The Colosseum_edited
... Colosseum due to its proximity to the statue. The emperor Nero caused quite a bit of trouble for the Roman population. A great fire of Rome destroyed the houses of many of the middle- and lower-class citizens of Rome. Instead of helping to rebuild their homes, however, Nero took over the land where ...
... Colosseum due to its proximity to the statue. The emperor Nero caused quite a bit of trouble for the Roman population. A great fire of Rome destroyed the houses of many of the middle- and lower-class citizens of Rome. Instead of helping to rebuild their homes, however, Nero took over the land where ...
The Romans
... countryman, would be most intensely aware--was the depopulation of rural Italy. • The farmers had been obliged to go to the war, and their farms fell into neglect and ruin as a result. • The Georgics, composed between 37 and 30 BC (the final period of the civil wars), is a superb plea for the restor ...
... countryman, would be most intensely aware--was the depopulation of rural Italy. • The farmers had been obliged to go to the war, and their farms fell into neglect and ruin as a result. • The Georgics, composed between 37 and 30 BC (the final period of the civil wars), is a superb plea for the restor ...
The Late Empire
... tetrarchy with himself as the Eastern ruler (Augustus of the East) and Maximian as ruler of the West. Each had a caesar, a vice-ruler, who was his heir. This political solution /attempt to retain order in the Roman Empire failed after Diocletian retired in 305. ...
... tetrarchy with himself as the Eastern ruler (Augustus of the East) and Maximian as ruler of the West. Each had a caesar, a vice-ruler, who was his heir. This political solution /attempt to retain order in the Roman Empire failed after Diocletian retired in 305. ...
35 Daily Life in the Roman Empire
... continued to meet, and senators had high status in society. They developed their own styles of clothing, which may have included special rings, pins, or togas (robes) trimmed with a wide purple stripe. Important senators hired personal bodyguards who carried fasces, bundles of sticks with an ax in t ...
... continued to meet, and senators had high status in society. They developed their own styles of clothing, which may have included special rings, pins, or togas (robes) trimmed with a wide purple stripe. Important senators hired personal bodyguards who carried fasces, bundles of sticks with an ax in t ...
133-27 BC - Mr. Hannigan
... actually inscribed on his coins. He was murdered by a conspiracy of some 60 odd senators a few weeks later. At this point the precedent of rule by one man had been established at Rome. The only question remained which of his supporters would most likely succeed him to this position. This turned out ...
... actually inscribed on his coins. He was murdered by a conspiracy of some 60 odd senators a few weeks later. At this point the precedent of rule by one man had been established at Rome. The only question remained which of his supporters would most likely succeed him to this position. This turned out ...
Unit 5 – Mediterranean Society: The Greek and Roman Phase
... From there on she would meet with her husband for almost entirely procreative reasons. Any Spartan man could abduct a wife, which led to a system of polyandry (many husbands, one wife or vice versa) in Sparta. Spartan women had many rights that other Greek women did not have. Namely, they could own ...
... From there on she would meet with her husband for almost entirely procreative reasons. Any Spartan man could abduct a wife, which led to a system of polyandry (many husbands, one wife or vice versa) in Sparta. Spartan women had many rights that other Greek women did not have. Namely, they could own ...
Global History and Geography II
... Etruscans, Republic, senate, consuls, tribunes, patricians, plebeians, Twelve Tables, Punic Wars, Hannibal Barca, dictator, Julius Caesar, Pompey, Marc Antony, Augustus/Octavian (to be covered on Thursday) 1. Describe the structure of the Roman Republic. How did the Latins’ experience with the Etrus ...
... Etruscans, Republic, senate, consuls, tribunes, patricians, plebeians, Twelve Tables, Punic Wars, Hannibal Barca, dictator, Julius Caesar, Pompey, Marc Antony, Augustus/Octavian (to be covered on Thursday) 1. Describe the structure of the Roman Republic. How did the Latins’ experience with the Etrus ...
