Reverse transcription-pcr (rt-pcr)
... Several techniques are available to detect and analyse RNA. Examples of these techniques are: Northern blots, Western blots, and RNase protection assay (RPA). Theses techniques are labour-intensive and requires large amount of fully intact RNA. ...
... Several techniques are available to detect and analyse RNA. Examples of these techniques are: Northern blots, Western blots, and RNase protection assay (RPA). Theses techniques are labour-intensive and requires large amount of fully intact RNA. ...
Gene targeting by hybridization-hydrolysis process
... A new technology used to specifically target any transcript from a complex population of single-strand cDNA molecules was applied to dramatically decrease the abundance of selected genes in cDNA libraries. This innovative procedure offers new alternatives to previous efforts focused on normalizing t ...
... A new technology used to specifically target any transcript from a complex population of single-strand cDNA molecules was applied to dramatically decrease the abundance of selected genes in cDNA libraries. This innovative procedure offers new alternatives to previous efforts focused on normalizing t ...
the list of 56 genes that the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics
... here as incidental findings, the analysis may not be technically equivalent to examining these genes as a primary finding. For example, clinical sequencing could have areas of diminished or absent coverage in the genes examined for incidental findings that would be filled in by Sanger sequencing or ...
... here as incidental findings, the analysis may not be technically equivalent to examining these genes as a primary finding. For example, clinical sequencing could have areas of diminished or absent coverage in the genes examined for incidental findings that would be filled in by Sanger sequencing or ...
Prokaryotes and Metabolic Diversity
... NOTE: Eukarya & Archaea are more closely related than either is to Bacteria See Fig. 27.12 ...
... NOTE: Eukarya & Archaea are more closely related than either is to Bacteria See Fig. 27.12 ...
CAIcal: A combined set of tools to assess codon usage adaptation
... were publicly available in databases, several statistical analyses addressing DNA composition have been performed. One of the parameters that first interested the scientist was codon usage [1]. It was soon discovered that a considerable heterogeneity in the codon usage exists between genes within sp ...
... were publicly available in databases, several statistical analyses addressing DNA composition have been performed. One of the parameters that first interested the scientist was codon usage [1]. It was soon discovered that a considerable heterogeneity in the codon usage exists between genes within sp ...
Concepts and relevance of genome
... is a sequence of more than three billion DNA bases that can be represented by one of four letters: A, C, G or T. Much of the genome sequence is identical or highly conserved across the human population, but every person’s genome is unique. A given person’s genome sequence is likely to differ from th ...
... is a sequence of more than three billion DNA bases that can be represented by one of four letters: A, C, G or T. Much of the genome sequence is identical or highly conserved across the human population, but every person’s genome is unique. A given person’s genome sequence is likely to differ from th ...
A Glossary of Molecular Biology Terms More can be found at http
... ATG or AUG: The codon for methionine; the translation initiation codon. Usually, protein translation can only start at a methionine codon (although this codon may be found elsewhere within the protein sequence as well). In eukaryotic DNA, the sequence is ATG; in RNA it is AUG. Usually, the first AUG ...
... ATG or AUG: The codon for methionine; the translation initiation codon. Usually, protein translation can only start at a methionine codon (although this codon may be found elsewhere within the protein sequence as well). In eukaryotic DNA, the sequence is ATG; in RNA it is AUG. Usually, the first AUG ...
Slides
... for a gene product, protein, or RNA §Genome - complete DNA base sequence of an organism §Replication - DNA synthesis involves complementary base pairing between the parental and newly synthesized strand ...
... for a gene product, protein, or RNA §Genome - complete DNA base sequence of an organism §Replication - DNA synthesis involves complementary base pairing between the parental and newly synthesized strand ...
Cloning a Gene for Over-expression and Purification
... ATG start codon present on the pET translation vectors.PflM A C-terminal His•Tag® sequence is availApaB isI(674) able. Unique sites are shown on the circle map. Note that the sequence numbered by the pBR322 convention, so the T7 expression region is reversed on the circular map. The cloning/expressi ...
... ATG start codon present on the pET translation vectors.PflM A C-terminal His•Tag® sequence is availApaB isI(674) able. Unique sites are shown on the circle map. Note that the sequence numbered by the pBR322 convention, so the T7 expression region is reversed on the circular map. The cloning/expressi ...
The search for small regulatory RNA
... Ambion Corp. http://www.ambion.com/techlib/resources/miRNA/mirna_pro.html ...
... Ambion Corp. http://www.ambion.com/techlib/resources/miRNA/mirna_pro.html ...
