in the gain of two electrons. This process of overlapping atoms is called covalent bonding. The substance that results from covalent bonding is called a covalent substance. The process of overlapping atoms will keep occurring for a particular atom until it ha ...
Slides for lecture 7 - Aleksey Kocherzhenko
... Standard enthalpy of formation" Change of enthalpy when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements, with all substances in their standard states at 1 bar " ...
... Standard enthalpy of formation" Change of enthalpy when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements, with all substances in their standard states at 1 bar " ...
Topic 2
... elements were arranged in order of atomic mass (A), they could be placed in horizontal rows such that the elements in the vertical columns had similar properties. – periodic table - tabular arrangement of elements in rows and columns, highlighting the regular repetition of properties of the elements ...
... elements were arranged in order of atomic mass (A), they could be placed in horizontal rows such that the elements in the vertical columns had similar properties. – periodic table - tabular arrangement of elements in rows and columns, highlighting the regular repetition of properties of the elements ...
chemistry
... 42 During a laboratory activity to investigate reaction rate, a student reacts 1.0-gram samples of solid zinc with 10.0-milliliter samples of HCl(aq). The table below shows information about the variables in five experiments the student performed. Reaction of Zn(s) with HCl(aq) ...
... 42 During a laboratory activity to investigate reaction rate, a student reacts 1.0-gram samples of solid zinc with 10.0-milliliter samples of HCl(aq). The table below shows information about the variables in five experiments the student performed. Reaction of Zn(s) with HCl(aq) ...
Honors Chemistry / SAT II
... spectrometer, exhibit the same lines in the yellow, green and blue spectral regions. This is evidence that (A) fluorescent lights contain fluorine gas (B) air is present in all fluorescent lights (C) there are no gases present in fluorescent lights (D) the same element is present in all the fluoresc ...
... spectrometer, exhibit the same lines in the yellow, green and blue spectral regions. This is evidence that (A) fluorescent lights contain fluorine gas (B) air is present in all fluorescent lights (C) there are no gases present in fluorescent lights (D) the same element is present in all the fluoresc ...
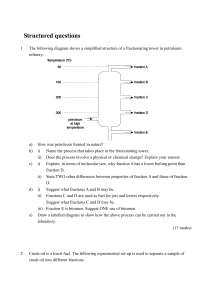
Structured questions
... ii) A component of the heavy fraction of petroleum has a molecular formula C12H26. In one of the reactions in Process 2, only a hydrocarbon and compound B are formed from this component. Write a chemical equation for the reaction involved. Catalytic hydration is employed to convert compound B into e ...
... ii) A component of the heavy fraction of petroleum has a molecular formula C12H26. In one of the reactions in Process 2, only a hydrocarbon and compound B are formed from this component. Write a chemical equation for the reaction involved. Catalytic hydration is employed to convert compound B into e ...
Regents Chemistry Topic Review Packet
... emits a specific amount of energy usually in the form of light. This can be used to identify an element (bright line spectrum). The instrument used to see the bright line spectrum is called a spectroscope. 10. The outermost electrons are called valence electrons. These affect the chemical properti ...
... emits a specific amount of energy usually in the form of light. This can be used to identify an element (bright line spectrum). The instrument used to see the bright line spectrum is called a spectroscope. 10. The outermost electrons are called valence electrons. These affect the chemical properti ...
Chemistry notes Important terms *Mass of element in a sample
... A relates to the number of electrons B relates to molecular volume Laws *law of multiple proportions if element A and B react to form tow compounds, the different masses of B than combine with a fixed mass of A can be expressed as a ratio of small whole numbers *law of mass conservation the total ma ...
... A relates to the number of electrons B relates to molecular volume Laws *law of multiple proportions if element A and B react to form tow compounds, the different masses of B than combine with a fixed mass of A can be expressed as a ratio of small whole numbers *law of mass conservation the total ma ...
Regents Chemistry Topic Review Packet
... emits a specific amount of energy usually in the form of light. This can be used to identify an element (bright line spectrum). The instrument used to see the bright line spectrum is called a spectroscope. 10. The outermost electrons are called valence electrons. These affect the chemical properti ...
... emits a specific amount of energy usually in the form of light. This can be used to identify an element (bright line spectrum). The instrument used to see the bright line spectrum is called a spectroscope. 10. The outermost electrons are called valence electrons. These affect the chemical properti ...
Unit 5 - Chemical Reactions - Student
... The substances that undergo a chemical reaction are the reactants. The new substances formed are the products. Special symbols are written after formulas in equations to show a substance’s state. The designations for solid, liquid, or gas, are (s), (l), and (g), respectively. A substance dissolv ...
... The substances that undergo a chemical reaction are the reactants. The new substances formed are the products. Special symbols are written after formulas in equations to show a substance’s state. The designations for solid, liquid, or gas, are (s), (l), and (g), respectively. A substance dissolv ...
File
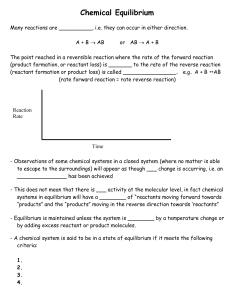
... - If this reaction takes place in a closed container, both reactants and products can be found - This is not considered to be a quantitative reaction - can be explained by considering the reverse reaction: CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g) - The equilibrium equation is CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g) - Using th ...
... - If this reaction takes place in a closed container, both reactants and products can be found - This is not considered to be a quantitative reaction - can be explained by considering the reverse reaction: CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g) - The equilibrium equation is CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g) - Using th ...
Solution Stoichiometry - Angelo State University
... • For a chemical reaction to occur, the reacting species have to come in close contact with each other. Most chemical reactions are performed in a solution (or in the gas phase) rather than in the solid state. • A solution consists of a smaller amount of one substance, the solute (usually a liquid o ...
... • For a chemical reaction to occur, the reacting species have to come in close contact with each other. Most chemical reactions are performed in a solution (or in the gas phase) rather than in the solid state. • A solution consists of a smaller amount of one substance, the solute (usually a liquid o ...
Carboxylic Acids - BSAK Chemistry weebly
... • The name of the major product is ethanamide • Unlike the reactions between ethanoyl chloride and water or ethanol, hydrogen chloride isn't produced – why not? ...
... • The name of the major product is ethanamide • Unlike the reactions between ethanoyl chloride and water or ethanol, hydrogen chloride isn't produced – why not? ...
Stoichiometric Calculations
... The limiting reactant, or limiting reagent, is the reactant present in the smallest stoichiometric amount. This is not necessarily the one with the smallest mass. The limiting reactant is the reactant you’ll run out of first, and it is the one that determines the maximum amount of product that can b ...
... The limiting reactant, or limiting reagent, is the reactant present in the smallest stoichiometric amount. This is not necessarily the one with the smallest mass. The limiting reactant is the reactant you’ll run out of first, and it is the one that determines the maximum amount of product that can b ...
x - A Level Tuition
... compared to 1.0 mol dm-3 nitric acid for the same number of moles of water formed. This is because some of the energy evolved from the neutralisation process is used to further dissociate the ethanoic acid completely. ...
... compared to 1.0 mol dm-3 nitric acid for the same number of moles of water formed. This is because some of the energy evolved from the neutralisation process is used to further dissociate the ethanoic acid completely. ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.