The Founding of the Republic
... commands, that had the force of law; however, one consul could override the other’s edict by stating, “veto,” which is Latin for “I forbid.” Thus the two consuls functioned as checks and balances on each other. The idea of the veto and the idea of checks and balances are two of the many Roman politi ...
... commands, that had the force of law; however, one consul could override the other’s edict by stating, “veto,” which is Latin for “I forbid.” Thus the two consuls functioned as checks and balances on each other. The idea of the veto and the idea of checks and balances are two of the many Roman politi ...
Glossary and Terms
... Century - A division of the Roman army made up of 80- 100 soldiers and led by a centurion. Circus - A large oval shaped stadium used for chariot races. Its other name is hippodrome. Citizen - A Roman citizen had certain rights and privileges including the right to vote. Only freeborn men were fully ...
... Century - A division of the Roman army made up of 80- 100 soldiers and led by a centurion. Circus - A large oval shaped stadium used for chariot races. Its other name is hippodrome. Citizen - A Roman citizen had certain rights and privileges including the right to vote. Only freeborn men were fully ...
to create the Roman Empire
... Severan Emperors: a new ruling family who attempted to halt the period of decline but were unable to hold onto power 235-284 A.D.: civil war broke out resulting in 22 emperors who ruled for short periods of time A series of plagues led to severe shortages in the labor force & military Decline in tra ...
... Severan Emperors: a new ruling family who attempted to halt the period of decline but were unable to hold onto power 235-284 A.D.: civil war broke out resulting in 22 emperors who ruled for short periods of time A series of plagues led to severe shortages in the labor force & military Decline in tra ...
Ancient Rome - ESM School District
... (not just Hebrews) Holy Bible = (Torah (old testament) + Teaching of Jesus (new testament) Follow the 10 commandments ...
... (not just Hebrews) Holy Bible = (Torah (old testament) + Teaching of Jesus (new testament) Follow the 10 commandments ...
The Roman Republic
... What did Horatius do to defend the Romans? What qualities does Horatius demonstrate in this passage? What is the moral of Livy’s account? What can we infer about Roman values based on this? ...
... What did Horatius do to defend the Romans? What qualities does Horatius demonstrate in this passage? What is the moral of Livy’s account? What can we infer about Roman values based on this? ...
the tragedy of julius caesar
... The Republic favored Pompey but his army was weaker and Caesar stormed the city unopposed. Once all political rivals were defeated, Caesar was named the Dictator of Rome. He hand picked members of the senate He decided, personally, which laws would be passed ...
... The Republic favored Pompey but his army was weaker and Caesar stormed the city unopposed. Once all political rivals were defeated, Caesar was named the Dictator of Rome. He hand picked members of the senate He decided, personally, which laws would be passed ...
Rome 6.1 - mrs
... He was a harsh tyrant and driven from power in 509 BC. The Romans declared they would never again be ruled by a king. They swore they would put to death anyone who plotted to make himself king. ...
... He was a harsh tyrant and driven from power in 509 BC. The Romans declared they would never again be ruled by a king. They swore they would put to death anyone who plotted to make himself king. ...
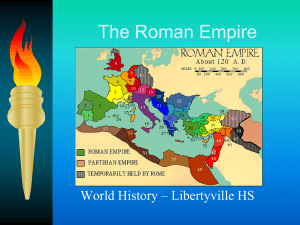
The Roman Empire
... Within 300 Years it had unified the whole Mediterranean into one empire. Intellectually, Rome was dominated by Greece, but its genius was in statecraft and law. Will go from Republic – to Empire – to 2 Empires – then will Fall @ 476 C.E. ...
... Within 300 Years it had unified the whole Mediterranean into one empire. Intellectually, Rome was dominated by Greece, but its genius was in statecraft and law. Will go from Republic – to Empire – to 2 Empires – then will Fall @ 476 C.E. ...
The Founding of Rome
... the Eastern Hemisphere. Later, the Roman armies used these same routes to conquer large amounts of territory and expand the empire along the Mediterranean. ...
