Empirical Formula
... Use the Periodic Table to determine the mass of 1 mole of Al 1 mole Al = 26.98 g Use this as a conversion factor for grams-to-moles 1 mol Al 10.0 g Al x 0.371 mol Al 26.98 g Copyright©2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. ...
... Use the Periodic Table to determine the mass of 1 mole of Al 1 mole Al = 26.98 g Use this as a conversion factor for grams-to-moles 1 mol Al 10.0 g Al x 0.371 mol Al 26.98 g Copyright©2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. ...
Diazotization-Coupling Reaction--
... 6. After all of the sulfanilic acid dissolves completely, remove the Erlenmeyer flask and allow it to cool to room temperature on the bench top. 7. Weigh 0.08-g sodium nitrite, NaNO2, and transfer it to the cooled Erlenmeyer flask; stir the solution until the solid dissolves. 8. Cool the 25-mL Erlen ...
... 6. After all of the sulfanilic acid dissolves completely, remove the Erlenmeyer flask and allow it to cool to room temperature on the bench top. 7. Weigh 0.08-g sodium nitrite, NaNO2, and transfer it to the cooled Erlenmeyer flask; stir the solution until the solid dissolves. 8. Cool the 25-mL Erlen ...
quantitative_chemistry
... special name to what is, in effect, just a number, but this is actually a very familiar practice: 1 mole corresponds to 6.022 × 1023 just as 1 dozen corresponds to 12 The mole is the basic counting unit used by chemists to indicate how many atoms, molecules, or ions they are dealing with. A chemist ...
... special name to what is, in effect, just a number, but this is actually a very familiar practice: 1 mole corresponds to 6.022 × 1023 just as 1 dozen corresponds to 12 The mole is the basic counting unit used by chemists to indicate how many atoms, molecules, or ions they are dealing with. A chemist ...
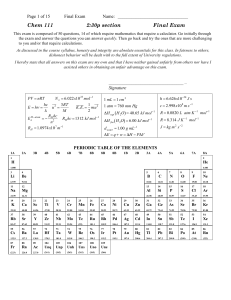
Chapter One Chemistry
... A sample of liquid has a mass of 24 g and a volume of 16 mL. What is the density of the liquid? ...
... A sample of liquid has a mass of 24 g and a volume of 16 mL. What is the density of the liquid? ...
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
C. 3.5 g
... exposed to sunlight for half an hour and then inverted over water. The volume of gas remained in the tube will be about ...
... exposed to sunlight for half an hour and then inverted over water. The volume of gas remained in the tube will be about ...
chemistry 2.1
... • how much is present in a chemical substance, or • how much is involved in a chemical reaction, for one or more chemicals. Significant figures indicate the level of accuracy of the data and/or apparatus. In calculations, final answers typically include three significant figures, and no rounding sho ...
... • how much is present in a chemical substance, or • how much is involved in a chemical reaction, for one or more chemicals. Significant figures indicate the level of accuracy of the data and/or apparatus. In calculations, final answers typically include three significant figures, and no rounding sho ...
Chemistry Entrance Material for Grade 11 to 12 Answer Key
... In all multiple choice questions, more than answer could be correct Section №: 1 Pure Substances Know where gaseous elements are located in the periodic table 01. What are the elements that are normally found as gases? H, N,O,F Cl, and Nobel gas 02. Where are these gaseous elements placed in the per ...
... In all multiple choice questions, more than answer could be correct Section №: 1 Pure Substances Know where gaseous elements are located in the periodic table 01. What are the elements that are normally found as gases? H, N,O,F Cl, and Nobel gas 02. Where are these gaseous elements placed in the per ...
Chemistry 8.2
... compounds exchange places in an aqueous solution to form two new compounds. • One of the compounds formed is usually a precipitate, an insoluble gas that bubbles out of the solution, or a molecular compound, usually water. • The other compound is often soluble and remains dissolved in solution. ...
... compounds exchange places in an aqueous solution to form two new compounds. • One of the compounds formed is usually a precipitate, an insoluble gas that bubbles out of the solution, or a molecular compound, usually water. • The other compound is often soluble and remains dissolved in solution. ...
H2 Chemistry Syllabus (9729)
... 2000) will generally be adopted although the traditional names sulfate, sulfite, nitrate, nitrite, sulfurous and nitrous acids will be used in question papers. Sulfur (and all compounds of sulfur) will be spelt with f (not with ph) in question papers, however candidates can use either spelling in th ...
... 2000) will generally be adopted although the traditional names sulfate, sulfite, nitrate, nitrite, sulfurous and nitrous acids will be used in question papers. Sulfur (and all compounds of sulfur) will be spelt with f (not with ph) in question papers, however candidates can use either spelling in th ...
Answers to NHSCE 2002 Part A Page 1
... have the same molecular formulae but different structural formulae or connectivity. These isomers are called constitutional isomers (their former name was structural isomers). The molecular formula of (CH3)2O is C2H6O, and the alcohol with this molecular formula is C2H5OH. (The formula CH3-O-CH3 i ...