The Roman Empire and Han China: A close comparison
... and soldiers They needed a continuing supply of slaves for their labor system Rome began to fade after 180 CE when expansion became impossible ...
... and soldiers They needed a continuing supply of slaves for their labor system Rome began to fade after 180 CE when expansion became impossible ...
Rome & Han China - Miami Beach Senior High School
... Dictators keep the peace during times of crisis Investors ...
... Dictators keep the peace during times of crisis Investors ...
Julius Caesar - SCHOOLinSITES
... • While religion was important to the Romans their worship services were often lacked emotion. • However, as the empire grew so did an new religion called Christianity. • Born as a movement within Judaism, it emphasized a more personal relationship with God. ...
... • While religion was important to the Romans their worship services were often lacked emotion. • However, as the empire grew so did an new religion called Christianity. • Born as a movement within Judaism, it emphasized a more personal relationship with God. ...
Roman Republic - Baylor School
... • Patricians were first recognized by the early kings and supposed to be descended from the original settlers of Rome. They were the upper class of Rome. ...
... • Patricians were first recognized by the early kings and supposed to be descended from the original settlers of Rome. They were the upper class of Rome. ...
Roman virtues - WordPress.com
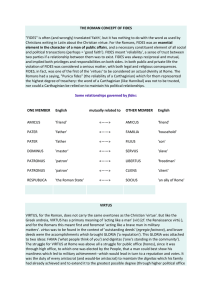
... THE ROMAN CONCEPT OF FIDES "FIDES" is often (and wrongly) translated 'faith', but it has nothing to do with the word as used by Christians writing in Latin about the Christian virtue. For the Romans, FIDES was an essential element in the character of a man of public affairs, and a necessary constitu ...
... THE ROMAN CONCEPT OF FIDES "FIDES" is often (and wrongly) translated 'faith', but it has nothing to do with the word as used by Christians writing in Latin about the Christian virtue. For the Romans, FIDES was an essential element in the character of a man of public affairs, and a necessary constitu ...
THE FALL OF ROME
... People began to barter for goods instead of using money. When Rome was at its weakest point, invaders swept into the empire. As fighting increased, the Roman government no longer had the ability to pay its soldiers so it began enlisting Germanic warriors to fight for them. All of this created a real ...
... People began to barter for goods instead of using money. When Rome was at its weakest point, invaders swept into the empire. As fighting increased, the Roman government no longer had the ability to pay its soldiers so it began enlisting Germanic warriors to fight for them. All of this created a real ...
Polybius and the Basis of Roman Imperialism The work of Polybius
... explicitly shows the Romans cleverly manipulating others into starting their wars. Like all historians ancient and modern, Polybius must have had his own synthetic interpretation, but comparison with other Greek authors reveals that attempts to find a key to his view of the Romans' ultimate intentio ...
... explicitly shows the Romans cleverly manipulating others into starting their wars. Like all historians ancient and modern, Polybius must have had his own synthetic interpretation, but comparison with other Greek authors reveals that attempts to find a key to his view of the Romans' ultimate intentio ...
Notes 20 The Roman
... − initially allied with Carthage in opposition to Greek interests − Roman kingdom or city-state established and growing in 600s-500s BCE − early on, an Etruscan quarter in Rome itself − prime location − on Tiber river, giving good sea access for trading − but inland, so safer from attack − centrally ...
... − initially allied with Carthage in opposition to Greek interests − Roman kingdom or city-state established and growing in 600s-500s BCE − early on, an Etruscan quarter in Rome itself − prime location − on Tiber river, giving good sea access for trading − but inland, so safer from attack − centrally ...
Gaul and Roman France
... proceeded more rapidly than the less complete romanization of the lower classes, who may have spoken a Latin language mixed with Gallic. The Gauls wore the Roman tunic instead of their traditional clothing. The Romano-Gauls generally lived in the vici, small villages similar to those in Italy, or in ...
... proceeded more rapidly than the less complete romanization of the lower classes, who may have spoken a Latin language mixed with Gallic. The Gauls wore the Roman tunic instead of their traditional clothing. The Romano-Gauls generally lived in the vici, small villages similar to those in Italy, or in ...
