Chapter 4 Nomenclature and Chemical Equations
... in the parenthesis tell us the states of the substances: s denotes a solid, l denotes a liquid, g denotes a gas and aq denotes an aqueous solution, i.e. a homogeneous mixture in water. Therefore, the above chemical equation informs us that solid sodium reacts with liquid water to give an aqueous ...
... in the parenthesis tell us the states of the substances: s denotes a solid, l denotes a liquid, g denotes a gas and aq denotes an aqueous solution, i.e. a homogeneous mixture in water. Therefore, the above chemical equation informs us that solid sodium reacts with liquid water to give an aqueous ...
Chapter 3
... One of cancer chemotherapy’s greatest success stories began with an accidental discovery. In 1964, Barnett Rosenberg and his research group at Michigan State University were studying the effect of an electric field on the growth of bacteria. Using platinum electrodes, they passed an electric current ...
... One of cancer chemotherapy’s greatest success stories began with an accidental discovery. In 1964, Barnett Rosenberg and his research group at Michigan State University were studying the effect of an electric field on the growth of bacteria. Using platinum electrodes, they passed an electric current ...
A2 2, Analytical, Transition Metals, Electrochemistry and
... 14 Iron(II) ions are part of the structure of haemoglobin. Many people supplement their diet by taking “iron tablets” which contain hydrated iron(II) sulfate, FeSO4.7H2O. ...
... 14 Iron(II) ions are part of the structure of haemoglobin. Many people supplement their diet by taking “iron tablets” which contain hydrated iron(II) sulfate, FeSO4.7H2O. ...
Reaction Energy
... • example: the Hf0 of carbon dioxide is –393.5 kJ per mol of gas produced. • Elements in their standard states are defined as having Hf0 = 0. • This indicates that carbon dioxide is more stable than the elements from which it was formed. ...
... • example: the Hf0 of carbon dioxide is –393.5 kJ per mol of gas produced. • Elements in their standard states are defined as having Hf0 = 0. • This indicates that carbon dioxide is more stable than the elements from which it was formed. ...
Folie 1
... pressures is equal to the total pressure. If the gases are perfect, then the partial pressure is also the pressure that each gas would exert if it were present alone in the container. ...
... pressures is equal to the total pressure. If the gases are perfect, then the partial pressure is also the pressure that each gas would exert if it were present alone in the container. ...
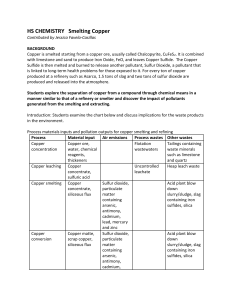
Smelting Copper
... 1. Write a balanced chemical equation for the single replacement reaction of copper (II) chloride with aluminum metal to produce copper metal and aluminum chloride. 1.a. Calculate the number of moles of copper (II) chloride used. 1. b. Calculate the number of moles of aluminum metal used. 2. Determi ...
... 1. Write a balanced chemical equation for the single replacement reaction of copper (II) chloride with aluminum metal to produce copper metal and aluminum chloride. 1.a. Calculate the number of moles of copper (II) chloride used. 1. b. Calculate the number of moles of aluminum metal used. 2. Determi ...
PDF Chapter 14 Chemical Kinetics
... 2. They must collide with enough energy to overcome an energy barrier to reaction called the activation energy. 3. They must collide in an orientation that allows the necessary bond‐breaking and forming needed to transform the reactants to the products. ...
... 2. They must collide with enough energy to overcome an energy barrier to reaction called the activation energy. 3. They must collide in an orientation that allows the necessary bond‐breaking and forming needed to transform the reactants to the products. ...
2 CHEMICAL ARITHMATICS W MODULE - 1
... In your previous classes, you have studied how to write chemical formula of a sustance. For example, water is represented by H2O, carbon dioxide is represented by CO2, methane is represented by CH4, dinitrogen penta oxide is represented by N2O5, and so on. You are aware, formula for a molecule uses ...
... In your previous classes, you have studied how to write chemical formula of a sustance. For example, water is represented by H2O, carbon dioxide is represented by CO2, methane is represented by CH4, dinitrogen penta oxide is represented by N2O5, and so on. You are aware, formula for a molecule uses ...
Unit 10: Chemical Reactions
... The substances that undergo a chemical reaction are the reactants. The new substances formed are the products. Special symbols are written after formulas in equations to show a substance’s state. The designations for solid, liquid, or gas, are (s), (l), and (g), respectively. A substance dissolv ...
... The substances that undergo a chemical reaction are the reactants. The new substances formed are the products. Special symbols are written after formulas in equations to show a substance’s state. The designations for solid, liquid, or gas, are (s), (l), and (g), respectively. A substance dissolv ...
Lab 1
... Our final answer, 7.6889 has 5 sig figs, the same number of sig figs as 53.822 because division looks for the number with the fewest sig figs (not like addition) so 53.822 has 5 sig figs and “7” is just a counting number (it is not a 1 sig fig number, but an infinite number of sig figs). ...
... Our final answer, 7.6889 has 5 sig figs, the same number of sig figs as 53.822 because division looks for the number with the fewest sig figs (not like addition) so 53.822 has 5 sig figs and “7” is just a counting number (it is not a 1 sig fig number, but an infinite number of sig figs). ...
