The Modest Beginnings of One Genome Project
... gels. I felt that if I had a better understanding of yeast genetics, perhaps the project might have been more successful. Thus, upon entering the Halvorson laboratory I was convinced I needed to learn how to do yeast genetics properly. At that time Susan Henry was a first-year postdoc and was conside ...
... gels. I felt that if I had a better understanding of yeast genetics, perhaps the project might have been more successful. Thus, upon entering the Halvorson laboratory I was convinced I needed to learn how to do yeast genetics properly. At that time Susan Henry was a first-year postdoc and was conside ...
12.3 How Is Biotechnology Used In Forensic Science?
... The test tube is heated to 90°C, which breaks the _________ bonds between complementary bases, separating the DNA into single strands. The temperature is lowered to about 50°C to allow the primers to form complementary base pairs with the original DNA strands. The temperature is raised to 70–72°C so ...
... The test tube is heated to 90°C, which breaks the _________ bonds between complementary bases, separating the DNA into single strands. The temperature is lowered to about 50°C to allow the primers to form complementary base pairs with the original DNA strands. The temperature is raised to 70–72°C so ...
A Novel Activity for Fungal Nitronate Monooxygenase: Detoxification
... (P3N), the highly toxic conjugate base form of the plant metabolite 3-nitropropionate (3NPA) and provides compelling evidence that the physiological role of NMO is detoxification. Thus, the enzyme appears to play a similar role as propionate-3-nitronate oxidase from Penicillium atrovenetum (1) and m ...
... (P3N), the highly toxic conjugate base form of the plant metabolite 3-nitropropionate (3NPA) and provides compelling evidence that the physiological role of NMO is detoxification. Thus, the enzyme appears to play a similar role as propionate-3-nitronate oxidase from Penicillium atrovenetum (1) and m ...
A type III-like restriction endonuclease functions as a major barrier to
... reveals important differences in their respective target recognition domains (TRDs) (Fig. S1). Each TRD binds to part of the recognition sequence, and identical sequences indicate identical recognition sequences, whereas differences in the TRD indicate different target sequences. Based on our sequen ...
... reveals important differences in their respective target recognition domains (TRDs) (Fig. S1). Each TRD binds to part of the recognition sequence, and identical sequences indicate identical recognition sequences, whereas differences in the TRD indicate different target sequences. Based on our sequen ...
Gene - Representing Genes
... any heritable change in the nucleotide sequence of a chromosome, which may occur either by the substitution of one nucleotide for another or by the translocation or inversion of a chromosome segment. In classical genetics, however, mutation was necessarily defined as a change in the intrinsic nature ...
... any heritable change in the nucleotide sequence of a chromosome, which may occur either by the substitution of one nucleotide for another or by the translocation or inversion of a chromosome segment. In classical genetics, however, mutation was necessarily defined as a change in the intrinsic nature ...
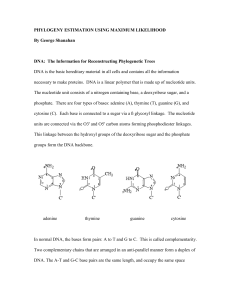
A protein-based phylogenetic tree for Gram
... terial groups that diverged at almost the same time; amino acid sequence homologies, for other proteins that are not so highly conserved, and gene-fusion events may be more appropriate methods (Ahmad & Jensen, 1989; Jensen & Ahmad, 1990). Furthermore, a study based on a very small number of genes co ...
... terial groups that diverged at almost the same time; amino acid sequence homologies, for other proteins that are not so highly conserved, and gene-fusion events may be more appropriate methods (Ahmad & Jensen, 1989; Jensen & Ahmad, 1990). Furthermore, a study based on a very small number of genes co ...
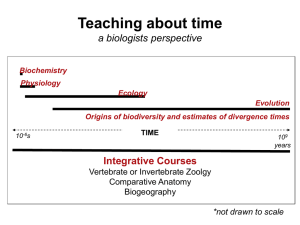
Teaching deep time through macroevolution and
... “tree” based on the similarity of characters--this is done by hand. [cladograms are visual representations of calculated relationships] 2. Students create character matrix and extract DNA/ sequence the 28s rRNA gene. [scaled up repetition, base pair differences are empirically determined] 3. Student ...
... “tree” based on the similarity of characters--this is done by hand. [cladograms are visual representations of calculated relationships] 2. Students create character matrix and extract DNA/ sequence the 28s rRNA gene. [scaled up repetition, base pair differences are empirically determined] 3. Student ...
