the element makes na RNA copy of itself which is reversed
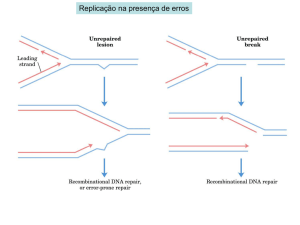
... Recombination at the Molecular Level • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on com ...
... Recombination at the Molecular Level • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on com ...
Student Notes
... is___________________, sequences that are present in multiple copies in the genome. ___________________________makeup much of the repetitive DNA. Stretches of DNA that moves from one location to another in the genome with the aid of an enzyme,____________________. ...
... is___________________, sequences that are present in multiple copies in the genome. ___________________________makeup much of the repetitive DNA. Stretches of DNA that moves from one location to another in the genome with the aid of an enzyme,____________________. ...
Cloning & Gene Therapy Notes
... disorder can detect some genes known to cause genetic disorders ...
... disorder can detect some genes known to cause genetic disorders ...
IntroBio520 - Nematode bioinformatics. Analysis tools and data
... science (derived from applied math, computer science, and statistics) to make the vast, diverse, and complex life sciences data more understandable and useful. It automates simple but repetitive types of analysis. ...
... science (derived from applied math, computer science, and statistics) to make the vast, diverse, and complex life sciences data more understandable and useful. It automates simple but repetitive types of analysis. ...
Human Genetics
... Gene expression refers to whether a gene is turned on or off from being transcribed and translated into protein Tracking gene expression can reveal new information about diseases and show how diseases are related to each other ...
... Gene expression refers to whether a gene is turned on or off from being transcribed and translated into protein Tracking gene expression can reveal new information about diseases and show how diseases are related to each other ...
to view and/or print October 2016 eDay assignment.
... Read Identical twins: same DNA, different environment and explain how two people with identical DNA can be different: ...
... Read Identical twins: same DNA, different environment and explain how two people with identical DNA can be different: ...
Nature Med. Germline Editing
... CRISPR-Cas9, transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs) and zinc finger nucleases (ZFNs) have all been used to genetically engineer human somatic cells and lab animals, including monkeys, but germline alterations in human germ cells and embryos have not—at the time of writing—been repo ...
... CRISPR-Cas9, transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs) and zinc finger nucleases (ZFNs) have all been used to genetically engineer human somatic cells and lab animals, including monkeys, but germline alterations in human germ cells and embryos have not—at the time of writing—been repo ...
Chapter 18 – 17 pts total - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... 10. Cancer cannot be inherited directly from your parents, but a predisposition can be inherited allowing cancer to “run in families”. Imagine that this topic comes up during a family reunion. Explain to aunt Sally how this works as she is certain that she has inherited the family “curse” of cancer ...
... 10. Cancer cannot be inherited directly from your parents, but a predisposition can be inherited allowing cancer to “run in families”. Imagine that this topic comes up during a family reunion. Explain to aunt Sally how this works as she is certain that she has inherited the family “curse” of cancer ...
Seeking an Increasingly Explicit Definition of Heredity
... Cracked genetic code- triplet mRNA codons specify each of the twenty amino acids. ...
... Cracked genetic code- triplet mRNA codons specify each of the twenty amino acids. ...
Answers to Gene technology exam 2011-10-18
... a) Competent cells: Cells treated to be permeable for uptake of DNA b) Transfection: Introduction of DNA into bacteria using non-viral metods also called transformation c) Phagemid: Combination of phage and plasmid containing F1 origin to be able to obtain SS-DNA d) Operons: Regulation sequence cont ...
... a) Competent cells: Cells treated to be permeable for uptake of DNA b) Transfection: Introduction of DNA into bacteria using non-viral metods also called transformation c) Phagemid: Combination of phage and plasmid containing F1 origin to be able to obtain SS-DNA d) Operons: Regulation sequence cont ...
Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... 5. Why did most scientists think the protein was the genetic material prior to the research of Griffith, Avery, and Hershey/Chase? 6. Understand Hershey and Chase’s experiment. 7. What information led to the discovery of the structure of the DNA molecule? 8. What are the three parts of a nucleotide? ...
... 5. Why did most scientists think the protein was the genetic material prior to the research of Griffith, Avery, and Hershey/Chase? 6. Understand Hershey and Chase’s experiment. 7. What information led to the discovery of the structure of the DNA molecule? 8. What are the three parts of a nucleotide? ...
Genetic Engineering II
... particular piece of DNA in the test tube (rather than in living cells like E. coli). • Very useful if only have small quantities such as blood or semen. • Use temperature changes to separate the DNA strand, add primers, polymerase and ta-dah... new strand is made. ...
... particular piece of DNA in the test tube (rather than in living cells like E. coli). • Very useful if only have small quantities such as blood or semen. • Use temperature changes to separate the DNA strand, add primers, polymerase and ta-dah... new strand is made. ...
Molecular Markers - Personal Web Pages
... May be part of or closely linked to a gene that makes a protein that affects cell survival May be part of controlling elements May be in the larger area of ‘non-coding’ DNA Markers have a known location What is being marked? ...
... May be part of or closely linked to a gene that makes a protein that affects cell survival May be part of controlling elements May be in the larger area of ‘non-coding’ DNA Markers have a known location What is being marked? ...
F4-6 Gene Regulation and Mutation Ch12,13
... a. Section of DNA that contains genes needed to produce particular proteins b. Operon responds to changes in environment 3. Parts of an operon a. Operator – segment of DNA that acts as on/off switch for transcription b. Promotor – section of DNA where RNA 1st binds c. Regulatory gene – makes repress ...
... a. Section of DNA that contains genes needed to produce particular proteins b. Operon responds to changes in environment 3. Parts of an operon a. Operator – segment of DNA that acts as on/off switch for transcription b. Promotor – section of DNA where RNA 1st binds c. Regulatory gene – makes repress ...
Alkaline Lysis Mini
... genomic level in higher eukaryotes. While significant progress has been made in understanding many of the molecular components of the recombination process in lower eukaryotes like the yeast S. cerevisiae, far less is known about similar functions in complex multi-cellular ...
... genomic level in higher eukaryotes. While significant progress has been made in understanding many of the molecular components of the recombination process in lower eukaryotes like the yeast S. cerevisiae, far less is known about similar functions in complex multi-cellular ...
What is Bioinformatics I?
... Phylogenetic analysis of molecular sequences with an emphasis on methods of phylogenetic inference and hypothesis testing. Gene and genome history, gene family evolution, inference of ancestral proteins, and phylogenetic analysis as a predictive tool. (3 weeks) ...
... Phylogenetic analysis of molecular sequences with an emphasis on methods of phylogenetic inference and hypothesis testing. Gene and genome history, gene family evolution, inference of ancestral proteins, and phylogenetic analysis as a predictive tool. (3 weeks) ...
E:Med - uni-freiburg.de
... Martin Vingron’s group • Sequence alignment • Microarray gene analysis • Gene regulation and evolution: – (combinatorial) TF DNA binding prediction – Histone modification gene expression – Factors affecting mutation rates ...
... Martin Vingron’s group • Sequence alignment • Microarray gene analysis • Gene regulation and evolution: – (combinatorial) TF DNA binding prediction – Histone modification gene expression – Factors affecting mutation rates ...
Prentice hall Biology Worksheets
... Short Answer On the lines provided, list the kinds of information that can be found by knowing the sequence of a DNA molecule. 4. __________________________________________________________________________________ 5. __________________________________________________________________________________ 6 ...
... Short Answer On the lines provided, list the kinds of information that can be found by knowing the sequence of a DNA molecule. 4. __________________________________________________________________________________ 5. __________________________________________________________________________________ 6 ...