The Recombinant DNA Controversy: A Contemporary
... DNA technology is about cloning organisms: plants, animals, and even people. It isn't. It is about cloning genes, bits of DNA. Perhaps an analogy will make the difference more meaningful. An automobile is a rather complex machine assembled from many simple parts, some as simple as a screw. For each ...
... DNA technology is about cloning organisms: plants, animals, and even people. It isn't. It is about cloning genes, bits of DNA. Perhaps an analogy will make the difference more meaningful. An automobile is a rather complex machine assembled from many simple parts, some as simple as a screw. For each ...
DNA – The Molecule of Life
... It takes E. coli less than an hour to copy each of the 5 million base pairs in its single chromosome and divide to form two identical daughter cells. A human cell can copy its 6 billion base pairs and divide into daughter cells in only a few hours. This process is remarkably accurate, with only one ...
... It takes E. coli less than an hour to copy each of the 5 million base pairs in its single chromosome and divide to form two identical daughter cells. A human cell can copy its 6 billion base pairs and divide into daughter cells in only a few hours. This process is remarkably accurate, with only one ...
Whole Genome Sequencing Identifies a Novel Factor Required for
... Unbiased genetic approaches have a unique ability to identify novel genes associated with specific biological pathways. Thanks to next generation sequencing, forward genetic strategies can be expanded into a wider range of model organisms. The formation of secretory granules, called mucocysts, in th ...
... Unbiased genetic approaches have a unique ability to identify novel genes associated with specific biological pathways. Thanks to next generation sequencing, forward genetic strategies can be expanded into a wider range of model organisms. The formation of secretory granules, called mucocysts, in th ...
Deletions of ultraconserved elements have no obvious phenotype
... enhancers in a mouse transgenic assay and that are near genes that exhibit marked phenotypes both when completely inactivated in the mouse and when their expression is altered due to other genomic modifications. Remarkably, all four resulting lines of mice lacking these ultraconserved elements were ...
... enhancers in a mouse transgenic assay and that are near genes that exhibit marked phenotypes both when completely inactivated in the mouse and when their expression is altered due to other genomic modifications. Remarkably, all four resulting lines of mice lacking these ultraconserved elements were ...
Barley Cbf3 Gene Identification, Expression Pattern, and Map Location
... ortholog of Arabidopsis COR47, which encodes an acidic SK3 cold-induced dehydrin. The wheat orthologs of barley Dhn8 and Arabidopsis COR47 are the WCOR410 genes (Danyluk et al., 1994), which also encode acidic SK3 cold-induced proteins. Dhn4 encodes a YSK2 dehydrin that is ABA inducible, prevalent d ...
... ortholog of Arabidopsis COR47, which encodes an acidic SK3 cold-induced dehydrin. The wheat orthologs of barley Dhn8 and Arabidopsis COR47 are the WCOR410 genes (Danyluk et al., 1994), which also encode acidic SK3 cold-induced proteins. Dhn4 encodes a YSK2 dehydrin that is ABA inducible, prevalent d ...
Human Heredity - Lyndhurst School
... What makes us human? We might try to answer that question by looking under the microscope to see what is inside a human cell. Not surprisingly, human cells look much like the cells of other animals. To find what makes us uniquely human, we have to look deeper, into the genetic instructions that build ...
... What makes us human? We might try to answer that question by looking under the microscope to see what is inside a human cell. Not surprisingly, human cells look much like the cells of other animals. To find what makes us uniquely human, we have to look deeper, into the genetic instructions that build ...
Agrobacterium-mediated DNA transfer, and then some
... dreds of thousands of T-DNA insertion mutations in the genomes of model plant species, such as Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) and Oryza sativa (rice). These T-DNA insertion libraries, intended to saturate the genome with mutations, are important tools for forward and reverse genetic studies to u ...
... dreds of thousands of T-DNA insertion mutations in the genomes of model plant species, such as Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) and Oryza sativa (rice). These T-DNA insertion libraries, intended to saturate the genome with mutations, are important tools for forward and reverse genetic studies to u ...
Cis
... paper, there are 402 single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with intronic regions of human PAX7, which is found on chromosome one. Of these 75 are present in the intronic gene region of PAX7 associated with alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (ARMS) mainly found in the 3 prime regions of introns 5,6,7 and ...
... paper, there are 402 single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with intronic regions of human PAX7, which is found on chromosome one. Of these 75 are present in the intronic gene region of PAX7 associated with alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (ARMS) mainly found in the 3 prime regions of introns 5,6,7 and ...
Bitter-Tasting Ability
... There is a single mismatch at position 143, where the primer has a G and the gene has an A. This mismatch is crucial to the PCR experiment, because the A in the PTC sequence is replaced by a G in each of the amplified products. This creates the first G of the HaeIII recognition sequence GGCC (this i ...
... There is a single mismatch at position 143, where the primer has a G and the gene has an A. This mismatch is crucial to the PCR experiment, because the A in the PTC sequence is replaced by a G in each of the amplified products. This creates the first G of the HaeIII recognition sequence GGCC (this i ...
Sensitive and Sequence-Specific DNA Assays
... produced from this reduction deposits onto the sensor surface, resulting in a considerable change in the SPR signal. ...
... produced from this reduction deposits onto the sensor surface, resulting in a considerable change in the SPR signal. ...
DNA-dependent protein kinase in nonhomologous end joining: a
... division, it is of the utmost importance that cells have a mechanism to counteract DSBs. In addition, DSBs are generated in developing B and T cells during normal V(D)J recombination, implying that a working DSB repair system is not only necessary for an effective defense against DNA-modifying agent ...
