The Hellenic Axel: The Greek Hellenization of Central Asia
... piecemeal manner with focus guided towards the invading Greeks or their Indian neighbors, rather than a construction of how these two forces interacted. Although some investigations have been made as to how the two entities intermingled, some of the aspects of this cultural communication must be fur ...
... piecemeal manner with focus guided towards the invading Greeks or their Indian neighbors, rather than a construction of how these two forces interacted. Although some investigations have been made as to how the two entities intermingled, some of the aspects of this cultural communication must be fur ...
The Gupta Dynasty was an ancient Indian empire that is
... In addition to the arts, the various sciences also made great advancements during the Gupta period. Aryabhata, a scholar of the time, postulated the notion that the earth was three dimensional and moved around the sun. He is also believed to be the first mathematician to come up with the concept of ...
... In addition to the arts, the various sciences also made great advancements during the Gupta period. Aryabhata, a scholar of the time, postulated the notion that the earth was three dimensional and moved around the sun. He is also believed to be the first mathematician to come up with the concept of ...
The Classical Period in China and India
... Indian culture synthesis of Harappan, Aryan, and other influences ...
... Indian culture synthesis of Harappan, Aryan, and other influences ...
Chapters 2 and 3: The Classical Period in China and
... Theravada Buddhism: philosophy rather than religion. Buddha a man, not god, practiced primarily in Sri Lanka Mahayana Buddhism: salvation religion. Buddha became a god, good and devout ...
... Theravada Buddhism: philosophy rather than religion. Buddha a man, not god, practiced primarily in Sri Lanka Mahayana Buddhism: salvation religion. Buddha became a god, good and devout ...
Lesson 3 Buddhism and India`s Golden Age
... Government The Maurya rulers united northern India into the first great Indian empire. Culture About 500 years after Asoka’s death, a new ruler united northern India and began a golden age of culture. ...
... Government The Maurya rulers united northern India into the first great Indian empire. Culture About 500 years after Asoka’s death, a new ruler united northern India and began a golden age of culture. ...
Lesson 3 Buddhism and India`s Golden Age p
... • The Maurya rulers united northern India into the first great Indian empire. • About 500 years after Asoka’s death, a new ruler united northern India and began a golden age of culture. ...
... • The Maurya rulers united northern India into the first great Indian empire. • About 500 years after Asoka’s death, a new ruler united northern India and began a golden age of culture. ...
Early Civilizations of India, Pakistan and China
... India faced a new threat from the west-Persia and then from the Macedonian general Alexander the Great Chandragupta Maurya founded the first great empire in India around 350 B.C. to 301 B.C. The Mauryan Empire waged war to gain power ...
... India faced a new threat from the west-Persia and then from the Macedonian general Alexander the Great Chandragupta Maurya founded the first great empire in India around 350 B.C. to 301 B.C. The Mauryan Empire waged war to gain power ...
India – Emergence of Civilization
... during the Mauryan dynasty, rock chambers served as meditation halls for traveling Buddhist monks. Initially, they resembled freestanding shrines of wood and thatch from the Vedic period but evolved into magnificent chapels carved deep into the mountainside, such as this one at Karli. ...
... during the Mauryan dynasty, rock chambers served as meditation halls for traveling Buddhist monks. Initially, they resembled freestanding shrines of wood and thatch from the Vedic period but evolved into magnificent chapels carved deep into the mountainside, such as this one at Karli. ...
Maps1PPTdownload
... based on the date either of his coronation or of his marriage. By the conclusion of his reign, his kingdom probably extended west to the present city of Allahabad and included Ayodhya and south Bihar. These regions were assigned to him by Puranas (ancient chronicles of early Sanskrit literature) com ...
... based on the date either of his coronation or of his marriage. By the conclusion of his reign, his kingdom probably extended west to the present city of Allahabad and included Ayodhya and south Bihar. These regions were assigned to him by Puranas (ancient chronicles of early Sanskrit literature) com ...
Tuesday, January 26th - Eastern Belief Systems2
... worship and prayer), loosened caste restrictions and enhanced the role of women Buddhist withdrawal to monasteries, less active lives within India ...
... worship and prayer), loosened caste restrictions and enhanced the role of women Buddhist withdrawal to monasteries, less active lives within India ...
Hinduism and Buddhism - Momin2015-2016
... to “things: in the world. Nirvana- ultimate reality, the end of the self and a reunion with the great World Soul The heart of this teaching is the Four Noble Truths ...
... to “things: in the world. Nirvana- ultimate reality, the end of the self and a reunion with the great World Soul The heart of this teaching is the Four Noble Truths ...