... the Eastern Hemisphere. Later, the Roman armies used these same routes to conquer large amounts of territory and expand the empire along the Mediterranean. ...
1. Do reading #1 and answer the following questions: * Who were
... * How did the office of dictator contribute to the balance and stability of the Roman Republic? * What were the requirements for Roman citizenship? What "rights" did Roman citizens have? * How "democratic" was the government of the early Roman Republic? 2. What was the purpose of the Twelve Tables ...
... * How did the office of dictator contribute to the balance and stability of the Roman Republic? * What were the requirements for Roman citizenship? What "rights" did Roman citizens have? * How "democratic" was the government of the early Roman Republic? 2. What was the purpose of the Twelve Tables ...
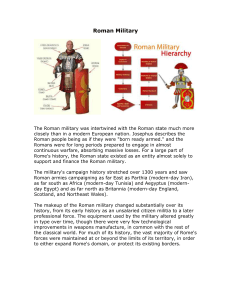
Roman Military - cloudfront.net
... history, from its early history as an unsalaried citizen militia to a later professional force. The equipment used by the military altered greatly in type over time, though there were very few technological improvements in weapons manufacture, in common with the rest of the classical world. For much ...
... history, from its early history as an unsalaried citizen militia to a later professional force. The equipment used by the military altered greatly in type over time, though there were very few technological improvements in weapons manufacture, in common with the rest of the classical world. For much ...
The Roman Empire
... In 44 B.C. Caesar was named dictator for life. He granted citizenship to many people in the provinces. He helped the poor by creating jobs through the construction of new public buildings. He increased pay for soldiers and started ...
... In 44 B.C. Caesar was named dictator for life. He granted citizenship to many people in the provinces. He helped the poor by creating jobs through the construction of new public buildings. He increased pay for soldiers and started ...
The Roman Empire
... control over the government • Senate still met, but had little real power (no legions) • Efficient bureaucracy, like the Han Chinese • Army socialized noncitizens to become loyal Roman citizens ...
... control over the government • Senate still met, but had little real power (no legions) • Efficient bureaucracy, like the Han Chinese • Army socialized noncitizens to become loyal Roman citizens ...
Untitled - StudyDaddy
... The Mediterranean Region Unit III examines two great military forces of the ancient Mediterranean world: Alexander the Great and the Roman Republic. In the Mediterranean region of this age, Rome commanded the armies, but Greece ruled the minds. This unit will also explore the cultural, political, an ...
... The Mediterranean Region Unit III examines two great military forces of the ancient Mediterranean world: Alexander the Great and the Roman Republic. In the Mediterranean region of this age, Rome commanded the armies, but Greece ruled the minds. This unit will also explore the cultural, political, an ...
ARCHITECTURE AND THE CITY. 2. COMMON
... Public spaces, as was argued in the previous article, are what make a city a city. They are the binding glue of the multiple interactions taking place in a city. It is a specific category of public spaces which makes visible the social and political bonds among the people inhabiting it: they turn pe ...
... Public spaces, as was argued in the previous article, are what make a city a city. They are the binding glue of the multiple interactions taking place in a city. It is a specific category of public spaces which makes visible the social and political bonds among the people inhabiting it: they turn pe ...
Augustus-Great Leader
... Augustus was a very good Roman leader. He knew how to control the Romans very well so he was very respected. He made people of higher power adjust to losing their power so, gradually took power away from the Senate. Augustus was very smart when it came to the military. He treated them with respect b ...
... Augustus was a very good Roman leader. He knew how to control the Romans very well so he was very respected. He made people of higher power adjust to losing their power so, gradually took power away from the Senate. Augustus was very smart when it came to the military. He treated them with respect b ...
File
... People of Italy • 2000 BCE – the Italic tribes settled in the central part of Italy • Latins were the most important of the Italic tribes. • Mainly good farmers who knew little about civilization. • Fights for the land between the Greeks, Etruscans and Latins ...
... People of Italy • 2000 BCE – the Italic tribes settled in the central part of Italy • Latins were the most important of the Italic tribes. • Mainly good farmers who knew little about civilization. • Fights for the land between the Greeks, Etruscans and Latins ...