Punic Wars
... sailors shocked the Carthaginians when they dropped gangways with sharp metal points on one end, called corvi, (crows or ravens) onto the decks of the Carthaginian ships. These bridges held the ships together while the Romans boarded the enemy vessels with their superior soldiers. ...
... sailors shocked the Carthaginians when they dropped gangways with sharp metal points on one end, called corvi, (crows or ravens) onto the decks of the Carthaginian ships. These bridges held the ships together while the Romans boarded the enemy vessels with their superior soldiers. ...
Soviets Brag: Moscow is the Third Rome, Seat of World Empire
... Filofei is then quoted: "All of Christianity will in the end be united into one realm under our rule." This is presented as the mission of "Holy Russia." It is emphasized that "Holy Russia is not an ethnic concept," confined to the domains of the Russians, but "a geographical concept," embracing "th ...
... Filofei is then quoted: "All of Christianity will in the end be united into one realm under our rule." This is presented as the mission of "Holy Russia." It is emphasized that "Holy Russia is not an ethnic concept," confined to the domains of the Russians, but "a geographical concept," embracing "th ...
Imperial Rome - British Museum
... continued to give advice about how the empire should be run but it was now under the control of the emperor. When Augustus died in AD 14, he passed the title of emperor on to his adopted son, Tiberius. Rome was ruled by emperors for the next 400 years. The Romans continued to expand the territory th ...
... continued to give advice about how the empire should be run but it was now under the control of the emperor. When Augustus died in AD 14, he passed the title of emperor on to his adopted son, Tiberius. Rome was ruled by emperors for the next 400 years. The Romans continued to expand the territory th ...
Week 5 in PowerPoint - campo7.com
... 5.3 Patrician landowners vs. small farmers • The patrician landowners, thanks to this leased public land and to the land they acquired reinvesting their profits, created huge estates mostly worked by the slaves (which also were made available in large numbers and at cheap prices by wars) • Little b ...
... 5.3 Patrician landowners vs. small farmers • The patrician landowners, thanks to this leased public land and to the land they acquired reinvesting their profits, created huge estates mostly worked by the slaves (which also were made available in large numbers and at cheap prices by wars) • Little b ...
Tuesday, Jan. 9
... 5.3 Patrician landowners vs. small farmers • The patrician landowners, thanks to this leased public land and to the land they acquired reinvesting their profits, created huge estates mostly worked by the slaves (which also were made available in large numbers and at cheap prices by wars) • Little b ...
... 5.3 Patrician landowners vs. small farmers • The patrician landowners, thanks to this leased public land and to the land they acquired reinvesting their profits, created huge estates mostly worked by the slaves (which also were made available in large numbers and at cheap prices by wars) • Little b ...
The Crisis of the Third Century and Christianity`s Emergence as the
... • The Roman Empire operated on an economy of plunder; it required plunder in order to generate wealth for the elite • Consequently the Romans continued to expand the Empire, despite the warning from Augustus • By the Late 2nd century the cost of maintaining the imperial borders had exceeded the Roma ...
... • The Roman Empire operated on an economy of plunder; it required plunder in order to generate wealth for the elite • Consequently the Romans continued to expand the Empire, despite the warning from Augustus • By the Late 2nd century the cost of maintaining the imperial borders had exceeded the Roma ...
Nubia - British Museum
... continued to give advice about how the empire should be run but it was now under the control of the emperor. When Augustus died in AD 14, he passed the title of emperor on to his adopted son, Tiberius. Rome was ruled by emperors for the next 400 years. The Romans continued to expand the territory th ...
... continued to give advice about how the empire should be run but it was now under the control of the emperor. When Augustus died in AD 14, he passed the title of emperor on to his adopted son, Tiberius. Rome was ruled by emperors for the next 400 years. The Romans continued to expand the territory th ...
