Purified Mouse Anti-p115 — 612260
... through the Golgi apparatus. The process involves the transport of vesicles carrying the proteins through a vectorial process of vesicle budding and fusion from the cis-compartment to the medial-compartment and the trans-compartment of the Golgi apparatus. p115 is a 959 amino acid protein located at ...
... through the Golgi apparatus. The process involves the transport of vesicles carrying the proteins through a vectorial process of vesicle budding and fusion from the cis-compartment to the medial-compartment and the trans-compartment of the Golgi apparatus. p115 is a 959 amino acid protein located at ...
Protein Folding File
... What type of bonding stabilizes alpha helices and beta sheets? In addition to H-bonding, what type of bonding leads to stronger covalent bonds between amino acids? After secondary structures are formed, what is the primary driving force for tertiary folding? A protein may not always fold ‘correctly’ ...
... What type of bonding stabilizes alpha helices and beta sheets? In addition to H-bonding, what type of bonding leads to stronger covalent bonds between amino acids? After secondary structures are formed, what is the primary driving force for tertiary folding? A protein may not always fold ‘correctly’ ...
SEDIMENTATION AND ELECTROPHORETIC METHODS An
... A Southern blot is a method routinely used in molecular biology to check for the presence of a DNA sequence in a DNA sample. Southern blotting combines gel electrophoresis for size separation of DNA with methods to transfer the size-separated DNA to a filter membrane for probe hybridization. The met ...
... A Southern blot is a method routinely used in molecular biology to check for the presence of a DNA sequence in a DNA sample. Southern blotting combines gel electrophoresis for size separation of DNA with methods to transfer the size-separated DNA to a filter membrane for probe hybridization. The met ...
Single particle cryo-EM of membrane proteins in lipid nanodisc
... In the last few years, major technological breakthroughs enabled single particle cryo-EM to become the technique of choice for structure determination of many challenging biological macromolecules. Atomic structures of many membrane proteins that are refractory to crystallization have now determined ...
... In the last few years, major technological breakthroughs enabled single particle cryo-EM to become the technique of choice for structure determination of many challenging biological macromolecules. Atomic structures of many membrane proteins that are refractory to crystallization have now determined ...
martakmalina proteins
... are formed by hydrogen bonding. Secondary structures are locally defined, meaning that there can be many different secondary motifs present in one single protein molecule. ...
... are formed by hydrogen bonding. Secondary structures are locally defined, meaning that there can be many different secondary motifs present in one single protein molecule. ...
Designer enzymes Donald Hilvert ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
... structure-function relationships in these macromolecules is at best incomplete. Nature has solved the problem of protein design through the mechanism of Darwinian evolution. From primitive precursors, recursive cycles of mutation, selection and amplification of molecules with favorable traits have g ...
... structure-function relationships in these macromolecules is at best incomplete. Nature has solved the problem of protein design through the mechanism of Darwinian evolution. From primitive precursors, recursive cycles of mutation, selection and amplification of molecules with favorable traits have g ...
General Reference - Methods Enzymol. 182 "Guide to Protein
... x Proteins differ in their thermal stability and ability to renature after thermal denaturation. Calmodulin is an excellent example of a protein that can be purified by thermal denaturation. ...
... x Proteins differ in their thermal stability and ability to renature after thermal denaturation. Calmodulin is an excellent example of a protein that can be purified by thermal denaturation. ...
Lecture_9
... Any antibody-producing cell synthesizes antibodies that recognize only one epitope. Each antibody-producing cell thus synthesizes a monoclonal antibody. Any antigen may have multiple epitopes. The antibodies produced to the antigen by different cells are said to be polyclonal. ...
... Any antibody-producing cell synthesizes antibodies that recognize only one epitope. Each antibody-producing cell thus synthesizes a monoclonal antibody. Any antigen may have multiple epitopes. The antibodies produced to the antigen by different cells are said to be polyclonal. ...
Getting things where they need to go: Protein Targeting
... 3 Stages: Budding, targeting/docking and fusion ...
... 3 Stages: Budding, targeting/docking and fusion ...