Characteristic Features of the Nucleotide Sequences of Yeast
... ORF's, however, only the one for MRP-L27was detected a significant degree of similarity to any MRP genes nor as a highly likely MRP-gene by running program Gene- to any other mitochondrial protein genes. Mark against the chromosome II sequence data in conIn addition to the known MRP genes, there wer ...
... ORF's, however, only the one for MRP-L27was detected a significant degree of similarity to any MRP genes nor as a highly likely MRP-gene by running program Gene- to any other mitochondrial protein genes. Mark against the chromosome II sequence data in conIn addition to the known MRP genes, there wer ...
What is Francisella? - Oregon State University
... Reported to be part of several countries biological warfare arsenal, including the United States • Aerosolization ...
... Reported to be part of several countries biological warfare arsenal, including the United States • Aerosolization ...
Patients - HAL
... The sequence variant c.618C>T (GCG>GTG ) changes the encoded amino acid (Ala196Val). It was found at the heterozygote state in two unrelated patients with recessive cone rod dystrophy (CRD) but not in 100 control chromosomes. One patient was a simplex case. He did not carry any other RRH sequence ch ...
... The sequence variant c.618C>T (GCG>GTG ) changes the encoded amino acid (Ala196Val). It was found at the heterozygote state in two unrelated patients with recessive cone rod dystrophy (CRD) but not in 100 control chromosomes. One patient was a simplex case. He did not carry any other RRH sequence ch ...
Repeat-induced point mutation and the population
... Repeat-induced point mutations (RIP) is a genome defense in fungi that hyper-mutates repetitive DNA and is suggested to limit the accumulation of transposable elements. The genome of Microbotryum violaceum has a high density of transposable elements compared to other fungi, but there is also evidenc ...
... Repeat-induced point mutations (RIP) is a genome defense in fungi that hyper-mutates repetitive DNA and is suggested to limit the accumulation of transposable elements. The genome of Microbotryum violaceum has a high density of transposable elements compared to other fungi, but there is also evidenc ...
Exam 2
... Lucilia cuprina, the sheep blowfly, lays its eggs in wounds and the wet fleece of sheep. The larvae hatch and burrow into the sheep’s skin, causing distress, reduced wool production and sometimes death. Particular chemicals were used in the past to control the L. cuprina but these became less effect ...
... Lucilia cuprina, the sheep blowfly, lays its eggs in wounds and the wet fleece of sheep. The larvae hatch and burrow into the sheep’s skin, causing distress, reduced wool production and sometimes death. Particular chemicals were used in the past to control the L. cuprina but these became less effect ...
Overview of Recombinant DNA Experiments Covered by
... The deliberate transfer of recombinant DNA, or DNA or RNA derived from recombinant DNA, into one or more human research participants are subject to the NIH Guidelines. This includes the transfer of DNA with defective viral vectors, such as retroviral, adenoviral and lentiviral vectors, along with th ...
... The deliberate transfer of recombinant DNA, or DNA or RNA derived from recombinant DNA, into one or more human research participants are subject to the NIH Guidelines. This includes the transfer of DNA with defective viral vectors, such as retroviral, adenoviral and lentiviral vectors, along with th ...
Unoshan_project
... their common ancestor. Its topology (form) and its length (sum of its branch lengths) characterize a phylogenetic tree. Each node of a tree is an estimation of the ancestor of the elements included in that node. Maximum Likelihood is a method for the inference of phylogeny. It evaluates a hypothesis ...
... their common ancestor. Its topology (form) and its length (sum of its branch lengths) characterize a phylogenetic tree. Each node of a tree is an estimation of the ancestor of the elements included in that node. Maximum Likelihood is a method for the inference of phylogeny. It evaluates a hypothesis ...
Potato Genome Sequencing Consortium: Final
... sequencing the genome much simpler. The genome sequencing process itself is quite simple nowadays, thanks to the recent development of ‘massively parallel’ next generation sequencing (NGS) methods which have revolutionised genome analysis. Basically potato DNA is isolated by a simple procedure used ...
... sequencing the genome much simpler. The genome sequencing process itself is quite simple nowadays, thanks to the recent development of ‘massively parallel’ next generation sequencing (NGS) methods which have revolutionised genome analysis. Basically potato DNA is isolated by a simple procedure used ...
Gene Gorging Mutagenesis for the Geobacteraceae
... I, of which one linear fragment is the mutant allele. 17. The multiple copies of this allele make it likely that it will replace the wild type allele on the chromosome; hence the name “gene gorging.” 18. Linearization of the mutant allele with I-Sce I forces a double crossover within the allele itse ...
... I, of which one linear fragment is the mutant allele. 17. The multiple copies of this allele make it likely that it will replace the wild type allele on the chromosome; hence the name “gene gorging.” 18. Linearization of the mutant allele with I-Sce I forces a double crossover within the allele itse ...
