Study Guide Chapters 8-9 Nucleic Acids, and Molecular Engineering
... 10. What is the Tm of DNA due too, which base pairs is it dependent upon, and why? From ‘melting’ of DNA what enzyme did we realize had to exist? What ‘chaperone’ like protein needed also to exist? What makes RNA polymerase unique in this regard? 11. What are hybrid heteroduplexes? What can you do w ...
... 10. What is the Tm of DNA due too, which base pairs is it dependent upon, and why? From ‘melting’ of DNA what enzyme did we realize had to exist? What ‘chaperone’ like protein needed also to exist? What makes RNA polymerase unique in this regard? 11. What are hybrid heteroduplexes? What can you do w ...
amino acids
... interact with each other in solution • The cumulative effects of many hydrophobic interactions can have a significant effect on the stability of a macromolecule ...
... interact with each other in solution • The cumulative effects of many hydrophobic interactions can have a significant effect on the stability of a macromolecule ...
CARBOXYL GROUPS The δ- and ε-carboxyl
... The δ- and ε-carboxyl groups of aspartic and glutamic acids, respectively, are the principal anionic groups in proteins. They are acidic groups with pK values usually between pH 4.5 and 5.0. They can be esterified under relatively mild conditions by reaction with one of several diazoacetate derivati ...
... The δ- and ε-carboxyl groups of aspartic and glutamic acids, respectively, are the principal anionic groups in proteins. They are acidic groups with pK values usually between pH 4.5 and 5.0. They can be esterified under relatively mild conditions by reaction with one of several diazoacetate derivati ...
#24926 HAAO A Antibod
... d by its ability to activa ate glutamate N-methyl-D-asspartate recceptors. Inccreased cerebral levelss of QUIN may partic cipate in th he ammatory dissorders. HAA AO has been n suggested to play a role in disorde ers pathogenesis of neurological and infla w altered tissue levelss of QUIN. Furthermor ...
... d by its ability to activa ate glutamate N-methyl-D-asspartate recceptors. Inccreased cerebral levelss of QUIN may partic cipate in th he ammatory dissorders. HAA AO has been n suggested to play a role in disorde ers pathogenesis of neurological and infla w altered tissue levelss of QUIN. Furthermor ...
Important advances in next generation genome editing
... One of these tricks they can do is to serve as a sort of stop sign for the cell. When the machinery that normally reads DNA arrives at the mutant HD gene, appropriately designed genome editing tools can call them off - telling them not to do their work at that precise gene. This results in no mutant ...
... One of these tricks they can do is to serve as a sort of stop sign for the cell. When the machinery that normally reads DNA arrives at the mutant HD gene, appropriately designed genome editing tools can call them off - telling them not to do their work at that precise gene. This results in no mutant ...
CELB30090 Advanced Cell Biology Prof. Jeremy C
... nervous system applied a silver nitrate‐based stain for several days to cerebellum nerve cells and saw darkly staining reticular network near the cell nucleus (Nobel Prize in 1906) characteristic morphology ‐ flattened, disk‐like membranous cisternae with dilated rims and associated vesicles & tub ...
... nervous system applied a silver nitrate‐based stain for several days to cerebellum nerve cells and saw darkly staining reticular network near the cell nucleus (Nobel Prize in 1906) characteristic morphology ‐ flattened, disk‐like membranous cisternae with dilated rims and associated vesicles & tub ...
EF-Tu PROTEIN DOMAINS
... Institute of Molecular Genetics AS CR, where I did my PhD studies, was the study of the primary structure, transcription regulation and functions of bacterial elongation factors Tu from Gram positive thermophilic bacterium Bacillus stearothermophilus and from Gram ...
... Institute of Molecular Genetics AS CR, where I did my PhD studies, was the study of the primary structure, transcription regulation and functions of bacterial elongation factors Tu from Gram positive thermophilic bacterium Bacillus stearothermophilus and from Gram ...