Chemical and physical changes
... 6. To be able to identify a simple substance or a compound according to wether it decomposes or not. 7. To know the hypotheses of the atomic theory. 8. To know what is a symbol and the meaning of a formula. 9. To know the name and the symbols of the most common elements. 10. To know the theoretical ...
... 6. To be able to identify a simple substance or a compound according to wether it decomposes or not. 7. To know the hypotheses of the atomic theory. 8. To know what is a symbol and the meaning of a formula. 9. To know the name and the symbols of the most common elements. 10. To know the theoretical ...
Predicting Reactions • AP Chemistry CLASSIFYING REACTIONS
... what happens when water is reduced at the cathode. 8. (Trick #2) When CuSO4(aq) is electrolyzed, you know that Cu° metal is going to form because copper's potential is higher than water. So, positive electrode will attract SO42- ions but SO42- can not further oxidize (full of oxygen and no more unsh ...
... what happens when water is reduced at the cathode. 8. (Trick #2) When CuSO4(aq) is electrolyzed, you know that Cu° metal is going to form because copper's potential is higher than water. So, positive electrode will attract SO42- ions but SO42- can not further oxidize (full of oxygen and no more unsh ...
Module 2 Alcohols, halogenoalkanes and analysis
... investigated their properties in the search for more useful materials. In the recent past, organic chemists have developed a broad range of original and exciting materials, such as pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, solvents and plastics. Halogenoalkanes are important starting materials for many synthet ...
... investigated their properties in the search for more useful materials. In the recent past, organic chemists have developed a broad range of original and exciting materials, such as pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, solvents and plastics. Halogenoalkanes are important starting materials for many synthet ...
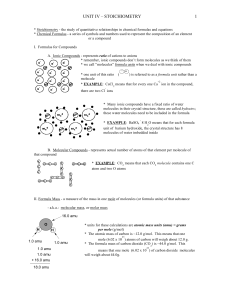
unit iv – stoichiometry 1
... * uses a mass spectrometer to separate atoms of different masses and determine the percent of the sample composed of that type of atom X. Finding Formulas of Compounds using laboratory data * empirical formula - simplest whole number ratio of elements (not necessarily the actual formula) EXAMPLE: th ...
... * uses a mass spectrometer to separate atoms of different masses and determine the percent of the sample composed of that type of atom X. Finding Formulas of Compounds using laboratory data * empirical formula - simplest whole number ratio of elements (not necessarily the actual formula) EXAMPLE: th ...
Chemical Equilibrium - The Gurukul Institute
... (NH4)2 CO3(s) ⇌ 2NH3(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(g) At a certain elevated temperature, the total pressure of the gases generated was 0.42 atm. At equilibrium. Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction. 10. if a given quantity of phosphorus pentachloride is heated at 250o C and allowed to come to equ ...
... (NH4)2 CO3(s) ⇌ 2NH3(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(g) At a certain elevated temperature, the total pressure of the gases generated was 0.42 atm. At equilibrium. Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction. 10. if a given quantity of phosphorus pentachloride is heated at 250o C and allowed to come to equ ...
Test - Regents
... Calculate the average atomic mass of element X. • Show a correct numerical setup in the space provided in your answer booklet. • Record your answer. [1] • Express your answer to the correct number of significant figures. [1] ...
... Calculate the average atomic mass of element X. • Show a correct numerical setup in the space provided in your answer booklet. • Record your answer. [1] • Express your answer to the correct number of significant figures. [1] ...
Lab # 18
... To balance equations, we follow these four rules: 1. Equations must be balanced so that the number of atoms of each element is equal on the left side (reactants) and on the right side (products) of the reaction. 2. We MUST NOT change the subscripts of any of the reactants or products; if we did that ...
... To balance equations, we follow these four rules: 1. Equations must be balanced so that the number of atoms of each element is equal on the left side (reactants) and on the right side (products) of the reaction. 2. We MUST NOT change the subscripts of any of the reactants or products; if we did that ...
2015 Dr. Jay L. Wile, All rights reserved.
... 3. A student does a chemical reaction with two chemicals. The total mass of the two chemicals is 45.0 grams. When she is done, she finds that the mass of all the chemicals she has collected is now only 34.5 grams. Has she collected all the products of the reaction? How do you know? ...
... 3. A student does a chemical reaction with two chemicals. The total mass of the two chemicals is 45.0 grams. When she is done, she finds that the mass of all the chemicals she has collected is now only 34.5 grams. Has she collected all the products of the reaction? How do you know? ...
Physical properties
... • Distillation is used to purify a compound by separating it from a non-volatile or less-volatile material. When different compounds in a mixture have different boiling points, they separate into individual components when the mixture is carefully distilled. • Distillation is the process of heating ...
... • Distillation is used to purify a compound by separating it from a non-volatile or less-volatile material. When different compounds in a mixture have different boiling points, they separate into individual components when the mixture is carefully distilled. • Distillation is the process of heating ...
Redox Balancing Worksheet
... The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to its charge. Thus the oxidation number of Cl in the Clion is -1, that for Mg in the Mg+2 ion is +2, and that for oxygen in O2- ion is -2. The sum of the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero if neutral, or equal to the charge if an ion. The oxidat ...
... The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to its charge. Thus the oxidation number of Cl in the Clion is -1, that for Mg in the Mg+2 ion is +2, and that for oxygen in O2- ion is -2. The sum of the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero if neutral, or equal to the charge if an ion. The oxidat ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.