Bacterial Classification, Structure and Function
... living organisms that establishes a tripartite division of all living organisms– bacteria, archaea and eucarya. His work is based on a comparison of 16s ribosomal RNA sequences. These sequences are highly conserved and undergo change at a slow, gradual and consistent rate. They are therefore useful ...
... living organisms that establishes a tripartite division of all living organisms– bacteria, archaea and eucarya. His work is based on a comparison of 16s ribosomal RNA sequences. These sequences are highly conserved and undergo change at a slow, gradual and consistent rate. They are therefore useful ...
nuclear structure (2): the nucleolus
... polymerase molecules. (3) The “branches” are the nascent 45S rRNA molecules. (4) At various locations along each “branch” (each nascent 45S rRNA molecule) are black dots. These are places where proteins have bound. (5) The nascent RNA molecules do not appear to be as long as the DNA template on whic ...
... polymerase molecules. (3) The “branches” are the nascent 45S rRNA molecules. (4) At various locations along each “branch” (each nascent 45S rRNA molecule) are black dots. These are places where proteins have bound. (5) The nascent RNA molecules do not appear to be as long as the DNA template on whic ...
Bacteria, Sex, and Systematics - Center for Philosophy of Biology at
... between organisms. Researchers sequence the genomes of different organisms, and based on the sequences coding for protein and RNA molecules, create phylogenetic trees. They conjecture that gene transfers occurred whenever they find disagreement between phylogenies of different genes. Third, recent i ...
... between organisms. Researchers sequence the genomes of different organisms, and based on the sequences coding for protein and RNA molecules, create phylogenetic trees. They conjecture that gene transfers occurred whenever they find disagreement between phylogenies of different genes. Third, recent i ...
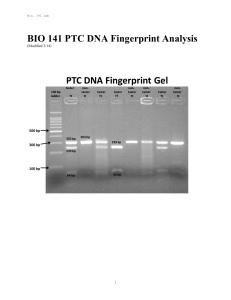
BIO 141 PTC DNA Fingerprint Analysis
... samples obtained at the crime scene, we can determine with a high degree of accuracy whether the suspect might be guilty of the crime. DNA fingerprinting is extremely useful in exonerating innocent people who are suspects in criminal cases. DNA’s structure resembles a twisted ladder called the doubl ...
... samples obtained at the crime scene, we can determine with a high degree of accuracy whether the suspect might be guilty of the crime. DNA fingerprinting is extremely useful in exonerating innocent people who are suspects in criminal cases. DNA’s structure resembles a twisted ladder called the doubl ...
Genomic Gene Clustering Analysis of Pathways
... on an average chromosome, and (3) the score should be normalized for genome and pathway size to allow comparative studies. To estimate the significance of the observed average clustering score of a pathway in a genome, it was compared to the distribution of 200 iterations of placing the same number ...
... on an average chromosome, and (3) the score should be normalized for genome and pathway size to allow comparative studies. To estimate the significance of the observed average clustering score of a pathway in a genome, it was compared to the distribution of 200 iterations of placing the same number ...
Supplementary Notes S1 (doc 64K)
... untouched. The resulting region is always centered on the original target (i.e. the same amount of flank is added to each side) 4. Probe extraction. Extracted probe sequences at 5 bp intervals from within each target region. Checked for ambiguous bases and counted the number of RepeatMasked bases. A ...
... untouched. The resulting region is always centered on the original target (i.e. the same amount of flank is added to each side) 4. Probe extraction. Extracted probe sequences at 5 bp intervals from within each target region. Checked for ambiguous bases and counted the number of RepeatMasked bases. A ...
Resources for the map-based cloning of tga1
... 96 deep well microtiter plates using a Retsch MM300 Mixer Mill. For a complete list of the marker loci, primer sequences, PCR conditions, gel conditions and restriction endonucleases for CAPS markers see Supplementary Information. Our mapping strategy involved first screening all 3106 F2 plants with ...
... 96 deep well microtiter plates using a Retsch MM300 Mixer Mill. For a complete list of the marker loci, primer sequences, PCR conditions, gel conditions and restriction endonucleases for CAPS markers see Supplementary Information. Our mapping strategy involved first screening all 3106 F2 plants with ...
HL7 V2.5.1 Genetic Test Result Message
... genomic and healthcare IT data standards may use this guide to extend these standards for support of clinical sequencing. Users of this guide must be familiar with the details of HL7 message construction and processing. This guide is not intended to be a tutorial on that subject. ...
... genomic and healthcare IT data standards may use this guide to extend these standards for support of clinical sequencing. Users of this guide must be familiar with the details of HL7 message construction and processing. This guide is not intended to be a tutorial on that subject. ...
