shortridge
... 3. Determine the mechanism of gene expression in the nervous system. The power of this approach is that it allows a direct correlation of specific gene products to their in vivo function. ...
... 3. Determine the mechanism of gene expression in the nervous system. The power of this approach is that it allows a direct correlation of specific gene products to their in vivo function. ...
Eukaryotic Genome: Organization, Regulation, and Evolution
... Systems for coordinating gene regulation probably arose early in evolutionary history and evolved by the duplication and distribution of control elements within the genome. ...
... Systems for coordinating gene regulation probably arose early in evolutionary history and evolved by the duplication and distribution of control elements within the genome. ...
Molecular evolution
... • Neutral Theory was developed to explain the evolution of DNA and protein sequences. This theory focuses on three processes: mutation, purifying selection, and random genetic drift • Mutation is at the root of all nucleotide and amino acid substitution that occur during evolution. Without mutation, ...
... • Neutral Theory was developed to explain the evolution of DNA and protein sequences. This theory focuses on three processes: mutation, purifying selection, and random genetic drift • Mutation is at the root of all nucleotide and amino acid substitution that occur during evolution. Without mutation, ...
Human Genome Project
... •Unlike the human's seemingly random distribution of gene-rich areas, many other organisms' genomes are more uniform, with genes evenly spaced throughout. •Humans have on average three times as many kinds of proteins as the fly or worm because of mRNA transcript "alternative splicing" and chemical m ...
... •Unlike the human's seemingly random distribution of gene-rich areas, many other organisms' genomes are more uniform, with genes evenly spaced throughout. •Humans have on average three times as many kinds of proteins as the fly or worm because of mRNA transcript "alternative splicing" and chemical m ...
EOC Checklist
... Independent assortment means that one gene and the way it separates will not affect another gene and the ways it separates. Independent assortment will happen if the genes are located on ___________________ chromosomes. In dihybrid crosses, if two genes assort independently from each other, and ...
... Independent assortment means that one gene and the way it separates will not affect another gene and the ways it separates. Independent assortment will happen if the genes are located on ___________________ chromosomes. In dihybrid crosses, if two genes assort independently from each other, and ...
PPT - Department of Computer Science
... • Particle swarm optimization (PSO) is a population based stochastic optimization technique and it is inspired by social behavior of bird flocking or fish schooling. • PSO shares many similarities with evolutionary computation techniques such as Genetic Algorithms (GA). But it is simpler and faster ...
... • Particle swarm optimization (PSO) is a population based stochastic optimization technique and it is inspired by social behavior of bird flocking or fish schooling. • PSO shares many similarities with evolutionary computation techniques such as Genetic Algorithms (GA). But it is simpler and faster ...
Part 1 – Genetics 101
... depend on whether the pathological gene comes from the mother or the father. Ex. : Prader-Willi Syndrome or Angelman Syndrome Prader Willi Syndrome is caused by a microdeletion on the chromosome 15, that is inherited from the father (or more rarely when there are two copies of the gene from the moth ...
... depend on whether the pathological gene comes from the mother or the father. Ex. : Prader-Willi Syndrome or Angelman Syndrome Prader Willi Syndrome is caused by a microdeletion on the chromosome 15, that is inherited from the father (or more rarely when there are two copies of the gene from the moth ...
- SGTB Khalsa College
... Introduct variation, ion to molecular basis Genetics of genetic information ...
... Introduct variation, ion to molecular basis Genetics of genetic information ...
DNA Cornell notes
... strands of DNA are built from the template strand, using DNA polymerase (enzyme) to bring in the nucleotides. Nucleotides on the leading strands are brought to the template strand in a continuous fashion. Nucleotides on the lagging strand are brought in segments known as Okazaki fragments. The Okaza ...
... strands of DNA are built from the template strand, using DNA polymerase (enzyme) to bring in the nucleotides. Nucleotides on the leading strands are brought to the template strand in a continuous fashion. Nucleotides on the lagging strand are brought in segments known as Okazaki fragments. The Okaza ...
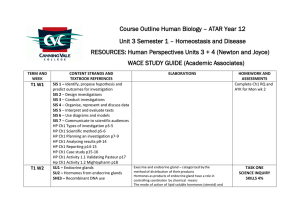
Course Outline Human Biology – ATAR Year 12 Unit 3 Semester 1
... SU17 – Transmission of pathogens HP Ch10 Pathogens p129-132 HP Ch10 Transmission of pathogens p132 ...
... SU17 – Transmission of pathogens HP Ch10 Pathogens p129-132 HP Ch10 Transmission of pathogens p132 ...
Townes-Brocks Syndrome - Humangenetik Freiburg
... De novo mutations in SALL1 mostly occur in about 87.5% on the paternally derived chromosome 16 without an obvious age effect [Bohm et al 2006]. If a SALL1 disease-causing mutation cannot be detected in the DNA extracted from the leukocytes of either parent, the two possible explanations are germline ...