Study Guide for Membranes and Transport
... describe the processes which allow monomers to be joined to form polymers as well as polymers to be broken down into monomers. give examples of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids including at least one location within a cell where each can be found. compare and contrast the str ...
... describe the processes which allow monomers to be joined to form polymers as well as polymers to be broken down into monomers. give examples of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids including at least one location within a cell where each can be found. compare and contrast the str ...
Protein?
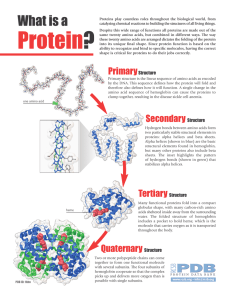
... catalyzing chemical reactions to building the structures of all living things. Despite this wide range of functions all proteins are made out of the same twenty amino acids, but combined in different ways. The way these twenty amino acids are arranged dictates the folding of the protein into its uni ...
... catalyzing chemical reactions to building the structures of all living things. Despite this wide range of functions all proteins are made out of the same twenty amino acids, but combined in different ways. The way these twenty amino acids are arranged dictates the folding of the protein into its uni ...
Figure 5.1 Rapid Diffusion of Membrane Proteins The fluid mosaic
... Integral to this model was earlier work by Frye and Edidin (1970). These researchers examined the movement of proteins within the cell membrane by constructing heterokaryons, cells comprised of nuclei from both mice and humans. By using fluorescent stains (red or green) that were specific either to ...
... Integral to this model was earlier work by Frye and Edidin (1970). These researchers examined the movement of proteins within the cell membrane by constructing heterokaryons, cells comprised of nuclei from both mice and humans. By using fluorescent stains (red or green) that were specific either to ...
Protein Aggregation in High-Protein Caramel
... Here, the caramel takes on a tapioca-like structure, with large visible aggregates of protein structures (Figure 1), as it loses its desirable smooth texture. There are two general categories of proteins in milk — the caseins (≈80%) and the serum proteins (≈20%). The various casein proteins form int ...
... Here, the caramel takes on a tapioca-like structure, with large visible aggregates of protein structures (Figure 1), as it loses its desirable smooth texture. There are two general categories of proteins in milk — the caseins (≈80%) and the serum proteins (≈20%). The various casein proteins form int ...
Protein Synthesis
... • Proteins play specific roles in an organism. – Support (elastin) – Transport (hemoglobin) – Control (hormones, insulin) – Immunity (antibodies) – Catalysis (enzymes) ...
... • Proteins play specific roles in an organism. – Support (elastin) – Transport (hemoglobin) – Control (hormones, insulin) – Immunity (antibodies) – Catalysis (enzymes) ...
Cell Membrane Structure & Function
... Membranes are “fluid mosaics” with proteins embedded in or attached to the membrane ...
... Membranes are “fluid mosaics” with proteins embedded in or attached to the membrane ...
I. Characteristics of amino acids and folding of nascent polypeptides
... sequence). Higher order folding (tertiary and quaternary structures) will ofter require the assistance of other proteins called molecular chaperones (Fig. 7.32). A chaperone interacts with a newly synthesized (nascent) polypeptide before it folds or with an improperly folded or unfolded protein (oft ...
... sequence). Higher order folding (tertiary and quaternary structures) will ofter require the assistance of other proteins called molecular chaperones (Fig. 7.32). A chaperone interacts with a newly synthesized (nascent) polypeptide before it folds or with an improperly folded or unfolded protein (oft ...
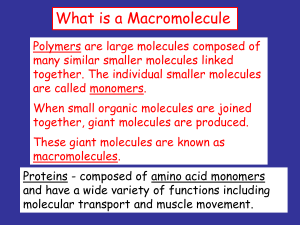
What is a Macromolecule
... IgD is almost exclusively found inserted into the membrane of B cells, where it somehow regulates the cell's activation. IgE is normally present in only trace amounts, but it is responsible for the symptoms of allergy. IgA--a doublet--guards the entrance to the body. It concentrates in body fluids s ...
... IgD is almost exclusively found inserted into the membrane of B cells, where it somehow regulates the cell's activation. IgE is normally present in only trace amounts, but it is responsible for the symptoms of allergy. IgA--a doublet--guards the entrance to the body. It concentrates in body fluids s ...
