CARBOHYDRATES: METABOLISM (cont.)
... – Proteins are assembled from a pool of 20 different amino acids – If one aa is absent then certain proteins cannot be synthesized – The body synthesizes amino acids from other compounds in the body (nonessential Amino Acids) – Only about half the necessary types of amino acids can be produced by th ...
... – Proteins are assembled from a pool of 20 different amino acids – If one aa is absent then certain proteins cannot be synthesized – The body synthesizes amino acids from other compounds in the body (nonessential Amino Acids) – Only about half the necessary types of amino acids can be produced by th ...
Rabbit anti-Sigma-1 Receptor Rabbit anti-Sigma
... The sigma (σ) receptor (sigma-1R, Oprs1 protein, opioid receptor sigma 1) and its agonists are implicated in a variety of cellular functions, biological processes and diseases, including cancer biology, psychosis, regulation of neurotransmitter function, motor, endocrine and immune systems.1 Two sig ...
... The sigma (σ) receptor (sigma-1R, Oprs1 protein, opioid receptor sigma 1) and its agonists are implicated in a variety of cellular functions, biological processes and diseases, including cancer biology, psychosis, regulation of neurotransmitter function, motor, endocrine and immune systems.1 Two sig ...
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: The way of diverting
... “MayaviShaktiya”, “Chamatkar” these things are beyond any religious belief but which used to happen and will continue to happen even in future if a person will have deep knowledge as well as better understanding of scientific concept behind it. This is again an example of the developed Vedic Science ...
... “MayaviShaktiya”, “Chamatkar” these things are beyond any religious belief but which used to happen and will continue to happen even in future if a person will have deep knowledge as well as better understanding of scientific concept behind it. This is again an example of the developed Vedic Science ...
Crystallization and X-Ray Crystallographic Studies of Wild
... complex, is a monomeric 268-residues protein (Mr = 28,600). αTS by itself catalyzes the cleavage of indole3-glycerol phosphate to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and indole, which is converted to tryptophan in tryptophan biosynthesis. Wild-type and P28L/Y173F double mutant α-subunits were overexpressed i ...
... complex, is a monomeric 268-residues protein (Mr = 28,600). αTS by itself catalyzes the cleavage of indole3-glycerol phosphate to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and indole, which is converted to tryptophan in tryptophan biosynthesis. Wild-type and P28L/Y173F double mutant α-subunits were overexpressed i ...
white - UWL faculty websites
... AseUHindIII fragment and ligated into the unique XhoI site of pRK3 between the scs element and the white regulatory sequences. After treatment with Klenow to create blunt termini the vector and insert DNA fragments were ligated together, the resultant vector is called pRK3hsneo (Fig. 3). Site-direct ...
... AseUHindIII fragment and ligated into the unique XhoI site of pRK3 between the scs element and the white regulatory sequences. After treatment with Klenow to create blunt termini the vector and insert DNA fragments were ligated together, the resultant vector is called pRK3hsneo (Fig. 3). Site-direct ...
Nutrition for Strength/Power Athletes
... • No studies have systematically addressed the quantity, type and timing of carbohydrate intake and linked acute physiological responses to chronic adaptations in strength/power athletes. ...
... • No studies have systematically addressed the quantity, type and timing of carbohydrate intake and linked acute physiological responses to chronic adaptations in strength/power athletes. ...
Nucleotide excision repair II: from yeast to mammals
... the value of the latter class for understanding the molecular basis of repair defects in humans. Overlap between mammalian and yeast genes Except for ERCC6 and possibly XPCC, all human genes have identified counterparts in the yeast system 26,~-33 (Table 3), with the level of sequence identity betwe ...
... the value of the latter class for understanding the molecular basis of repair defects in humans. Overlap between mammalian and yeast genes Except for ERCC6 and possibly XPCC, all human genes have identified counterparts in the yeast system 26,~-33 (Table 3), with the level of sequence identity betwe ...
mRNA and protein abundance for glutathione-S
... promoter regions and 3’UTRs The comparative analysis can be illustrated by considering a known regulatory motif. The 8-mer TGACCTTG is known to be a binding site of the Err-α protein and to occur in the promoters of many genes induced during mitochondrial biogenesis. The promoter of the GABPA gene c ...