... division, it is of the utmost importance that cells have a mechanism to counteract DSBs. In addition, DSBs are generated in developing B and T cells during normal V(D)J recombination, implying that a working DSB repair system is not only necessary for an effective defense against DNA-modifying agent ...
BMC Genomics
... composition than the core genome, and thus may highlight DNA segments of different origins. Genetic content of the SSRs in S. pyogenes M1 SF370 The cumulative TA-skew of strain SF370 contains five major SSRs (Fig. 1B). The nucleotide sequence of four of them corresponds to the four prophages (370.1, ...
... composition than the core genome, and thus may highlight DNA segments of different origins. Genetic content of the SSRs in S. pyogenes M1 SF370 The cumulative TA-skew of strain SF370 contains five major SSRs (Fig. 1B). The nucleotide sequence of four of them corresponds to the four prophages (370.1, ...
M-protein and other intrinsic virulence factors of Streptococcus
... composition than the core genome, and thus may highlight DNA segments of different origins. Genetic content of the SSRs in S. pyogenes M1 SF370 The cumulative TA-skew of strain SF370 contains five major SSRs (Fig. 1B). The nucleotide sequence of four of them corresponds to the four prophages (370.1, ...
... composition than the core genome, and thus may highlight DNA segments of different origins. Genetic content of the SSRs in S. pyogenes M1 SF370 The cumulative TA-skew of strain SF370 contains five major SSRs (Fig. 1B). The nucleotide sequence of four of them corresponds to the four prophages (370.1, ...
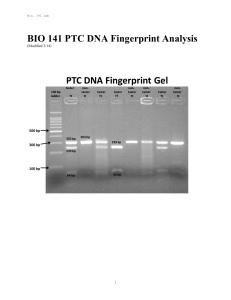
BIO 141 PTC DNA Fingerprint Analysis
... Knowing that you could have one or the other or both of the PTC alleles encoded in your DNA is interesting, but not nearly as interesting a being able to experimentally “see” the difference between both forms of the gene. One way to tell the difference between the PAV and AVI alleles is to take adva ...
... Knowing that you could have one or the other or both of the PTC alleles encoded in your DNA is interesting, but not nearly as interesting a being able to experimentally “see” the difference between both forms of the gene. One way to tell the difference between the PAV and AVI alleles is to take adva ...
- Murdoch Research Repository
... random 7.5 kb fragments of host DNA between B. hyodysenteriae cells (Matson et al., 2007). Analysis of VSH-1 in B. hyodysenteriae strain B204 has shown that it is located in a 16.3 kb region of the genome, and includes three “modules” or sets of operons of late function genes encoding the prophage c ...
... random 7.5 kb fragments of host DNA between B. hyodysenteriae cells (Matson et al., 2007). Analysis of VSH-1 in B. hyodysenteriae strain B204 has shown that it is located in a 16.3 kb region of the genome, and includes three “modules” or sets of operons of late function genes encoding the prophage c ...
Gene duplication and evolutionary novelty in
... recombination events, and through reverse-transcriptasemediated generation of cDNAs capable of genomic reintegration (retropositioning) (Hurles, 2004; Freeling et al., 2008). A considerable body of literature exists for each of these categories, but to our knowledge the relative rates of gene duplic ...
... recombination events, and through reverse-transcriptasemediated generation of cDNAs capable of genomic reintegration (retropositioning) (Hurles, 2004; Freeling et al., 2008). A considerable body of literature exists for each of these categories, but to our knowledge the relative rates of gene duplic ...
MEDICAL BIOLOGY AND GENERAL GENETICS
... – structural (membranes are components of all cell organelles except ribosomes and centrosomes); – barrier (protects the cell from external factors and sustains its composition); – metabolic (many enzymes are located on membranes); receptor (receives signals, recognizes substances). 4 Methods of pas ...
... – structural (membranes are components of all cell organelles except ribosomes and centrosomes); – barrier (protects the cell from external factors and sustains its composition); – metabolic (many enzymes are located on membranes); receptor (receives signals, recognizes substances). 4 Methods of pas ...
Origin, genetic diversity, and genome structure of the domestic dog
... The implication of these results for genetic studies of dogs is that despite intense selection for phenotypic uniformity within breeds, the genetic diversity within many dog breeds is similar to that in wild gray wolf populations. Consequently, breeds without a closely controlled history of inbreedi ...
... The implication of these results for genetic studies of dogs is that despite intense selection for phenotypic uniformity within breeds, the genetic diversity within many dog breeds is similar to that in wild gray wolf populations. Consequently, breeds without a closely controlled history of inbreedi ...
The sequence of a gene encoding convicilin from pea
... protein. This inserted sequence is very hydrophilic and has a high proportion of charged and acidic residues; it is of a similar amino acid composition to the sequences found near the C-terminal of the a-subunit in pea legumin genes, but is not directly homologous with them. Comparison of this seque ...
... protein. This inserted sequence is very hydrophilic and has a high proportion of charged and acidic residues; it is of a similar amino acid composition to the sequences found near the C-terminal of the a-subunit in pea legumin genes, but is not directly homologous with them. Comparison of this seque ...
bioinformatics
... distantly related organisms, the most commonly used features for comparative maps are protein coding genes, both because of their ubiquity and because of the ability of local alignment search tools to detect the relationship among highly diverged protein sequences. When multiple pairs of homologous ...
... distantly related organisms, the most commonly used features for comparative maps are protein coding genes, both because of their ubiquity and because of the ability of local alignment search tools to detect the relationship among highly diverged protein sequences. When multiple pairs of homologous ...