Getting things where they need to go: Protein Targeting
... The catecholamine theory of affective disorder What sorts of situations could result in this condition? (what would alter the amount of signaling at a synapse?) 1) Don’t make enough neurotransmitter 2) Make it but don’t package it into vesicles or don’t release it correctly 3) Make/ release but rece ...
... The catecholamine theory of affective disorder What sorts of situations could result in this condition? (what would alter the amount of signaling at a synapse?) 1) Don’t make enough neurotransmitter 2) Make it but don’t package it into vesicles or don’t release it correctly 3) Make/ release but rece ...
ppt - Scientific Data Analysis Lab
... which lack a fixed tertiary structure, essentially being partially or fully unfolded. Such disordered regions have been shown to be involved in a variety of functions, including DNA recognition, modulation of specificity/affinity of protein binding, molecular threading, activation by cleavage, and c ...
... which lack a fixed tertiary structure, essentially being partially or fully unfolded. Such disordered regions have been shown to be involved in a variety of functions, including DNA recognition, modulation of specificity/affinity of protein binding, molecular threading, activation by cleavage, and c ...
21. Membranes
... a. Adjacent phospholipids move around constantly, while proteins, being larger, will move more slowly. i. Phospholipids can be propelled by the cytoskeleton, motor proteins, or temperature (similar to Brownian motion). ii. By the same token, the cytoskeleton can hold membrane components in place. b. ...
... a. Adjacent phospholipids move around constantly, while proteins, being larger, will move more slowly. i. Phospholipids can be propelled by the cytoskeleton, motor proteins, or temperature (similar to Brownian motion). ii. By the same token, the cytoskeleton can hold membrane components in place. b. ...
Methyl CpG binding protein 2 binding sites on chromosome 22 in
... and recruit other proteins to deactivate the gene. By identifying the location of bound MBDs we can hypothesize which genes have been repressed. The purpose of this lab is to determine the binding sites of MBD2 on chromosome 22 in hepatocellular carcinoma B cells. To accomplish this, cells are cultu ...
... and recruit other proteins to deactivate the gene. By identifying the location of bound MBDs we can hypothesize which genes have been repressed. The purpose of this lab is to determine the binding sites of MBD2 on chromosome 22 in hepatocellular carcinoma B cells. To accomplish this, cells are cultu ...
Template to create a scientific poster
... calorimetry revealed that the I480N mutant differs significantly in its affinity for ADP, ATP, and peptide substrate. This mutant also displayed significant different reaction entropy as compared to the WT HSPA1A (N=4; bars= S.D.; p values are the results of a student’s t-test). The S16Y mutant diff ...
... calorimetry revealed that the I480N mutant differs significantly in its affinity for ADP, ATP, and peptide substrate. This mutant also displayed significant different reaction entropy as compared to the WT HSPA1A (N=4; bars= S.D.; p values are the results of a student’s t-test). The S16Y mutant diff ...
BLM 3 7 FluidMosaicModelAnswers File
... fluid consistency. Various types of proteins are scattered throughout this phospholipid bilayer. Both the phospholipids and proteins move among each other. The lipid bilayer represents the “fluid” part of the fluid-mosaic model, while the various proteins found embedded in the cell membrane account ...
... fluid consistency. Various types of proteins are scattered throughout this phospholipid bilayer. Both the phospholipids and proteins move among each other. The lipid bilayer represents the “fluid” part of the fluid-mosaic model, while the various proteins found embedded in the cell membrane account ...
Protein 101
... •How does this fit with Rx for athletes •Upper end of range clearly exceeds Rx for “athlete” Rx •*1.2-1.4 g/d /kg for endurance athletes *1.4-1.8 g/d/kg for strength athletes are adequate to support the ...
... •How does this fit with Rx for athletes •Upper end of range clearly exceeds Rx for “athlete” Rx •*1.2-1.4 g/d /kg for endurance athletes *1.4-1.8 g/d/kg for strength athletes are adequate to support the ...
Escherichia coli
... • Difficult to study Due to hydrophobic and amphiphilic nature Less than 1% of high resolution 3D structures known ...
... • Difficult to study Due to hydrophobic and amphiphilic nature Less than 1% of high resolution 3D structures known ...
The Cell Membrane
... 2. Carrier or Transport Proteins- binding site on protein surface "grabs" certain molecules and pulls them into the cell. ...
... 2. Carrier or Transport Proteins- binding site on protein surface "grabs" certain molecules and pulls them into the cell. ...
Lecture 1: Fundamentals of Protein Structure
... Conserved (the residue is generally similar, e.g. negatively charged) Not conserved (can be many different residues in different species) ...
... Conserved (the residue is generally similar, e.g. negatively charged) Not conserved (can be many different residues in different species) ...
Spectrophotometric methods for determination of proteins
... refers to descriptions or distinctions based on some quality or characteristic rather than on some quantity or measured value. It can be a form of analysis that yields the identity of a compound. ...
... refers to descriptions or distinctions based on some quality or characteristic rather than on some quantity or measured value. It can be a form of analysis that yields the identity of a compound. ...
