Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae
... suitable for genetic manipulation - first eukaryotic organism stabily transformed with exogenous nonreplicative DNA, by integration into the genome, via homologous recombination (Hinnen et al., 1978) ...
... suitable for genetic manipulation - first eukaryotic organism stabily transformed with exogenous nonreplicative DNA, by integration into the genome, via homologous recombination (Hinnen et al., 1978) ...
Chapter 13 Selective breeding is a technique of choosing specific
... polymerase (the enzyme that copies DNA) and the 4 nucleotide bases. Some of the bases have a chemical dye added to them. By reading the colored bases on the new copied strand, they can figure out the sequence on the original strand. To change it, short sequences of DNA made in the laboratory can be ...
... polymerase (the enzyme that copies DNA) and the 4 nucleotide bases. Some of the bases have a chemical dye added to them. By reading the colored bases on the new copied strand, they can figure out the sequence on the original strand. To change it, short sequences of DNA made in the laboratory can be ...
Draft data leave geneticists with a mountain still to climb
... from the 10X it originally promised in 1998, although the company says its sequence covers 99% of the genome. On the basis of the data presented publicly, it is impossible to verify whether Celera’s assembly is correctly orientated and ordered throughout the genome. But Celera has also produced a se ...
... from the 10X it originally promised in 1998, although the company says its sequence covers 99% of the genome. On the basis of the data presented publicly, it is impossible to verify whether Celera’s assembly is correctly orientated and ordered throughout the genome. But Celera has also produced a se ...
Is socialism against human nature?
... leadership, possessiveness, aggression, social and sexual inequality and an alleged drive to be territorial but, again, all these are behaviour patterns that reflect capitalism. The arrival of capitalism is a relatively recent phenomenon within human history, ninety per cent of which has been spent ...
... leadership, possessiveness, aggression, social and sexual inequality and an alleged drive to be territorial but, again, all these are behaviour patterns that reflect capitalism. The arrival of capitalism is a relatively recent phenomenon within human history, ninety per cent of which has been spent ...
Please pass last week`s warm up to the aisle. HW # 63: Read and
... Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes in total Here are some human chromosomes inside a cell, which have been made to fluoresce. ...
... Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes in total Here are some human chromosomes inside a cell, which have been made to fluoresce. ...
14.1_214-218
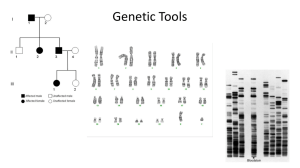
... Human Pedigrees A chart used to analyze the pattern of inheritance that shows the relationships in a family is a pedigree. Pedigrees can be used to determine the nature of genes and alleles associated with inherited human traits. ...
... Human Pedigrees A chart used to analyze the pattern of inheritance that shows the relationships in a family is a pedigree. Pedigrees can be used to determine the nature of genes and alleles associated with inherited human traits. ...
Human Genomics ppt
... Some RNAs (tRNA, rRNA, snRNA, mtRNA) don’t code for proteins that are translated. However, these are still referred to as genes-they are specific functional gene products. Other DNA sequences regulate the transcription of other genes and can act like genes in some ways. ...
... Some RNAs (tRNA, rRNA, snRNA, mtRNA) don’t code for proteins that are translated. However, these are still referred to as genes-they are specific functional gene products. Other DNA sequences regulate the transcription of other genes and can act like genes in some ways. ...
NONRANDOM GENE DISTRIBUTION ON HUMAN CHROMOSOMES
... * Corresponding author: Department of Biology, College of Sciences, Shiraz University, Shiraz 71454, Iran. E-mail addresses: [email protected] AND [email protected] ABSTRACT Human chromosomes are heterogeneous in structure and function. This is the reason for specific banding patterns produced by ...
... * Corresponding author: Department of Biology, College of Sciences, Shiraz University, Shiraz 71454, Iran. E-mail addresses: [email protected] AND [email protected] ABSTRACT Human chromosomes are heterogeneous in structure and function. This is the reason for specific banding patterns produced by ...
BIO 132: Genes and People
... Illustrating how changes to the DNA sequence may or may not change the proteins made and therefore affect the traits of the next generation i.e. initiation of disease In class group assignment Topic 10: Cytogenetics Week 11: discussion of how chromosome segregation impacts next generation Ex: Down s ...