Grade 12 Unit 4 - Amazon Web Services
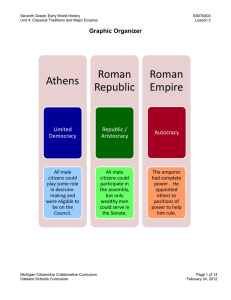
... Were the city-states always democracies? No, if we look back four more centuries we see that kings had ruled the city-states for centuries. They were concerned mostly with personal power and did little for the poor people who were barely surviving on what little they could farm from the land. Nobles ...
... Were the city-states always democracies? No, if we look back four more centuries we see that kings had ruled the city-states for centuries. They were concerned mostly with personal power and did little for the poor people who were barely surviving on what little they could farm from the land. Nobles ...
AP Practice #21 - White Plains Public Schools
... 2. C, because the excerpts show that the merchants discussed equal and fair exchange of their goods 3. C, because Mesopotamia was located in the Fertile Crescent and the documents show discussion among merchants 4. D, because it was achieved after the fall of the Roman Empire in the Byzantine Empire ...
... 2. C, because the excerpts show that the merchants discussed equal and fair exchange of their goods 3. C, because Mesopotamia was located in the Fertile Crescent and the documents show discussion among merchants 4. D, because it was achieved after the fall of the Roman Empire in the Byzantine Empire ...
Roman Empire
... Soon after that victory, Octavian became The assassination of Roman ruler Julius Caesar in 44 BCE led to civil war. Over the the sole ruler of Rome. He took the name Augustus Caesar and the title princeps next 13 years, the Roman world suffered first one . he oman ep lic was from an ongoing struggle ...
... Soon after that victory, Octavian became The assassination of Roman ruler Julius Caesar in 44 BCE led to civil war. Over the the sole ruler of Rome. He took the name Augustus Caesar and the title princeps next 13 years, the Roman world suffered first one . he oman ep lic was from an ongoing struggle ...
1. The Etruscans ruled Rome between 616 and 509 B.C.E. 2. The
... 2. In 451 B.C.E., patricians agreed to write down laws on the Twelve Tables. In 367 B.C.E., one of the two Roman consuls was required to be a plebeian. In 287 B.C.E., plebeian assemblies could pass laws for all Roman citizens and could nominate consuls, tribunes, and members of the Senate. 3. Othe ...
... 2. In 451 B.C.E., patricians agreed to write down laws on the Twelve Tables. In 367 B.C.E., one of the two Roman consuls was required to be a plebeian. In 287 B.C.E., plebeian assemblies could pass laws for all Roman citizens and could nominate consuls, tribunes, and members of the Senate. 3. Othe ...
Rome and Early Christianity Section 1
... system of laws to keep peace within their expanding empire. ...
... system of laws to keep peace within their expanding empire. ...
Chapter 5 An Age of Empires: Rome and Han China, 753 B.C.E.
... and tried hard to edit the Roman system of government, while still maintaining the Republic. He never claimed to be a king or emperor, but a princeps, “the first among equals”, in the restored Republic, which led to the name of this period being the Roman Principate. Augustus died in 14 C.E after 45 ...
... and tried hard to edit the Roman system of government, while still maintaining the Republic. He never claimed to be a king or emperor, but a princeps, “the first among equals”, in the restored Republic, which led to the name of this period being the Roman Principate. Augustus died in 14 C.E after 45 ...
EMPIRES OF INDIA AND CHINA
... Rome began as a small city-state in Italy. In 509 B.C., the Romans overthrew the Etruscan king who ruled their area. They set up a republic, a government in which the people choose the officials. At first, patricians, or members of the upper class, controlled the government. Eventually, commoners, o ...
... Rome began as a small city-state in Italy. In 509 B.C., the Romans overthrew the Etruscan king who ruled their area. They set up a republic, a government in which the people choose the officials. At first, patricians, or members of the upper class, controlled the government. Eventually, commoners, o ...