... De novo mutations in SALL1 mostly occur in about 87.5% on the paternally derived chromosome 16 without an obvious age effect [Bohm et al 2006]. If a SALL1 disease-causing mutation cannot be detected in the DNA extracted from the leukocytes of either parent, the two possible explanations are germline ...
Keystone Review Packet
... o centrioles separate and take up positions on opposite sides of the nucleus focal point that helps organize spindle (fan-like microtubule structure that helps separate the chromosomes chromosomes attach to spindle at the centromere plants do not have centrioles ...
... o centrioles separate and take up positions on opposite sides of the nucleus focal point that helps organize spindle (fan-like microtubule structure that helps separate the chromosomes chromosomes attach to spindle at the centromere plants do not have centrioles ...
Biology Keystone Review Packet This packet contains information to
... o centrioles separate and take up positions on opposite sides of the nucleus focal point that helps organize spindle (fan-like microtubule structure that helps separate the chromosomes chromosomes attach to spindle at the centromere plants do not have centrioles ...
... o centrioles separate and take up positions on opposite sides of the nucleus focal point that helps organize spindle (fan-like microtubule structure that helps separate the chromosomes chromosomes attach to spindle at the centromere plants do not have centrioles ...
Influence of Mutation Type and Location on Phenotype
... Rett syndrome (RTT) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that almost exclusively affects girls. It is caused by mutations in the MECP2 gene that encodes the methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2). In this study we correlated mutation type and location with the severity of the phenotype in 123 girls with R ...
... Rett syndrome (RTT) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that almost exclusively affects girls. It is caused by mutations in the MECP2 gene that encodes the methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2). In this study we correlated mutation type and location with the severity of the phenotype in 123 girls with R ...
Biology
... 27. (1pt) The “guardian angel gene” codes for a protein that will destroy the cell that it is in, if it turns cancerous. If the mutation in the previous question occurs in p53, how many of the cells resulting from mitosis of this cell will carry the mutation? ...
... 27. (1pt) The “guardian angel gene” codes for a protein that will destroy the cell that it is in, if it turns cancerous. If the mutation in the previous question occurs in p53, how many of the cells resulting from mitosis of this cell will carry the mutation? ...
... the gene are on or off in that cell. Every gene has at least one enhancer. Unlike the genes themselves, whose coding regions are readily identified because of the genetic code’s fairly simple grammar, enhancers cannot be recognized solely on the basis of their DNA sequences and must be identified ex ...
Herbicide resistance in Hydrilla verticillata and Other Aquatic Plants
... Molecular genetic method to identify resistance conferring mutations: PCR and sequence the hydrilla pds gene region containing codon 304 Double-stranded DNA template ...
... Molecular genetic method to identify resistance conferring mutations: PCR and sequence the hydrilla pds gene region containing codon 304 Double-stranded DNA template ...
Ciliate Codon Translator Program Manual
... genes throughout history. This is most often done through finding the dN/dS ratio (that is, the ratio of changes in DNA that results in a new protein over the changes that produce no change in the protein). Results greater than 1 indicate that there is a positive selective pressure occurring on thes ...
... genes throughout history. This is most often done through finding the dN/dS ratio (that is, the ratio of changes in DNA that results in a new protein over the changes that produce no change in the protein). Results greater than 1 indicate that there is a positive selective pressure occurring on thes ...
Biology II, Genetics - Southwest Allen County Schools
... Southwest Allen County Schools Science Curriculum 2011-2017 Human Genetics UNIT 2 Desired Results What should students know and be able to do? (Include state standards and SACS expectations.) The student will understand the structure and function of DNA with applications regarding replication, gene ...
... Southwest Allen County Schools Science Curriculum 2011-2017 Human Genetics UNIT 2 Desired Results What should students know and be able to do? (Include state standards and SACS expectations.) The student will understand the structure and function of DNA with applications regarding replication, gene ...
Chromosome “theory” of inheritance
... I mentioned that the position of CFTR on that specific spot of chr. 7 is invariant between humans. It is the case, however, that – when one compares the genomes of two different human beings – one sees a difference, on average once every 1,000 bp (typically, a single base pair change, known as a SNP ...
... I mentioned that the position of CFTR on that specific spot of chr. 7 is invariant between humans. It is the case, however, that – when one compares the genomes of two different human beings – one sees a difference, on average once every 1,000 bp (typically, a single base pair change, known as a SNP ...
Chapter 11 Study Guide
... What chromosomes can human sperm and egg have? What chromosomes determine a female? Male? How many chromosomes does a normal human have? How many are autosomes? Sex chromosomes? What is the difference between a somatic mutation and a gamete mutation in terms of its offspring? What is the difference ...
... What chromosomes can human sperm and egg have? What chromosomes determine a female? Male? How many chromosomes does a normal human have? How many are autosomes? Sex chromosomes? What is the difference between a somatic mutation and a gamete mutation in terms of its offspring? What is the difference ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.