... Illustrating how changes to the DNA sequence may or may not change the proteins made and therefore affect the traits of the next generation i.e. initiation of disease In class group assignment Topic 10: Cytogenetics Week 11: discussion of how chromosome segregation impacts next generation Ex: Down s ...
CST Review
... BI1. d. Students know the central dogma of molecular biology outlines the flow of information from transcription of ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the nucleus to translation of proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. BI2. a. Students know meiosis is an early step in sexual reproduction in which the pairs ...
... BI1. d. Students know the central dogma of molecular biology outlines the flow of information from transcription of ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the nucleus to translation of proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. BI2. a. Students know meiosis is an early step in sexual reproduction in which the pairs ...
CST Review
... BI1. d. Students know the central dogma of molecular biology outlines the flow of information from transcription of ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the nucleus to translation of proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. BI2. a. Students know meiosis is an early step in sexual reproduction in which the pairs ...
... BI1. d. Students know the central dogma of molecular biology outlines the flow of information from transcription of ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the nucleus to translation of proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. BI2. a. Students know meiosis is an early step in sexual reproduction in which the pairs ...
Chromosomes and Mutations Chromosomes and
... Each human has 23 sets (pairs) of chromosomes, or 46 total chromosomes ...
... Each human has 23 sets (pairs) of chromosomes, or 46 total chromosomes ...
Chapter 20 - BEHS Science
... Utilizes chromosome walking to identify the distance between. –Use a series of probes to identify the DNA sequence of various restriction fragments, and ultimately the entire length of DNA sample. ...
... Utilizes chromosome walking to identify the distance between. –Use a series of probes to identify the DNA sequence of various restriction fragments, and ultimately the entire length of DNA sample. ...
genes - Brookwood High School
... A. Principle of probability can be used to predict outcomes of genetic crosses. What is the probability that a tossed coin will come up heads? ...
... A. Principle of probability can be used to predict outcomes of genetic crosses. What is the probability that a tossed coin will come up heads? ...
Genetic Tools
... • Genes that are carried on the X chromosome are called Sex-linked genes. • Traits determined by sex-linked genes are called sexlinked traits. • Because of this, sex-linked traits are most often seen in males who only have one copy of the X ...
... • Genes that are carried on the X chromosome are called Sex-linked genes. • Traits determined by sex-linked genes are called sexlinked traits. • Because of this, sex-linked traits are most often seen in males who only have one copy of the X ...
Supplementary material for Part XY (Siepel lab analysis)
... These ARGs were then used to look at several statistics of interest, including: Pop assignment: For a given individual and genomic location, a population assignment of either “European”, “Asian”, “African”, or “unknown” was made. This was done by tracing the two lineages coming from an individual (o ...
... These ARGs were then used to look at several statistics of interest, including: Pop assignment: For a given individual and genomic location, a population assignment of either “European”, “Asian”, “African”, or “unknown” was made. This was done by tracing the two lineages coming from an individual (o ...
1) Lecture notes: mechanisms of gene activation
... Lecture, part 1, Feb 5, 2015 Overview: Gene Activation ...
... Lecture, part 1, Feb 5, 2015 Overview: Gene Activation ...
Transcription and Translation Exercise
... 7. The allele of the gene above is dominant and codes for red kernel pigment (it is designated as R). Another allele of this gene, the r allele (which is recessive), codes for white kernel pigment and is the result of a mutation in the R allele. In the r allele, the second nucleotide (base) in the s ...
... 7. The allele of the gene above is dominant and codes for red kernel pigment (it is designated as R). Another allele of this gene, the r allele (which is recessive), codes for white kernel pigment and is the result of a mutation in the R allele. In the r allele, the second nucleotide (base) in the s ...
Chapter 13 Genetic Engineering
... cells from a single cell. – Bacteria is easy to clone (unicellular) – What about multicellular organisms? – Ian Wilmut cloned the first sheep. DOLLY. ...
... cells from a single cell. – Bacteria is easy to clone (unicellular) – What about multicellular organisms? – Ian Wilmut cloned the first sheep. DOLLY. ...
genetics
... RNA transcriptase and therefore makes the gene unable to be expressed. Fragile X Syndrome is a disorder that appears to be a consequence of gene imprinting. Extracellular Genes Not all DNA is associated with chromosomes in the nucleus of Eukaryotic cells. The mitochondria and plastids in plant cells ...