Cells - Part 2 Nucleus
... • DNA Replication (Ch. 21, pp. 434 - 436)! • Protein Synthesis (Ch. 21, pp 436 - 441) ! ...
... • DNA Replication (Ch. 21, pp. 434 - 436)! • Protein Synthesis (Ch. 21, pp 436 - 441) ! ...
Chapter 5: Structure and function of macromolecules
... In addition to primary structure, protein conformation is also dependent on protein's environment (e.g. changes in temp, pH, of salt concentration can lead to protein denaturation ( unfolding of protein with resultant loss of function) (Fig 5.23) We still can not fully predict the 3-D conformation b ...
... In addition to primary structure, protein conformation is also dependent on protein's environment (e.g. changes in temp, pH, of salt concentration can lead to protein denaturation ( unfolding of protein with resultant loss of function) (Fig 5.23) We still can not fully predict the 3-D conformation b ...
lecture3
... inhibition pattern and the inhibitor does not bear any obvious structural relationship to the substrate. The enzyme exhibits extreme specificity with regard to the regulator molecule. (5) Allosteric enzymes have an oligomeric organization. They are composed of more than one polypeptide chain and hav ...
... inhibition pattern and the inhibitor does not bear any obvious structural relationship to the substrate. The enzyme exhibits extreme specificity with regard to the regulator molecule. (5) Allosteric enzymes have an oligomeric organization. They are composed of more than one polypeptide chain and hav ...
UNIT 3 Biochem Test Study Guide
... ●Chapter 6 in the book, especially page 167 (take a book home if needed) & 924-928 ●all your notes from Unit 3 Concepts Listed Below: What does organic mean? Indicators used in the lab (Identifying Organic Compound) and what each identifies How to make models of molecules, how to draw them and how t ...
... ●Chapter 6 in the book, especially page 167 (take a book home if needed) & 924-928 ●all your notes from Unit 3 Concepts Listed Below: What does organic mean? Indicators used in the lab (Identifying Organic Compound) and what each identifies How to make models of molecules, how to draw them and how t ...
Genetically engineered single-chain antibody fusion proteins
... Detection of rabies antigen in brain impressions Like the d-FAT, Recombinant Colorimetric Immunohistochemical test was performed on brain touch impressions to detect rabies virus antigen but the product of the reaction can be observed by light microscopy Mouse brain impressions with RV infectio ...
... Detection of rabies antigen in brain impressions Like the d-FAT, Recombinant Colorimetric Immunohistochemical test was performed on brain touch impressions to detect rabies virus antigen but the product of the reaction can be observed by light microscopy Mouse brain impressions with RV infectio ...
Ex2 answers
... The positive pole. RNA is negatively charged so it will be attracted to the positive pole. RNA is negative because it is made of nucleotides, and part of every nucleotide is a phosphate group, and phosphate groups are very negative. (b, 5 pts) Towards which pole of the gel will the Hrt1 protein run? ...
... The positive pole. RNA is negatively charged so it will be attracted to the positive pole. RNA is negative because it is made of nucleotides, and part of every nucleotide is a phosphate group, and phosphate groups are very negative. (b, 5 pts) Towards which pole of the gel will the Hrt1 protein run? ...
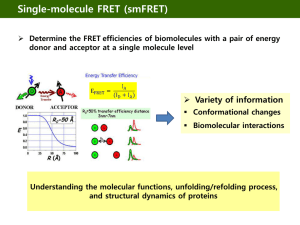
Single molecule analysis - Biomolecular Engineering Laboratory
... Composed of a core domain plus ATP and AMP lids ...
... Composed of a core domain plus ATP and AMP lids ...
"non-natural" amino acids - RIKEN Systems and Structural Biology
... one such technology. RIKEN Systems and Structural Biology Center (SSBC) conducts research in expanding the genetic code, the set of rules that translate information encoded in DNA into proteins, to incorporate non-natural amino acids into proteins site-specifically. This technology can provide powerf ...
