Practical Applications of DNA Technology
... B. Problem: Eukaryotic genes of interest may be too large to clone easily because they contain introns, which prevent correct expression of the gene by bacterial cells, which lack RNA-splicing machinery. Solution: Scientists can make artificial eukaryotic genes that lack introns Solution: Artificial ...
... B. Problem: Eukaryotic genes of interest may be too large to clone easily because they contain introns, which prevent correct expression of the gene by bacterial cells, which lack RNA-splicing machinery. Solution: Scientists can make artificial eukaryotic genes that lack introns Solution: Artificial ...
Genetic Variation
... Since all cells in our body contain DNA, there are lots of places for mutations to occur; however, not all mutations matter for evolution. Somatic mutations occur in non-reproductive cells and won't be passed onto offspring. For example, the golden color on half of this Red Delicious apple was cause ...
... Since all cells in our body contain DNA, there are lots of places for mutations to occur; however, not all mutations matter for evolution. Somatic mutations occur in non-reproductive cells and won't be passed onto offspring. For example, the golden color on half of this Red Delicious apple was cause ...
Name: Pd.: ____ Section 11.1 The Work of Gregor Mendel (p. 308
... 5. If T represents the allele for tall and t represents the allele for short and you cross a TT plant with a Tt plant: a. Which parent is homozygous dominant? _________________________________ b. Which parent is heterozygous? __________________________________________ c. What is (are) the genotype(s ...
... 5. If T represents the allele for tall and t represents the allele for short and you cross a TT plant with a Tt plant: a. Which parent is homozygous dominant? _________________________________ b. Which parent is heterozygous? __________________________________________ c. What is (are) the genotype(s ...
FREE Sample Here
... 16. In DNA replication, the leading strand is the strand that has which conformation? A) 5 to 3 B) 3 to 5 C) Both strands are leading 17. Which of the following is a purine? A) Thymine B) Cytosine C) Adenine D) Alanine 18. Which of the following does not play a role in DNA replication? A) RNA pr ...
... 16. In DNA replication, the leading strand is the strand that has which conformation? A) 5 to 3 B) 3 to 5 C) Both strands are leading 17. Which of the following is a purine? A) Thymine B) Cytosine C) Adenine D) Alanine 18. Which of the following does not play a role in DNA replication? A) RNA pr ...
Abstract Microbial source tracking (MST) is a powerful emerging
... that are “fingerprinted” by a variety of biochemical or molecular protocols. Fecal bacteria of unknown source (isolated from polluted waters) are compared against the library to look for fingerprint. To date this has been the most widely used approach. The second uses DNA sequences in fecal organism ...
... that are “fingerprinted” by a variety of biochemical or molecular protocols. Fecal bacteria of unknown source (isolated from polluted waters) are compared against the library to look for fingerprint. To date this has been the most widely used approach. The second uses DNA sequences in fecal organism ...
1 Forward and Reverse Genetics 1. Background What is the function
... or at non-essential amino acid positions. This method is good for fine-scale mutagenesis. b) homologous recombination - works in bacteria, yeast, mice and other mammals. It does not work well in Drosophila, although a complex experimental approach has been developed. This method has been used to kno ...
... or at non-essential amino acid positions. This method is good for fine-scale mutagenesis. b) homologous recombination - works in bacteria, yeast, mice and other mammals. It does not work well in Drosophila, although a complex experimental approach has been developed. This method has been used to kno ...
IntroducTon to Biological sequences
... – The sugar is ribose – U is used in place of T • A strand of RNA can be thought of as a string composed of the four leRers: A, C, G, U • RNA is single stranded – More flexible tha ...
... – The sugar is ribose – U is used in place of T • A strand of RNA can be thought of as a string composed of the four leRers: A, C, G, U • RNA is single stranded – More flexible tha ...