APWH CH9 Quiz: India
... A the conquests brought India, Persia, and Mesopotamia together as one country. B) foreign religions began to take root in Indian society. C) the Greeks dominated Indian history for centuries. D) the intrusions destroyed many petty kingdoms and created a political vacuum. E) All these answers are co ...
... A the conquests brought India, Persia, and Mesopotamia together as one country. B) foreign religions began to take root in Indian society. C) the Greeks dominated Indian history for centuries. D) the intrusions destroyed many petty kingdoms and created a political vacuum. E) All these answers are co ...
India WHI.4
... • Asoka’s rule began in 274 B.C.E. built an empire that covered two-thirds of India. • He converted to Buddhism (from Hinduism) and spread the religion through China and Asia using missionaries. •Asoka issued laws of humanity- free hospitals, veterinary clinics, good roads, allowed people to practic ...
... • Asoka’s rule began in 274 B.C.E. built an empire that covered two-thirds of India. • He converted to Buddhism (from Hinduism) and spread the religion through China and Asia using missionaries. •Asoka issued laws of humanity- free hospitals, veterinary clinics, good roads, allowed people to practic ...
Ancient India
... for about 500 years until the Gupta Empire is established in AD 320. India now united, will become prosperous again. ...
... for about 500 years until the Gupta Empire is established in AD 320. India now united, will become prosperous again. ...
There`s more on the other side!
... Chandragupta Maurya Magadha/ Nanda Family Mauryan Empire How Chandragupta conquered his empire Chandragupta’s army & taxes Katuilya & the Arthasastra Description of India under Chandragupta Asoka Battle of Kalinga & its impact on Asoka Asoka’s edicts Religious toleration Asoka’s improvements to the ...
... Chandragupta Maurya Magadha/ Nanda Family Mauryan Empire How Chandragupta conquered his empire Chandragupta’s army & taxes Katuilya & the Arthasastra Description of India under Chandragupta Asoka Battle of Kalinga & its impact on Asoka Asoka’s edicts Religious toleration Asoka’s improvements to the ...
Buddhist Art Dharmachakra – Eight-Spoke Wheel
... Ashoka maintained his army, and he maintained the secret police and network of spies that he had inherited as a part of his extensive and powerful bureaucracy. He kept his hold over Kalinga, and he did not allow the thousands of people abducted from Kalinga to return there. He announced his intentio ...
... Ashoka maintained his army, and he maintained the secret police and network of spies that he had inherited as a part of his extensive and powerful bureaucracy. He kept his hold over Kalinga, and he did not allow the thousands of people abducted from Kalinga to return there. He announced his intentio ...
INDUS RIVER VALLEY (Map pg
... -Monks and Nuns took vows of poverty, Non-violence, and No marriage -Buddha's teachings first written in the 1st century BCE (100-1 BCE) -Missionaries spread Buddhism all over Asia, but it never took hold in INDIA -HINDUS teach that the Buddha is just another incarnation (AVATAR) of Vishnu. ...
... -Monks and Nuns took vows of poverty, Non-violence, and No marriage -Buddha's teachings first written in the 1st century BCE (100-1 BCE) -Missionaries spread Buddhism all over Asia, but it never took hold in INDIA -HINDUS teach that the Buddha is just another incarnation (AVATAR) of Vishnu. ...
File - Mr. Williams
... • After the Buddha’s death, his followers continued to spread his teachings, and within 200 years, Buddhism had spread through most of India. • King Asoka became Buddhist and built temples, schools, and sent missionaries (people who work to spread their religious beliefs) throughout Asia). • 360 mil ...
... • After the Buddha’s death, his followers continued to spread his teachings, and within 200 years, Buddhism had spread through most of India. • King Asoka became Buddhist and built temples, schools, and sent missionaries (people who work to spread their religious beliefs) throughout Asia). • 360 mil ...
India
... o Est. racial mix – beginnings of caste system o Vedas Unit Two (600 BCE to 600 CE) - Develops into small regional kingdoms by 6th century BCE = decentralized - Buddhism (Siddhartha Gautama) around 500 BCE - Alexander invades (320s BCE) - Mauryans (320s BCE to 2nd c. BCE) o Fills power vacuum left b ...
... o Est. racial mix – beginnings of caste system o Vedas Unit Two (600 BCE to 600 CE) - Develops into small regional kingdoms by 6th century BCE = decentralized - Buddhism (Siddhartha Gautama) around 500 BCE - Alexander invades (320s BCE) - Mauryans (320s BCE to 2nd c. BCE) o Fills power vacuum left b ...
