Document
... 1) Werner Arber: enzymes which cut DNA at specific sites called "restriction enzymes” because restrict host range for certain bacteriophage ...
... 1) Werner Arber: enzymes which cut DNA at specific sites called "restriction enzymes” because restrict host range for certain bacteriophage ...
DNA and Genes - Mecca Hosting Client Sites on rhode
... 7. Each set of three nitrogen basesthat .E ...
... 7. Each set of three nitrogen basesthat .E ...
Vocab table - Genetics and variation teacher
... The mutual exchange of pieces of chromosome where groups of genes can be swapped ...
... The mutual exchange of pieces of chromosome where groups of genes can be swapped ...
Genetics Syllabus
... Available Equipment and Materials, Storage Location: K’NEX education kits for DNA, Replication and Transcription in 813. DNA models in 813. Unit #2: Transmission Genetics Objectives: Know Mendelian Laws of inheritance. Understand dominant and recessive modes of inheritance. Diagram monohybrid and di ...
... Available Equipment and Materials, Storage Location: K’NEX education kits for DNA, Replication and Transcription in 813. DNA models in 813. Unit #2: Transmission Genetics Objectives: Know Mendelian Laws of inheritance. Understand dominant and recessive modes of inheritance. Diagram monohybrid and di ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... the main chromosome where it can transfer many genes at one time. 4. they do not require conjugation for gene transfer. ...
... the main chromosome where it can transfer many genes at one time. 4. they do not require conjugation for gene transfer. ...
Heredity
... genes in human DNA, determine the sequences of the 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up human DNA, store this information in databases, improve tools for data analysis, transfer related technologies to the private sector, and address the ethical, legal, and social issues (ELSI) that may arise ...
... genes in human DNA, determine the sequences of the 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up human DNA, store this information in databases, improve tools for data analysis, transfer related technologies to the private sector, and address the ethical, legal, and social issues (ELSI) that may arise ...
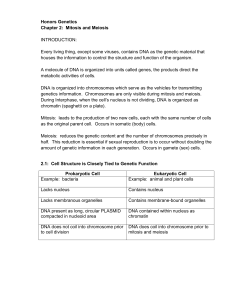
Honors Genetics Chapter 2: Mitosis and Meiosis INTRODUCTION
... Chapter 2: Mitosis and Meiosis INTRODUCTION: Every living thing, except some viruses, contains DNA as the genetic material that houses the information to control the structure and function of the organism. A molecule of DNA is organized into units called genes, the products direct the metabolic acti ...
... Chapter 2: Mitosis and Meiosis INTRODUCTION: Every living thing, except some viruses, contains DNA as the genetic material that houses the information to control the structure and function of the organism. A molecule of DNA is organized into units called genes, the products direct the metabolic acti ...
PRE-AP Stage 3 – Learning Plan
... ACCELERATE: PREAP – purines, pyrimidines, Chromosomal abnormalitites, gene mutations, cancer, enzymes GROUP: K’nex kits-building a DNA model, K’NEX kits-modeling DNA replication, transcription and translation ...
... ACCELERATE: PREAP – purines, pyrimidines, Chromosomal abnormalitites, gene mutations, cancer, enzymes GROUP: K’nex kits-building a DNA model, K’NEX kits-modeling DNA replication, transcription and translation ...
Analysis of immunoglobulin heavy chain V
... ) are introduced to maximize sequence fit. Signals for RNA-splicing are overlined. ...
... ) are introduced to maximize sequence fit. Signals for RNA-splicing are overlined. ...
BIO113H - willisworldbio
... A ________ marker is a gene that makes it possible to distinguish bacteria that carry the plasmid (and the foreign DNA) from those that don’t. These markers allows us to distinguish that plasmid from other cells that does not have the __________ DNA. After transformation the cells are treated with ...
... A ________ marker is a gene that makes it possible to distinguish bacteria that carry the plasmid (and the foreign DNA) from those that don’t. These markers allows us to distinguish that plasmid from other cells that does not have the __________ DNA. After transformation the cells are treated with ...
Lezione 25 - 26 mercoledì 11 maggio 2011
... simple to use, and flexible, but have the drawback of leaving recombination site sequences in the final construct, adding an extra 8 to 13 amino acids to the expressed protein. We have devised a simple and rapid subcloning strategy to transfer any DNA fragment of interest from an entry clone into an ...