... have the same molecular formulae but different structural formulae or connectivity. These isomers are called constitutional isomers (their former name was structural isomers). The molecular formula of (CH3)2O is C2H6O, and the alcohol with this molecular formula is C2H5OH. (The formula CH3-O-CH3 i ...
class xii – preparatory examination - 1
... than water.The gas is also soluble in CCl4.Its solution in alcohol is used as an antiseptic.Identify ‘A’ and ‘B’ and explain the observations. 12. Which is more acidic-phenol or p-nitrophenol ? Explain. 13. How will you distinguish between : ...
... than water.The gas is also soluble in CCl4.Its solution in alcohol is used as an antiseptic.Identify ‘A’ and ‘B’ and explain the observations. 12. Which is more acidic-phenol or p-nitrophenol ? Explain. 13. How will you distinguish between : ...
111 Exam IV outline
... 1. The forward reaction (⇀ ) and reverse (↽ ) reactions are occurring simultaneously. 2. The rate for the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction and a dynamic equilibrium is achieved. 3. The ratio of the concentrations of the products to reactants is constant. B. THE EQUILIBRI ...
... 1. The forward reaction (⇀ ) and reverse (↽ ) reactions are occurring simultaneously. 2. The rate for the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction and a dynamic equilibrium is achieved. 3. The ratio of the concentrations of the products to reactants is constant. B. THE EQUILIBRI ...
ppt
... If the concentrations at one point in the reaction are: [CO(g)] = 4.00 mol/L, [H2O(g)] = 2.00 mol/L, [CO2(g)] = 4.00 mol/L, and [H2(g)] = 2.00 mol/L. Determine whether the reaction has reached equilibrium, and, if not, in which direction it will proceed to establish equilibrium. ...
... If the concentrations at one point in the reaction are: [CO(g)] = 4.00 mol/L, [H2O(g)] = 2.00 mol/L, [CO2(g)] = 4.00 mol/L, and [H2(g)] = 2.00 mol/L. Determine whether the reaction has reached equilibrium, and, if not, in which direction it will proceed to establish equilibrium. ...
Continued on Next page
... What Is Required? (a) Add the enthalpy change to the thermochemical equation. (b) Calculate ∆H for the reaction of 5.00 mol of P4O10 with excess water. (c) Calculate ∆H for the reaction in which 235 g of H3PO4(aq) is formed. What Is Given? You are given the balanced chemical equation and the corresp ...
... What Is Required? (a) Add the enthalpy change to the thermochemical equation. (b) Calculate ∆H for the reaction of 5.00 mol of P4O10 with excess water. (c) Calculate ∆H for the reaction in which 235 g of H3PO4(aq) is formed. What Is Given? You are given the balanced chemical equation and the corresp ...
DO NOW - PBworks
... Answer the DO NOW in your INB. Sometime tectonic plates do not move easily past one another, and the plates become stuck. Forces build up, and when the plates finally move, tension is released, as shown below. The sudden movement of the plates is caused by – A. The mass of the plates B. The weight o ...
... Answer the DO NOW in your INB. Sometime tectonic plates do not move easily past one another, and the plates become stuck. Forces build up, and when the plates finally move, tension is released, as shown below. The sudden movement of the plates is caused by – A. The mass of the plates B. The weight o ...
Document
... 0.5 mL), catalystQNI was added (6.0 mg, 0.01 mmol, 10 mol%) in one load. The reaction mixture was stirred for 1 min and placed in freezer (20 °C) for 2 days without stirring. The reaction mixture was monitored by 19F NMR for conversion and diastereoselectivity, and loaded on to preparative TLC plate ...
... 0.5 mL), catalystQNI was added (6.0 mg, 0.01 mmol, 10 mol%) in one load. The reaction mixture was stirred for 1 min and placed in freezer (20 °C) for 2 days without stirring. The reaction mixture was monitored by 19F NMR for conversion and diastereoselectivity, and loaded on to preparative TLC plate ...
“No Score” from Exam 1??
... Connecting microscopic (atoms) to macroscopic (weight) using Important Connections • Avogadro!s number (NA): Connects molecules (or atoms) to moles • Molar Mass (in g/mol) connects mass to moles; connects experimentally measured property to moles (or molecules) of substance; the molar mass (in g/mo ...
... Connecting microscopic (atoms) to macroscopic (weight) using Important Connections • Avogadro!s number (NA): Connects molecules (or atoms) to moles • Molar Mass (in g/mol) connects mass to moles; connects experimentally measured property to moles (or molecules) of substance; the molar mass (in g/mo ...
Electro-Kinetics
... • The linear relationship between Levich current and the square root of the rotation rate is obvious from the Levich plot. A linear least squares fit of the data produces an equation for the best straight line passing through the data. The specific experiment shown, the electrode area, A, was 0.1963 ...
... • The linear relationship between Levich current and the square root of the rotation rate is obvious from the Levich plot. A linear least squares fit of the data produces an equation for the best straight line passing through the data. The specific experiment shown, the electrode area, A, was 0.1963 ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.