Human Genetics
... Recombination Rates Recombination (usually) occurs only between homologous chromosomes. Each pair of homologs undergoes at least one crossover during meiosis, but multiple crossovers can also occur. The probability that two loci recombine is an increasing function of the physical distance (number of ...
... Recombination Rates Recombination (usually) occurs only between homologous chromosomes. Each pair of homologs undergoes at least one crossover during meiosis, but multiple crossovers can also occur. The probability that two loci recombine is an increasing function of the physical distance (number of ...
12859_2006_1447_MOESM4_ESM
... comparisons of nucleotide and protein sequences available for a given gene. Additional features such as the tissue specificity, protein domains, GC ratio, and Gene Ontology are annotated computationally for each exon that is alternatively spliced. Out of 6,309 genes, SpliceInfo has identified 203,64 ...
... comparisons of nucleotide and protein sequences available for a given gene. Additional features such as the tissue specificity, protein domains, GC ratio, and Gene Ontology are annotated computationally for each exon that is alternatively spliced. Out of 6,309 genes, SpliceInfo has identified 203,64 ...
Butterfly gene flow goes berserk
... that the rare event of hybridization, that is, the production of viable offspring by the interbreeding of individuals from two such species, can facilitate adaptation through the process of genome ‘introgression’. Thus, a region of the genome that encodes a potentially advantageous phenotype, such a ...
... that the rare event of hybridization, that is, the production of viable offspring by the interbreeding of individuals from two such species, can facilitate adaptation through the process of genome ‘introgression’. Thus, a region of the genome that encodes a potentially advantageous phenotype, such a ...
Malignant Hyperthermia: Investigation for the Uninitiated
... identified and tracked through a proband’s pedigree. Once the disease gene is known, specific mutations are sought. Given that in the case of the main MH-related gene, a single base substitution in more than 15,000 nucleotides may be the target, this is an enormous task. Although it is possible to s ...
... identified and tracked through a proband’s pedigree. Once the disease gene is known, specific mutations are sought. Given that in the case of the main MH-related gene, a single base substitution in more than 15,000 nucleotides may be the target, this is an enormous task. Although it is possible to s ...
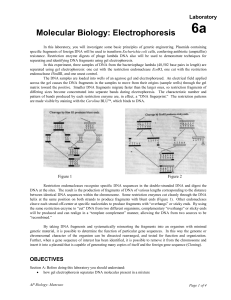
Lab 6: Electrophoresis
... helix at the same position on both strands to produce fragments with blunt ends (Figure 1). Other endonucleses cleave each strand off-center at specific nucleotides to produce fragments with “overhangs” or sticky ends. By using the same restriction enzyme to “cut” DNA from two different organisms, c ...
... helix at the same position on both strands to produce fragments with blunt ends (Figure 1). Other endonucleses cleave each strand off-center at specific nucleotides to produce fragments with “overhangs” or sticky ends. By using the same restriction enzyme to “cut” DNA from two different organisms, c ...
Nucleic Acid Biochemistry - American Society of Cytopathology
... • Other 4 types of histones along with DNA forms nucleosomes • Each nucleosome consists of 146 bp DNA and 8 histones (2 pairs of each) • DNA is wrapped around the histone core • These histones contain lysine residues which provide a positive charge—which interacts well with the negative charged D ...
... • Other 4 types of histones along with DNA forms nucleosomes • Each nucleosome consists of 146 bp DNA and 8 histones (2 pairs of each) • DNA is wrapped around the histone core • These histones contain lysine residues which provide a positive charge—which interacts well with the negative charged D ...
Comprehension Question
... accepted by scholars of that time? Include in your answer some evidence in favor of the idea, observations that seemed to support the idea, or other rationale for accepting the idea. Answer: Answers will vary but should include specific evidence or observations that support the idea. Examples: Pange ...
... accepted by scholars of that time? Include in your answer some evidence in favor of the idea, observations that seemed to support the idea, or other rationale for accepting the idea. Answer: Answers will vary but should include specific evidence or observations that support the idea. Examples: Pange ...
New Perspectives on Rickettsial Evolution from New
... distributions of VNTRs for all species were greatly skewed toward values less than the average genome compositions. This is somewhat surprising as typically 2/3 of the VNTR are located within coding sequences which are somewhat higher in G+C% than intergenic regions. However, factors contributing to ...
... distributions of VNTRs for all species were greatly skewed toward values less than the average genome compositions. This is somewhat surprising as typically 2/3 of the VNTR are located within coding sequences which are somewhat higher in G+C% than intergenic regions. However, factors contributing to ...