... simple to use, and flexible, but have the drawback of leaving recombination site sequences in the final construct, adding an extra 8 to 13 amino acids to the expressed protein. We have devised a simple and rapid subcloning strategy to transfer any DNA fragment of interest from an entry clone into an ...
What Have We Learned From Unicellular Genomes?
... Japanese & European scientists have tried to identify the essential genes of B. subtilis. They have found that only 192 genes are indispensable to life. ...
... Japanese & European scientists have tried to identify the essential genes of B. subtilis. They have found that only 192 genes are indispensable to life. ...
Name Date Period BioTechnology: Web Quest Part 1
... Review both animations & the above questions. You need to have a good understanding of this process for the labs in this unit! Part 3 – DNA Fingerprinting (an application of biotechnology) Go to http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/sheppard/analyze.html In this section you will solve a “crime” by doing a “D ...
... Review both animations & the above questions. You need to have a good understanding of this process for the labs in this unit! Part 3 – DNA Fingerprinting (an application of biotechnology) Go to http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/sheppard/analyze.html In this section you will solve a “crime” by doing a “D ...
DNA 1: Today`s story, logic & goals
... Association of anxiety-related traits with a polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene regulatory region. Pubmed ...
... Association of anxiety-related traits with a polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene regulatory region. Pubmed ...
file
... • The set of all genes required for an organism is the organism’s GENOME. • Human genome has 3,000,000,000 bases divided into 23 linear segments (chromosomes). • A gene has on average 1340 DNA bases, thus specifying a protein of about 447 amino acids. • Humans have about 35,000 genes = 40,000,000 DN ...
... • The set of all genes required for an organism is the organism’s GENOME. • Human genome has 3,000,000,000 bases divided into 23 linear segments (chromosomes). • A gene has on average 1340 DNA bases, thus specifying a protein of about 447 amino acids. • Humans have about 35,000 genes = 40,000,000 DN ...
Genomics I - Faculty Web Pages
... The same forward and reverse primers PCRamplify different allele lengths for a microsatellite ...
... The same forward and reverse primers PCRamplify different allele lengths for a microsatellite ...
Genomics I
... The same forward and reverse primers PCRamplify different allele lengths for a microsatellite ...
... The same forward and reverse primers PCRamplify different allele lengths for a microsatellite ...
DNA & Heredity
... different traits can segregate independently during gamete formation – This help to account for the many genetic variations observed in plants and animals ...
... different traits can segregate independently during gamete formation – This help to account for the many genetic variations observed in plants and animals ...
... Human Genomics • The sequence of bases can be determined for individual genes and entire genomes • This genetic information can be used to find the function of different genes. • Entire genomes can be compared using single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). (These are differences between individuals ...
THE IMPORTANCE OF BIOTECHNOLOGY
... ◦ Resistance to Tomato yellow leaf curl virus (TYLCV-Is) Production of tomatoes for human consumption, either fresh or processed UW-Madison, Hebrew Univ., UWI ...
... ◦ Resistance to Tomato yellow leaf curl virus (TYLCV-Is) Production of tomatoes for human consumption, either fresh or processed UW-Madison, Hebrew Univ., UWI ...
12_Clicker_Questions
... b. Restriction enzymes cut up DNA taken from the environment and used as a nutrient source. c. Restriction enzymes remove the excess DNA that results from DNA replication. d. Restriction enzymes cut invading viral DNA sequences at specific sequences, disrupting the viral DNA genes. © 2010 Pearson Ed ...
... b. Restriction enzymes cut up DNA taken from the environment and used as a nutrient source. c. Restriction enzymes remove the excess DNA that results from DNA replication. d. Restriction enzymes cut invading viral DNA sequences at specific sequences, disrupting the viral DNA genes. © 2010 Pearson Ed ...
Chapter 16-17 review sheet
... 5. Explain why the ends of chromosomes get shorter with each replication. 6. Describe the role of telomeres in DNA. Why do we need these repeats on the ends of our chromosomes? Why must cancer activate its telomerase genes? In what other cell type(s) do we find telomerase? 7. Make sure you can trans ...
... 5. Explain why the ends of chromosomes get shorter with each replication. 6. Describe the role of telomeres in DNA. Why do we need these repeats on the ends of our chromosomes? Why must cancer activate its telomerase genes? In what other cell type(s) do we find telomerase? 7. Make sure you can trans ...
Genomic library

A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities. Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.