Can ecology help genomics: the genome as ecosystem?
... phenotype could be due to genetic redundancy, but it could also be masked by the permissive environments in which most mutants are screened (Gilliland et al., 1998; Meagher et al., 2000). In addition to being an experimental science, ecology is also a highly mathematical discipline. While some cell ...
... phenotype could be due to genetic redundancy, but it could also be masked by the permissive environments in which most mutants are screened (Gilliland et al., 1998; Meagher et al., 2000). In addition to being an experimental science, ecology is also a highly mathematical discipline. While some cell ...
Definitions for annotating CDS sequences
... In the final clone, if a STOP codon is always present, regardless whether it derives from the target sequence or a nearby universal sequence (such as a cloning linker or the vector), this clone format is called “closed” (Examples C-E). Corollary: If your cloning strategy supplies a STOP codon in a 3 ...
... In the final clone, if a STOP codon is always present, regardless whether it derives from the target sequence or a nearby universal sequence (such as a cloning linker or the vector), this clone format is called “closed” (Examples C-E). Corollary: If your cloning strategy supplies a STOP codon in a 3 ...
- Wiley Online Library
... disequilibrium to specific patterns of DNA restriction site polymorphism, referred to as the -globin gene cluster or RFLP haplotypes. Analysis of these haplotypes in the -globin gene cluster has been useful in determining the chromosomal background of -thalassemia mutations in several human popul ...
... disequilibrium to specific patterns of DNA restriction site polymorphism, referred to as the -globin gene cluster or RFLP haplotypes. Analysis of these haplotypes in the -globin gene cluster has been useful in determining the chromosomal background of -thalassemia mutations in several human popul ...
File - Molecular Biology 2
... of genes, still, isolating any one gene is like searching for the proverbial needle in a haystack. Most techniques used in the analysis of genes and other DNA sequences require that the sequence be available in significant quantities in pure or essentially pure form. How can one identify the segment ...
... of genes, still, isolating any one gene is like searching for the proverbial needle in a haystack. Most techniques used in the analysis of genes and other DNA sequences require that the sequence be available in significant quantities in pure or essentially pure form. How can one identify the segment ...
Disease Genomics Part 2 - Medical Sciences Division
... • Excellent functional genomics resources – The comparison between a human phenotype and a mouse phenotype is often very readily interpretable. – Other useful organisms include the fly, the worm and even yeast • Useful as they have well-curated data for many genes ...
... • Excellent functional genomics resources – The comparison between a human phenotype and a mouse phenotype is often very readily interpretable. – Other useful organisms include the fly, the worm and even yeast • Useful as they have well-curated data for many genes ...
Growth hormone genotyping by MspI restriction enzyme and PCR
... and pulsatile manner, the pattern of which plays important role in postnatal longitudinal growth and development, tissue growth, lactation, reproduction, as well as protein, lipid and carbohydrate metabolism (Dybus et al. 2002). GH gene with its functional and positional potential has been widely us ...
... and pulsatile manner, the pattern of which plays important role in postnatal longitudinal growth and development, tissue growth, lactation, reproduction, as well as protein, lipid and carbohydrate metabolism (Dybus et al. 2002). GH gene with its functional and positional potential has been widely us ...
modeling, visualization, and discovery for cluster
... Obviously, VISDA’s projection suite framework is scalable and extensive to incorporate various existing clustering and visualization algorithms to increase the chance of revealing data structure of interest. When all the projections are made and shown to the user, the user will be asked to select on ...
... Obviously, VISDA’s projection suite framework is scalable and extensive to incorporate various existing clustering and visualization algorithms to increase the chance of revealing data structure of interest. When all the projections are made and shown to the user, the user will be asked to select on ...
Metagenomics

Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental samples. The broad field may also be referred to as environmental genomics, ecogenomics or community genomics. While traditional microbiology and microbial genome sequencing and genomics rely upon cultivated clonal cultures, early environmental gene sequencing cloned specific genes (often the 16S rRNA gene) to produce a profile of diversity in a natural sample. Such work revealed that the vast majority of microbial biodiversity had been missed by cultivation-based methods. Recent studies use either ""shotgun"" or PCR directed sequencing to get largely unbiased samples of all genes from all the members of the sampled communities. Because of its ability to reveal the previously hidden diversity of microscopic life, metagenomics offers a powerful lens for viewing the microbial world that has the potential to revolutionize understanding of the entire living world. As the price of DNA sequencing continues to fall, metagenomics now allows microbial ecology to be investigated at a much greater scale and detail than before.