Datasheet - Santa Cruz Biotechnology
... MND1 (G-4): sc-377319. Western blot analysis of MND1 expression in Jurkat (A), K-562 (B) and HeLa (C) nuclear extracts and HeLa (D), Jurkat (E) and K-562 (F) whole cell lysates. ...
... MND1 (G-4): sc-377319. Western blot analysis of MND1 expression in Jurkat (A), K-562 (B) and HeLa (C) nuclear extracts and HeLa (D), Jurkat (E) and K-562 (F) whole cell lysates. ...
The Biotechnology Age: Issues and Impacts
... Isolate proteins from leaves and detect proteins using antibodies Use a microscope to find where PDIs and green fluorescent protein are located in the cell. ...
... Isolate proteins from leaves and detect proteins using antibodies Use a microscope to find where PDIs and green fluorescent protein are located in the cell. ...
Sample Preparation II
... separated by means of a suitable electrophoresis technique such as SDS-PAGE or Twodimensional Electrophoresis. ...
... separated by means of a suitable electrophoresis technique such as SDS-PAGE or Twodimensional Electrophoresis. ...
Short Answer – Answer briefly and completely on your answer sheet.
... 46. Process of molecules moving out of a cell 47. First scientist to describe cells 48. and 49. Scientists involved with formulating cell theory. Short Answer – Answer briefly and completely on your answer sheet. 50. Describe the “fluid mosaic model” and why it is named this. 51. List three possible ...
... 46. Process of molecules moving out of a cell 47. First scientist to describe cells 48. and 49. Scientists involved with formulating cell theory. Short Answer – Answer briefly and completely on your answer sheet. 50. Describe the “fluid mosaic model” and why it is named this. 51. List three possible ...
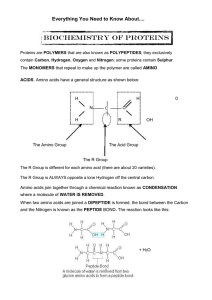
Proteins
... 7) How many amino acids are combined to form a dipeptide? ____2_______ a tripeptide? _____3______ How large are most proteins? __larger than 50 amino acids but typically hundreds of amino acids long ...
... 7) How many amino acids are combined to form a dipeptide? ____2_______ a tripeptide? _____3______ How large are most proteins? __larger than 50 amino acids but typically hundreds of amino acids long ...
Applications of spectroscopy
... • Laser T-jump methodology has evolved into one of the most versatile and generally applicable methods for studying fast biomolecular kinetics. ...
... • Laser T-jump methodology has evolved into one of the most versatile and generally applicable methods for studying fast biomolecular kinetics. ...
lab2 precipitation of casein at isoelectric point
... PH = Pka + log{ (casein acetate sodium )÷ (acetic acid)} Maximum precipitation can be obtained at the isoelectric point by addition of some reagents such as, ethanol which dehydrates the molecule and allow neutralization of charge ...
... PH = Pka + log{ (casein acetate sodium )÷ (acetic acid)} Maximum precipitation can be obtained at the isoelectric point by addition of some reagents such as, ethanol which dehydrates the molecule and allow neutralization of charge ...
Topology of membrane protein
... 2. Anionic lipids: - binding of positively charged residues by electrostatic interactions 3. ∆Ψ: - favorable electrostatic interactions - electrophoretic effect 4. Potential within the membrane - positive inside, due to dipole effects ...
... 2. Anionic lipids: - binding of positively charged residues by electrostatic interactions 3. ∆Ψ: - favorable electrostatic interactions - electrophoretic effect 4. Potential within the membrane - positive inside, due to dipole effects ...
Flexibility of a polypeptide chain
... For instance, a helix-turn-helix motif, often found in DNA-binding proteins some polypeptide chains fold into 2 or more compact globular units or regions that are connected by flexible regions, these are called domains (30-400 amino acids long) ...
... For instance, a helix-turn-helix motif, often found in DNA-binding proteins some polypeptide chains fold into 2 or more compact globular units or regions that are connected by flexible regions, these are called domains (30-400 amino acids long) ...
Western blot

The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot) is a widely used analytical technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. It uses gel electrophoresis to separate native proteins by 3-D structure or denatured proteins by the length of the polypeptide. The proteins are then transferred to a membrane (typically nitrocellulose or PVDF), where they are stained with antibodies specific to the target protein. The gel electrophoresis step is included in western blot analysis to resolve the issue of the cross-reactivity of antibodies.There are many reagent companies that specialize in providing antibodies (both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies) against tens of thousands of different proteins. Commercial antibodies can be expensive, although the unbound antibody can be reused between experiments. This method is used in the fields of molecular biology, immunogenetics and other molecular biology disciplines. A number of search engines, such as CiteAb, Antibodypedia, and SeekProducts, are available that can help researchers find suitable antibodies for use in western blotting.Other related techniques include dot blot analysis, immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry where antibodies are used to detect proteins in tissues and cells by immunostaining, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).The method originated in the laboratory of Harry Towbin at the Friedrich Miescher Institute. The name western blot was given to the technique by W. Neal Burnette and is a play on the name Southern blot, a technique for DNA detection developed earlier by Edwin Southern. Detection of RNA is termed northern blot and was developed by George Stark at Stanford.