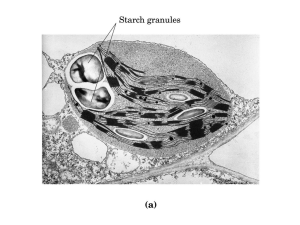
Math, or the Lack of, In a Biology Classroom
... genome projects. Other applications are amino acid and nucleic acid sequence alignment, protein structure prediction, and virtual evolution. ...
... genome projects. Other applications are amino acid and nucleic acid sequence alignment, protein structure prediction, and virtual evolution. ...
P8010Datasheet-Lot0921211
... disulfide-linked chains of approximately 27 kDa and 16 kDa. On SDS-PAGE, the reduced chains have apparent molecular weights of 30 kDa and 20 kDa. ...
... disulfide-linked chains of approximately 27 kDa and 16 kDa. On SDS-PAGE, the reduced chains have apparent molecular weights of 30 kDa and 20 kDa. ...
FPIA - IMGT
... 1. Both the receptor and the ligand proteins are defined by their ability to interact 2. The distinction between receptor and ligand for a protein cannot be done on ‘soluble’ or ‘membrane’ 3. The distinction between receptor and ligand for a membrane protein in the immune system is relative and defi ...
... 1. Both the receptor and the ligand proteins are defined by their ability to interact 2. The distinction between receptor and ligand for a protein cannot be done on ‘soluble’ or ‘membrane’ 3. The distinction between receptor and ligand for a membrane protein in the immune system is relative and defi ...
Organelles Worksheet
... 7. a. Which structure is selectively permeable? b. What substance is permeable to cell membranes? 8. What is the difference between plant cell vacuoles and animal cell vacuoles? ...
... 7. a. Which structure is selectively permeable? b. What substance is permeable to cell membranes? 8. What is the difference between plant cell vacuoles and animal cell vacuoles? ...
From Gene to Protein
... • Post-translational modifications can have both structural and regulatory functions. • Important modifications include methylation, acetylation, ubiquitinylation, and sumoylation. • The most common regulatory reaction in molecular biology is the reversible phosphorylation of amino acid side chains ...
... • Post-translational modifications can have both structural and regulatory functions. • Important modifications include methylation, acetylation, ubiquitinylation, and sumoylation. • The most common regulatory reaction in molecular biology is the reversible phosphorylation of amino acid side chains ...
Carbohydrates – Complex (Polysaccharides)
... A typical tetrasaccharide linker (blue) connects a glycosamino-glycan—in this case chondroitin 4-sulfate (orange)—to a Ser residue (pink) in the core protein. The xylose residue at the reducing end of the linker is joined by its anomeric carbon to the hydroxyl of the Ser residue. ...
... A typical tetrasaccharide linker (blue) connects a glycosamino-glycan—in this case chondroitin 4-sulfate (orange)—to a Ser residue (pink) in the core protein. The xylose residue at the reducing end of the linker is joined by its anomeric carbon to the hydroxyl of the Ser residue. ...
Next-generation protein drugs
... biologics, such as therapeutic antibodies1, suffer from drawbacks, such as the requirement for an expensive mammalian cell production system and the need for intravenous, intramuscular or subcutaneous injection (with molecular weights of around 150,000, they are too large to be administered by any o ...
... biologics, such as therapeutic antibodies1, suffer from drawbacks, such as the requirement for an expensive mammalian cell production system and the need for intravenous, intramuscular or subcutaneous injection (with molecular weights of around 150,000, they are too large to be administered by any o ...
The Chemical Building Blocks of Life
... • Polysacharides- more than 2 monosacharides joined together. ...
... • Polysacharides- more than 2 monosacharides joined together. ...
TABLE 3–1 Some Common Types of Enzymes
... break down nucleic acids by hydrolyzing bonds between nucleotides. break down proteins by hydrolyzing bonds between amino acids. general name used for enzymes that synthesize molecules in anabolic reactions by condensing two smaller molecules together. catalyze the rearrangement of bonds within a si ...