... RNA transcriptase and therefore makes the gene unable to be expressed. Fragile X Syndrome is a disorder that appears to be a consequence of gene imprinting. Extracellular Genes Not all DNA is associated with chromosomes in the nucleus of Eukaryotic cells. The mitochondria and plastids in plant cells ...
Génmanipuláció
... Once the cells have performed their part of the procedure, the end result is a new piece of DNA inserted into the chromosome. The rest of the genome is unaltered but the single targeted locus has been replaced with the engineered construct and some of its flanking DNA . ...
... Once the cells have performed their part of the procedure, the end result is a new piece of DNA inserted into the chromosome. The rest of the genome is unaltered but the single targeted locus has been replaced with the engineered construct and some of its flanking DNA . ...
Cancer Genetics
... repression of transcription. Although there is little evidence so far that any of the human HDACs have specific gene-regulatory roles, it has been shown that HDAC4 and HDAC5, but not HDAC1 or HDAC3, can inhibit myogenesis by associating with MEF2 and repressing MYOD activity 41. Furthermore, studies ...
... repression of transcription. Although there is little evidence so far that any of the human HDACs have specific gene-regulatory roles, it has been shown that HDAC4 and HDAC5, but not HDAC1 or HDAC3, can inhibit myogenesis by associating with MEF2 and repressing MYOD activity 41. Furthermore, studies ...
document
... modENCODE 2010. An exhaustive effort was made to confirm and extend these inferences by experimental work, called the modENCODE project for Model Organism Encyclopedia of DNA Elements, following a similar study of 1% of the human genome. It was done for both D. melanogaster and C. elegans. An exhau ...
... modENCODE 2010. An exhaustive effort was made to confirm and extend these inferences by experimental work, called the modENCODE project for Model Organism Encyclopedia of DNA Elements, following a similar study of 1% of the human genome. It was done for both D. melanogaster and C. elegans. An exhau ...
Sunlight Water Entropy
... [18] Systematic microRNAome profiling reveals the roles of microRNAs in milk protein extremely well-ordered state of matter in more or less complicated organic compounds, which serve them asmetabolism and quality: insights on low-quality forage utilization foodstuffs. After utilizing it they return ...
... [18] Systematic microRNAome profiling reveals the roles of microRNAs in milk protein extremely well-ordered state of matter in more or less complicated organic compounds, which serve them asmetabolism and quality: insights on low-quality forage utilization foodstuffs. After utilizing it they return ...
Human genome

The human genome is the complete set of nucleic acid sequence for humans (Homo sapiens), encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA genes and noncoding DNA. Haploid human genomes, which are contained in germ cells (the egg and sperm gamete cells created in the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction before fertilization creates a zygote) consist of three billion DNA base pairs, while diploid genomes (found in somatic cells) have twice the DNA content. While there are significant differences among the genomes of human individuals (on the order of 0.1%), these are considerably smaller than the differences between humans and their closest living relatives, the chimpanzees (approximately 4%) and bonobos. Humans share 50% of their DNA with bananas.The Human Genome Project produced the first complete sequences of individual human genomes, with the first draft sequence and initial analysis being published on February 12, 2001. The human genome was the first of all vertebrates to be completely sequenced. As of 2012, thousands of human genomes have been completely sequenced, and many more have been mapped at lower levels of resolution. The resulting data are used worldwide in biomedical science, anthropology, forensics and other branches of science. There is a widely held expectation that genomic studies will lead to advances in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases, and to new insights in many fields of biology, including human evolution.Although the sequence of the human genome has been (almost) completely determined by DNA sequencing, it is not yet fully understood. Most (though probably not all) genes have been identified by a combination of high throughput experimental and bioinformatics approaches, yet much work still needs to be done to further elucidate the biological functions of their protein and RNA products. Recent results suggest that most of the vast quantities of noncoding DNA within the genome have associated biochemical activities, including regulation of gene expression, organization of chromosome architecture, and signals controlling epigenetic inheritance.There are an estimated 20,000-25,000 human protein-coding genes. The estimate of the number of human genes has been repeatedly revised down from initial predictions of 100,000 or more as genome sequence quality and gene finding methods have improved, and could continue to drop further. Protein-coding sequences account for only a very small fraction of the genome (approximately 1.5%), and the rest is associated with non-coding RNA molecules, regulatory DNA sequences, LINEs, SINEs, introns, and sequences for which as yet no function has been elucidated.