Auxiliary Soldiers
... given a “diploma” – an inscribed bronze. It was also after this retirement and granting of citizenship that he was allowed to marry although there is evidence of informal arrangements, often with local women, prior to that point. It has been suggested that many Legionaries, who had to be citizens, w ...
... given a “diploma” – an inscribed bronze. It was also after this retirement and granting of citizenship that he was allowed to marry although there is evidence of informal arrangements, often with local women, prior to that point. It has been suggested that many Legionaries, who had to be citizens, w ...
6.7 Students analyze the geographic, political, economic, religious
... gaining legal protections against patrician power and access to high political offices. The Early Republic also witnessed the conquest of the Italian peninsula, whose fertile valleys and coastal plains produced bountiful harvests of wheat, wine, olive oil, and wool. Rome defeated its nearby neighbor ...
... gaining legal protections against patrician power and access to high political offices. The Early Republic also witnessed the conquest of the Italian peninsula, whose fertile valleys and coastal plains produced bountiful harvests of wheat, wine, olive oil, and wool. Rome defeated its nearby neighbor ...
GAIUS OCTAVIUS THURINUS
... Caesar. • In 27-31 b.c., Julius Caesar died making Augustus ______ at age ___. • He ruled for ___ years and nearly _________ the size of the empire. ...
... Caesar. • In 27-31 b.c., Julius Caesar died making Augustus ______ at age ___. • He ruled for ___ years and nearly _________ the size of the empire. ...
Chapter 33-The Rise of the Roman Republic Chapter 33
... 8. Rome was a republic but the ____ __________ held all of the power. 9. Explain how the government structure in Rome benefitted the patricians at the expense of the plebeians. 10. Explain what happened in the conflict of the orders. Which side finally backed down? 11. Explain the role of the tribun ...
... 8. Rome was a republic but the ____ __________ held all of the power. 9. Explain how the government structure in Rome benefitted the patricians at the expense of the plebeians. 10. Explain what happened in the conflict of the orders. Which side finally backed down? 11. Explain the role of the tribun ...
Byzantine: The Eastern Roman EmpireMARCH OF
... Originally Indo-European Slavic tribes also invaded the Balkans at this time, stripping away these western territories from the Eastern Roman Empire, even threatening Constantinople itself. Byzantium barely survived the main Slavic invasions, when a new Asiatic invasion by a tribe called the Avars t ...
... Originally Indo-European Slavic tribes also invaded the Balkans at this time, stripping away these western territories from the Eastern Roman Empire, even threatening Constantinople itself. Byzantium barely survived the main Slavic invasions, when a new Asiatic invasion by a tribe called the Avars t ...
Roman agriculture

Agriculture in ancient Rome was not only a necessity, but was idealized among the social elite as a way of life. Cicero considered farming the best of all Roman occupations. In his treatise On Duties, he declared that ""of all the occupations by which gain is secured, none is better than agriculture, none more profitable, none more delightful, none more becoming to a free man."" When one of his clients was derided in court for preferring a rural lifestyle, Cicero defended country life as ""the teacher of economy, of industry, and of justice"" (parsimonia, diligentia, iustitia). Cato, Columella, Varro and Palladius wrote handbooks on farming practice.The staple crop was spelt, and bread was the mainstay of every Roman table. In his treatise De agricultura (""On Farming"", 2nd century BC), Cato wrote that the best farm was a vineyard, followed by an irrigated garden, willow plantation, olive orchard, meadow, grain land, forest trees, vineyard trained on trees, and lastly acorn woodlands.Though Rome relied on resources from its many provinces acquired through conquest and warfare, wealthy Romans developed the land in Italy to produce a variety of crops. ""The people living in the city of Rome constituted a huge market for the purchase of food produced on Italian farms.""Land ownership was a dominant factor in distinguishing the aristocracy from the common person, and the more land a Roman owned, the more important he would be in the city. Soldiers were often rewarded with land from the commander they served. Though farms depended on slave labor, free men and citizens were hired at farms to oversee the slaves and ensure that the farms ran smoothly.