... one such technology. RIKEN Systems and Structural Biology Center (SSBC) conducts research in expanding the genetic code, the set of rules that translate information encoded in DNA into proteins, to incorporate non-natural amino acids into proteins site-specifically. This technology can provide powerf ...
Quiz 3 Practice - philipdarrenjones.com
... Last part of Ch. 21 (DNA and Biotechnology) Most of Ch. 4 (Body Organization, Homeostasis, and the Integumentary System) First part of Ch. 5 (The Skeletal System) ...
... Last part of Ch. 21 (DNA and Biotechnology) Most of Ch. 4 (Body Organization, Homeostasis, and the Integumentary System) First part of Ch. 5 (The Skeletal System) ...
molecular biology and phylogeny
... PROCEDURES: You have already done and discussed the activity entitled "Making Cladograms". The final cladogram produced in that activity (using anatomical similarities) is shown below. The provided chart shows the amino acid sequence in a protein that is homologous (same) for the 20 organisms shown, ...
... PROCEDURES: You have already done and discussed the activity entitled "Making Cladograms". The final cladogram produced in that activity (using anatomical similarities) is shown below. The provided chart shows the amino acid sequence in a protein that is homologous (same) for the 20 organisms shown, ...
structure-tertiary-text
... structure then form domains, which fold independently of the rest of the protein; ...
... structure then form domains, which fold independently of the rest of the protein; ...
Forever Lite® Meal Replacement – Chocolate, Vanilla
... nutritious kick of vitamins, minerals, proteins and carbohydrates. Rich in proteins for bodybuilding, growth and repair, two shakes a day provide most of the Daily Value of vitamins and minerals. Each shake contains many amino acids (including all 8 essential ones). To protect against free radicals, ...
... nutritious kick of vitamins, minerals, proteins and carbohydrates. Rich in proteins for bodybuilding, growth and repair, two shakes a day provide most of the Daily Value of vitamins and minerals. Each shake contains many amino acids (including all 8 essential ones). To protect against free radicals, ...
1D17 – BMI201 Page 1 of 3 Code Questions Answers 1 Discuss the
... configuration onlyl around C2. Similarly galactose is 4-epimer of glucose because these two have different configuration only around C4 Proteins are characterized by their size and shape, amino acid composition and sequence, isoelectric point, hydrophobicity, and biological affinity. Differences in ...
... configuration onlyl around C2. Similarly galactose is 4-epimer of glucose because these two have different configuration only around C4 Proteins are characterized by their size and shape, amino acid composition and sequence, isoelectric point, hydrophobicity, and biological affinity. Differences in ...
Overview ...........................................................
... assemble a 2-D protein from individual amino acids using models. Finally, participants will fold their 2-D protein into a specific 3-D shape that, if they are successful, will fit a receptor, just like a lock and key. They learn about the huge numbers of configurations possible of proteins and their ...
... assemble a 2-D protein from individual amino acids using models. Finally, participants will fold their 2-D protein into a specific 3-D shape that, if they are successful, will fit a receptor, just like a lock and key. They learn about the huge numbers of configurations possible of proteins and their ...
Two-hybrid screening
Two-hybrid screening (also known as yeast two-hybrid system or Y2H) is a molecular biology technique used to discover protein–protein interactions (PPIs) and protein–DNA interactions by testing for physical interactions (such as binding) between two proteins or a single protein and a DNA molecule, respectively.The premise behind the test is the activation of downstream reporter gene(s) by the binding of a transcription factor onto an upstream activating sequence (UAS). For two-hybrid screening, the transcription factor is split into two separate fragments, called the binding domain (BD) and activating domain (AD). The BD is the domain responsible for binding to the UAS and the AD is the domain responsible for the activation of transcription. The Y2H is thus a protein-fragment complementation assay.