Vragen voor tentamen Protein Engineering (8S080)
... of shampoos and is therefore interested to develop new ingredients for the their anti-dandruff shampoos that would target specifically this type of yeast, without affecting other microorganisms living on the skin. One attractive possibility would be to develop M. furfur specific antibodies. a. What ...
... of shampoos and is therefore interested to develop new ingredients for the their anti-dandruff shampoos that would target specifically this type of yeast, without affecting other microorganisms living on the skin. One attractive possibility would be to develop M. furfur specific antibodies. a. What ...
Chemicals
... Huh7 and RepBlast cells. Lipoproteins were isolated as described in material and method section. Lipoproteins were concentrated and washed with 1XPBS at 3000 rpm at 5°C for 3h using vivaspin columns (Sartorius Stedim Biotech). Equal amount of lipoproteins were brought to a final volume of 1 ml with ...
... Huh7 and RepBlast cells. Lipoproteins were isolated as described in material and method section. Lipoproteins were concentrated and washed with 1XPBS at 3000 rpm at 5°C for 3h using vivaspin columns (Sartorius Stedim Biotech). Equal amount of lipoproteins were brought to a final volume of 1 ml with ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint
... to probe at molecular level the interaction of nanoparticles within complex biological systems (cells, tissue and organs). An important requirement for nanomedicine is that these techniques must be rapid, inexpensive and non invasive for in vitro and in vivo diagnostics. ...
... to probe at molecular level the interaction of nanoparticles within complex biological systems (cells, tissue and organs). An important requirement for nanomedicine is that these techniques must be rapid, inexpensive and non invasive for in vitro and in vivo diagnostics. ...
The molecular architecture, macro-organization and functions of the
... Light-harvesting complex II (LHCII), the major antenna pigment-protein complex of plants and green algae, is the most abundant membrane protein on Earth. The primary function of LHCII is to capture sunlight and transfer the excitation energy to the photochemical reaction centers – with up to nearly ...
... Light-harvesting complex II (LHCII), the major antenna pigment-protein complex of plants and green algae, is the most abundant membrane protein on Earth. The primary function of LHCII is to capture sunlight and transfer the excitation energy to the photochemical reaction centers – with up to nearly ...
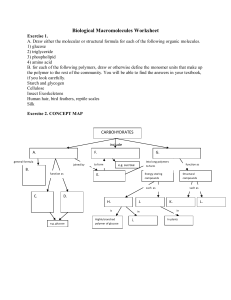
Biological Macromolecules Worksheet
... 1. What are the building block unit of proteins? How do these building blocks differ from each other? 2. List three structural differences and one functional difference between DNA and RNA. 3. The most abundant protein in your body is collagen which is a type of _________________ protein. 4. _______ ...
... 1. What are the building block unit of proteins? How do these building blocks differ from each other? 2. List three structural differences and one functional difference between DNA and RNA. 3. The most abundant protein in your body is collagen which is a type of _________________ protein. 4. _______ ...
Western blot

The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot) is a widely used analytical technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. It uses gel electrophoresis to separate native proteins by 3-D structure or denatured proteins by the length of the polypeptide. The proteins are then transferred to a membrane (typically nitrocellulose or PVDF), where they are stained with antibodies specific to the target protein. The gel electrophoresis step is included in western blot analysis to resolve the issue of the cross-reactivity of antibodies.There are many reagent companies that specialize in providing antibodies (both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies) against tens of thousands of different proteins. Commercial antibodies can be expensive, although the unbound antibody can be reused between experiments. This method is used in the fields of molecular biology, immunogenetics and other molecular biology disciplines. A number of search engines, such as CiteAb, Antibodypedia, and SeekProducts, are available that can help researchers find suitable antibodies for use in western blotting.Other related techniques include dot blot analysis, immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry where antibodies are used to detect proteins in tissues and cells by immunostaining, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).The method originated in the laboratory of Harry Towbin at the Friedrich Miescher Institute. The name western blot was given to the technique by W. Neal Burnette and is a play on the name Southern blot, a technique for DNA detection developed earlier by Edwin Southern. Detection of RNA is termed northern blot and was developed by George Stark at Stanford.