No Slide Title
... Zorastrianism, and Buddhism – Called his system “Justice” – Executed by Mobar Kartir – Saint Augustine originally a Manichean! ...
... Zorastrianism, and Buddhism – Called his system “Justice” – Executed by Mobar Kartir – Saint Augustine originally a Manichean! ...
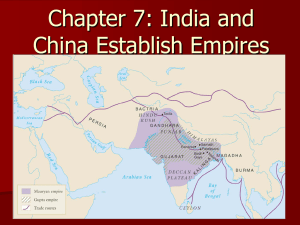
Chapter 7: India and China Establish Empires
... How did the Mauryan Empire, the Golden Age, and Asoka affect the development of India? ...
... How did the Mauryan Empire, the Golden Age, and Asoka affect the development of India? ...
5. INDIAN EMPIRES - myteacherpages.com
... I. Mauryan Empire (321 BC – 184 BC) 2. Asoka – Chandragupta’s grandson C. Converted to Buddhism after one battle a. Spread the teachings of Buddhism throughout India and Asia b. Allowed Hindu people to practice their religion, caste system remained ...
... I. Mauryan Empire (321 BC – 184 BC) 2. Asoka – Chandragupta’s grandson C. Converted to Buddhism after one battle a. Spread the teachings of Buddhism throughout India and Asia b. Allowed Hindu people to practice their religion, caste system remained ...
Ancient India History The Indus Valley Civilisation, Harrapa | Aryans
... 3300-2800 BC. Harappa and the city of Mohenjo-Daro were the greatest achievements of the Indus valley civilization. These cities are well known for their impressive, organized and regular layout. Then came Aryans who composed these evocative hymns to nature and celebrated life exuberantly referred t ...
... 3300-2800 BC. Harappa and the city of Mohenjo-Daro were the greatest achievements of the Indus valley civilization. These cities are well known for their impressive, organized and regular layout. Then came Aryans who composed these evocative hymns to nature and celebrated life exuberantly referred t ...
Maurya Empire

The Maurya Empire, also known as the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in ancient India, ruled by the Maurya dynasty from 322–185 BCE. Originating from the kingdom of Magadha in the Indo-Gangetic Plain (modern Bihar, eastern Uttar Pradesh) in the eastern side of the Indian subcontinent, the empire had its capital city at Pataliputra (modern Patna).The Empire was founded in 322 BCE by Chandragupta Maurya, who had overthrown the Nanda Dynasty and rapidly expanded his power westwards across central and western India, alongside Chanakya's help, taking advantage of the disruptions of local powers in the wake of the withdrawal westward by Alexander the Great's armies. By 316 BCE the empire had fully occupied Northwestern India, defeating and conquering the satraps left by Alexander. Chandragupta then defeated the invasion led by Seleucus I, a Macedonian general from Alexander's army, gaining additional territory west of the Indus River.The Maurya Empire was one of the largest empires of the world in its time. It was also the largest empire ever in the Indian subcontinent. At its greatest extent, the empire stretched to the north along the natural boundaries of the Himalayas, to the east into Assam, to the west into Balochistan (south west Pakistan and south east Iran) and the Hindu Kush mountains of what is now Afghanistan. The Empire was expanded into India's central and southern regions by the emperors Chandragupta and Bindusara, but it excluded a small portion of unexplored tribal and forested regions near Kalinga (modern Odisha), until it was conquered by Ashoka. It declined for about 50 years after Ashoka's rule ended, and it dissolved in 185 BCE with the foundation of the Shunga dynasty in Magadha.Under Chandragupta and his successors, internal and external trade, agriculture and economic activities, all thrived and expanded across India thanks to the creation of a single and efficient system of finance, administration, and security. After the Kalinga War, the Empire experienced nearly half a century of peace and security under Ashoka. Mauryan India also enjoyed an era of social harmony, religious transformation, and expansion of the sciences and of knowledge. Chandragupta Maurya's embrace of Jainism increased social and religious renewal and reform across his society, while Ashoka's embrace of Buddhism has been said to have been the foundation of the reign of social and political peace and non-violence across all of India. Ashoka sponsored the spreading of Buddhist ideals into Sri Lanka, Southeast Asia, West Asia and Mediterranean Europe.The population of the empire has been estimated to be about 50–60 million, making the Mauryan Empire one of the most populous empires of Antiquity. Archaeologically, the period of Mauryan rule in South Asia falls into the era of Northern Black Polished Ware (NBPW). The Arthashastra and the Edicts of Ashoka are the primary sources of written records of Mauryan times. The Lion Capital of Ashoka at Sarnath has been made the national emblem of India.