Chapter 6 Notes in format
... Around 600 B.C., Etruscan kings begin to rule Rome Kings build Rome’s first temples and public centers Romans overthrow cruel Etruscan king in 509 B.C. Romans found a republic—government in which citizens elect leaders Patricians and Plebeians Different groups struggle for power in early Roman Repub ...
... Around 600 B.C., Etruscan kings begin to rule Rome Kings build Rome’s first temples and public centers Romans overthrow cruel Etruscan king in 509 B.C. Romans found a republic—government in which citizens elect leaders Patricians and Plebeians Different groups struggle for power in early Roman Repub ...
Western Civilization
... • These barbarians were looking for good agricultural land on which to settle • Between the 2nd and 5th centuries grew large enough to challenge Rome • Initially, barbarians lived in small villages that made up clans that made up tribes ...
... • These barbarians were looking for good agricultural land on which to settle • Between the 2nd and 5th centuries grew large enough to challenge Rome • Initially, barbarians lived in small villages that made up clans that made up tribes ...
ROME
... and involved 70,000 slaves – they managed to defeat several armies before being caught and crucified • Family – Headed by the paterfamilias – the family father • Was the oldest living male and had extensive powers over his family – Extended family – included wife, sons with their wives and children, ...
... and involved 70,000 slaves – they managed to defeat several armies before being caught and crucified • Family – Headed by the paterfamilias – the family father • Was the oldest living male and had extensive powers over his family – Extended family – included wife, sons with their wives and children, ...
File
... Paterfamilias – oldest dominant male of the family Slavery by conquest, not race Manumission possible ...
... Paterfamilias – oldest dominant male of the family Slavery by conquest, not race Manumission possible ...
Viewing the Temple of Jupiter in Ancient Rome
... only the foundations remain today, and scholars have long debated the size of the structure, the massive scale of the foundations and the descriptions of the building given by ancient authors (Dion. Hal. Ant. Rom. 4.61.3-4) make it clear that the temple was one of the most obvious and recognizable l ...
... only the foundations remain today, and scholars have long debated the size of the structure, the massive scale of the foundations and the descriptions of the building given by ancient authors (Dion. Hal. Ant. Rom. 4.61.3-4) make it clear that the temple was one of the most obvious and recognizable l ...
Class Notes: Chapter 7, Lesson 2
... 2. This legend provides Rome with a noble, strong beginning. B. The Birth of a Republic 1. Between 600 and 509 B. C. , Rome was ruled by seven different kings. 2. In 509 B. C. , however, the people established a republic (government where citizens have the right to choose their leaders). (a) A repub ...
... 2. This legend provides Rome with a noble, strong beginning. B. The Birth of a Republic 1. Between 600 and 509 B. C. , Rome was ruled by seven different kings. 2. In 509 B. C. , however, the people established a republic (government where citizens have the right to choose their leaders). (a) A repub ...
ROMAN EXPANSION & THE PUNIC WARS
... • The Romans also set up permanent military settlements called COLONIAE to defend strategic locations. ...
... • The Romans also set up permanent military settlements called COLONIAE to defend strategic locations. ...
Education in ancient Rome

Education in Ancient Rome progressed from an informal, familial system of education in the early Republic to a tuition-based system during the late Republic and the Empire. The Roman education system was based on the Greek system – and many of the private tutors in the Roman system were Greek slaves or freedmen. Due to the extent of Rome's power, the methodology and curriculum used in Rome was copied in its provinces, and thereby proved the basis for education systems throughout later Western civilization. Organized education remained relatively rare, and there are few primary sources or accounts of the Roman educational process until the 2nd century AD. Due to the extensive power wielded by the paterfamilias over Roman families, the level and quality of education provided to Roman children varied drastically from family to family; nevertheless, Roman popular morality came eventually to expect fathers to have their children educated to some extent, and a complete advanced education was expected of any Roman who wished to enter politics.