CAPT TEST in GENETICS, EVOLUTION and BIODIVERSITY
... CAPT TEST in GENETICS, EVOLUTION and BIODIVERSITY Name:__________________ GENETICS: 1. _____ What statement is most correct: A. all humans genes are located outside the nucleus of the cell. B. A human only has one gene for each trait C. Most organisms have two genes for each trait, one on each of th ...
... CAPT TEST in GENETICS, EVOLUTION and BIODIVERSITY Name:__________________ GENETICS: 1. _____ What statement is most correct: A. all humans genes are located outside the nucleus of the cell. B. A human only has one gene for each trait C. Most organisms have two genes for each trait, one on each of th ...
Materials and Methods S1 Construction of recombinant HSV
... the Red recombination system of bacteriophage inserted into its genome [2]. E. coli DY380 containing the respective BAC were transformed with linear recombination DNA fragments by electroporation and grown at 32C with the appropriate antibiotics for positive selection. At each mutagenesis step, c ...
... the Red recombination system of bacteriophage inserted into its genome [2]. E. coli DY380 containing the respective BAC were transformed with linear recombination DNA fragments by electroporation and grown at 32C with the appropriate antibiotics for positive selection. At each mutagenesis step, c ...
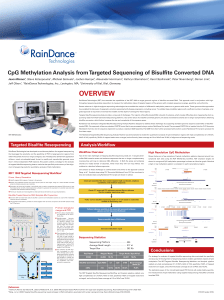
CpG methylation analysis from targeted
... RainDance Technologies (RDT) has extended the capabilities of the RDT 1000 to target genomic regions of bisulfite converted DNA. This approach used in conjunction with highthroughput sequencing enables researchers to measure the methylation status of targeted regions of the genome with complete sequ ...
... RainDance Technologies (RDT) has extended the capabilities of the RDT 1000 to target genomic regions of bisulfite converted DNA. This approach used in conjunction with highthroughput sequencing enables researchers to measure the methylation status of targeted regions of the genome with complete sequ ...
Evolution of DNA by celluLar automata HC Lee Department of
... – “Alien” DNA (continuously replenished) – All fragments have same fixed length ...
... – “Alien” DNA (continuously replenished) – All fragments have same fixed length ...
What do I have to know to feel confident and prepared for the DNA
... 11. How much DNA do you share with each of your parents? 100% of your DNA came from your parents. 50% from Mom and 50% from dad. 12. How much DNA do you share with your siblings? Since you have a 50:50 chance of the getting the same allele from dad as a sibling and you have a 50:50 chance of the get ...
... 11. How much DNA do you share with each of your parents? 100% of your DNA came from your parents. 50% from Mom and 50% from dad. 12. How much DNA do you share with your siblings? Since you have a 50:50 chance of the getting the same allele from dad as a sibling and you have a 50:50 chance of the get ...
Chromosome Number Mutations
... is still one present to code for vital life functions NOTE: one X must be present, without an X, life ceases ...
... is still one present to code for vital life functions NOTE: one X must be present, without an X, life ceases ...
4. Course administrator
... Fundamentals of genes, gene expression and regulation, and proteins What are biological databases? 1st Midterm EXAM Genome sequencing Protein bioinformatics Phylogeny/phylogenetics Gene expression analysis and microarray 2nd Midterm EXAM Practical bioinformatics-case examples Human genome project Hu ...
... Fundamentals of genes, gene expression and regulation, and proteins What are biological databases? 1st Midterm EXAM Genome sequencing Protein bioinformatics Phylogeny/phylogenetics Gene expression analysis and microarray 2nd Midterm EXAM Practical bioinformatics-case examples Human genome project Hu ...
Powerpoint Presentation: DNA Supercoiling
... Uncoiled the DNA of a human would stretch 2m The average diameter of a nucleus is 10µm The problem: To pack the DNA into the nucleus and yet have access to the genetic information. ...
... Uncoiled the DNA of a human would stretch 2m The average diameter of a nucleus is 10µm The problem: To pack the DNA into the nucleus and yet have access to the genetic information. ...
Genomic library

A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities. Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.