... promoter regions and 3’UTRs The comparative analysis can be illustrated by considering a known regulatory motif. The 8-mer TGACCTTG is known to be a binding site of the Err-α protein and to occur in the promoters of many genes induced during mitochondrial biogenesis. The promoter of the GABPA gene c ...
ION BINDING TO BIO
... Recent studies indicate that the ion specificity of protein association to a large extent is governed by interactions between salt ions and the macromolecular surface (5). Then for pH
... Recent studies indicate that the ion specificity of protein association to a large extent is governed by interactions between salt ions and the macromolecular surface (5). Then for pH
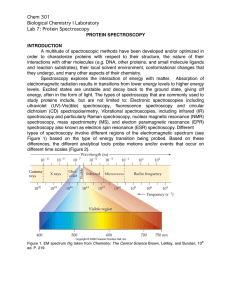
Chem 301 Biological Chemistry I Laboratory Lab 7: Protein
... moments that, when exposed to an external magnetic field, will align either with (lower energy) or against (higher energy) the applied field. These two energy states are the energy states that are “probed” by NMR. Nuclei that are “spin-1/2 nuclei” have NMR signals; these include 1H, 13C, 15N, 19F, a ...
... moments that, when exposed to an external magnetic field, will align either with (lower energy) or against (higher energy) the applied field. These two energy states are the energy states that are “probed” by NMR. Nuclei that are “spin-1/2 nuclei” have NMR signals; these include 1H, 13C, 15N, 19F, a ...
Chapter 10 Notes
... • Alpha helix requires 21-25 residues per transmembrane strand • Beta-strand requires only 9-11 residues per transmembrane strand • Thus, with beta strands , a given amount of genetic material can make a larger number of trans-membrane segments ...
... • Alpha helix requires 21-25 residues per transmembrane strand • Beta-strand requires only 9-11 residues per transmembrane strand • Thus, with beta strands , a given amount of genetic material can make a larger number of trans-membrane segments ...
EC->PDB
... – protein sequence (which may be different from those found in sequence databases, e.g., if the protein has been engineered to facilitate crystallisation) – the method by which the structure was obtained – crystal packing and refinement information – secondary structure information (e.g., helix from ...
... – protein sequence (which may be different from those found in sequence databases, e.g., if the protein has been engineered to facilitate crystallisation) – the method by which the structure was obtained – crystal packing and refinement information – secondary structure information (e.g., helix from ...
Recovery Nutrition
... carbohydrates within 30 minutes of completing an intense workout will synthesize twice as much muscle glycogen as if you wait several hours before refueling. Essentially, the two most important components of recovery are replenishing the glycogen fuel burned during the workout, and rebuilding the mu ...
... carbohydrates within 30 minutes of completing an intense workout will synthesize twice as much muscle glycogen as if you wait several hours before refueling. Essentially, the two most important components of recovery are replenishing the glycogen fuel burned during the workout, and rebuilding the mu ...
Document
... Location in the sequence. For lines with a class prediction it is always 1. For cleavage sites it is the last amino acid of the signal peptide relative to the predicted cleavage site. Location same as above except that for cleavage sites it is the first amino acids after the cleavage site. Score. Fo ...
... Location in the sequence. For lines with a class prediction it is always 1. For cleavage sites it is the last amino acid of the signal peptide relative to the predicted cleavage site. Location same as above except that for cleavage sites it is the first amino acids after the cleavage site. Score. Fo ...
Chapter Five - DORAS
... pTTQ18 allows for selection of the plasmid. The lacZα gene is encoded within the MCS allowing blue/white selection of clones. Given that the ptac promoter is repressed by lacI, the lacIq gene had been cloned into this vector to allow the correct stoichiometry to exist between LacI and the ptac promo ...
... pTTQ18 allows for selection of the plasmid. The lacZα gene is encoded within the MCS allowing blue/white selection of clones. Given that the ptac promoter is repressed by lacI, the lacIq gene had been cloned into this vector to allow the correct stoichiometry to exist between LacI and the ptac promo ...
Translation: A Four
... modifications will occur to the protein[s] (called post-translational modification): – 1) glycosylation -- addition of carbohydrate to the protein; – 2) phosphorylation -- add a phosphate; – 3) proteolytic cleavage -- proteins may be synthesized in an inactive form and require cleavage to become act ...
... modifications will occur to the protein[s] (called post-translational modification): – 1) glycosylation -- addition of carbohydrate to the protein; – 2) phosphorylation -- add a phosphate; – 3) proteolytic cleavage -- proteins may be synthesized in an inactive form and require cleavage to become act ...
Take home message 2.7
... • In ionic bonds, one atom transfers its electrons to another and the two oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other, forming a compound • Hydrogen bonds, which are weaker than covalent and ionic bonds, involve the attraction between a hydrogen atom and a polar molecule. ...
... • In ionic bonds, one atom transfers its electrons to another and the two oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other, forming a compound • Hydrogen bonds, which are weaker than covalent and ionic bonds, involve the attraction between a hydrogen atom and a polar molecule. ...
Hemoglobin
... genes responsible for synthesis of α or β chains (see Fig.) leading to premature death of RBCs. Types: β -thalassemia: When synthesis of β chains is decreased or absent. There are two copies of the gene responsible for synthesis of β chains. Individuals with β globin gene defects have either : -β -t ...
... genes responsible for synthesis of α or β chains (see Fig.) leading to premature death of RBCs. Types: β -thalassemia: When synthesis of β chains is decreased or absent. There are two copies of the gene responsible for synthesis of β chains. Individuals with β globin gene defects have either : -β -t ...
malt - CSU, Chico
... Enzymes developed during germination and used during mashing Amylases: Produce food for yeast and mouthfeel for the beer. a – amylase is a random a 1-4 cutter. Cleaves amylose into random pieces and amylopectin into dextrins. Temp opt. 70-75°C b – amylase cleaves off maltose units from starch. Leav ...
... Enzymes developed during germination and used during mashing Amylases: Produce food for yeast and mouthfeel for the beer. a – amylase is a random a 1-4 cutter. Cleaves amylose into random pieces and amylopectin into dextrins. Temp opt. 70-75°C b – amylase cleaves off maltose units from starch. Leav ...
SECTION 2 - CELL FUNCTION AND BIOCHEMICAL MEASUREMENT
... 11. Plasma proteins contribute to the colloid osmotic pressure of the blood, which is needed for fluid balance. Plasma proteins also serve as circulating enzymes, hormones, transport molecules, and antibodies. Although the liver is a major source of plasma proteins, these molecules can originate fro ...
... 11. Plasma proteins contribute to the colloid osmotic pressure of the blood, which is needed for fluid balance. Plasma proteins also serve as circulating enzymes, hormones, transport molecules, and antibodies. Although the liver is a major source of plasma proteins, these molecules can originate fro ...
Weeks 3-4 Essential Questions March 8-18
... HS-LS1-1 Construct an explanation based on evidence for how the structure of DNA determines the structure of proteins which carry out the essential functions of life through systems of specialized cells ...
... HS-LS1-1 Construct an explanation based on evidence for how the structure of DNA determines the structure of proteins which carry out the essential functions of life through systems of specialized cells ...
Two-hybrid screening
Two-hybrid screening (also known as yeast two-hybrid system or Y2H) is a molecular biology technique used to discover protein–protein interactions (PPIs) and protein–DNA interactions by testing for physical interactions (such as binding) between two proteins or a single protein and a DNA molecule, respectively.The premise behind the test is the activation of downstream reporter gene(s) by the binding of a transcription factor onto an upstream activating sequence (UAS). For two-hybrid screening, the transcription factor is split into two separate fragments, called the binding domain (BD) and activating domain (AD). The BD is the domain responsible for binding to the UAS and the AD is the domain responsible for the activation of transcription. The Y2H is thus a protein-fragment complementation assay.