... break down nucleic acids by hydrolyzing bonds between nucleotides. break down proteins by hydrolyzing bonds between amino acids. general name used for enzymes that synthesize molecules in anabolic reactions by condensing two smaller molecules together. catalyze the rearrangement of bonds within a si ...
3-20
... – permeable to nonpolar, uncharged molecules -- oxygen, CO2, steroids – permeable to water which flows through gaps that form in hydrophobic core of membrane as phospholipids move about ...
... – permeable to nonpolar, uncharged molecules -- oxygen, CO2, steroids – permeable to water which flows through gaps that form in hydrophobic core of membrane as phospholipids move about ...
were performed essentially as described previously (Witt et al
... Interaction of between nebulin and titin. To survey for the residues in titin mediating binding to nebulin, we used a SPOTS blot membrane (JPT, Berlin) that displays exon 4 – exon 7 of titin (see also EMBL data library, accession AJ277892) as a series of 31 overlapping residues (peptides were acetyl ...
... Interaction of between nebulin and titin. To survey for the residues in titin mediating binding to nebulin, we used a SPOTS blot membrane (JPT, Berlin) that displays exon 4 – exon 7 of titin (see also EMBL data library, accession AJ277892) as a series of 31 overlapping residues (peptides were acetyl ...
Examination in Gene Technology, TFKE38 2011-10-18
... plasmid was ligated with the Pvu1 digested gene coding for protein X and the mixture was transformed into E. coli cells. a) What antibiotics should be added to the medium (agarplate) to select cells that have incorporated the gene for proteinX? (2 p) b) After transformation colonies were obtained th ...
... plasmid was ligated with the Pvu1 digested gene coding for protein X and the mixture was transformed into E. coli cells. a) What antibiotics should be added to the medium (agarplate) to select cells that have incorporated the gene for proteinX? (2 p) b) After transformation colonies were obtained th ...
IMMUNOLOGY
... Immune system learns it job by practicing, if you give it nothing to practice on, it will find something (grass, pollen, food allergies, etc.) ...
... Immune system learns it job by practicing, if you give it nothing to practice on, it will find something (grass, pollen, food allergies, etc.) ...
Summary for Chapter 6 – Protein: Amino Acids
... Digestion is facilitated mostly by the stomach’s acid and enzymes, which first denature dietary proteins, then cleave them into smaller polypeptides and some amino acids. Pancreatic and intestinal enzymes split these polypeptides further, to oligo-, tri-, and dipeptides, and then split most of these ...
... Digestion is facilitated mostly by the stomach’s acid and enzymes, which first denature dietary proteins, then cleave them into smaller polypeptides and some amino acids. Pancreatic and intestinal enzymes split these polypeptides further, to oligo-, tri-, and dipeptides, and then split most of these ...
What is PCM Synergy? PCM synergy is a quality blend is a multi
... contains a high level of BCAAs (branch chain amino acids) which are vital in the manufacture, maintenance and repair of muscles. The rapid absorption of the BCAAs allows the protein to be more readily available for muscle building sooner. PCM synergy is also one of best tasting supplements available ...
... contains a high level of BCAAs (branch chain amino acids) which are vital in the manufacture, maintenance and repair of muscles. The rapid absorption of the BCAAs allows the protein to be more readily available for muscle building sooner. PCM synergy is also one of best tasting supplements available ...
Chapter 5 Problem set
... ____22. Because membranes exhibit selective permeability, concentrations of dissolved substances can increase on one side of the membrane or the other. ____23. A water concentration gradient is influenced by the number of solute molecules present on both sides of the membrane. ____24. The relative c ...
... ____22. Because membranes exhibit selective permeability, concentrations of dissolved substances can increase on one side of the membrane or the other. ____23. A water concentration gradient is influenced by the number of solute molecules present on both sides of the membrane. ____24. The relative c ...
1333 - Protein Engineer / Structural Biologist
... Meticulous organization, record keeping and reporting. ...
... Meticulous organization, record keeping and reporting. ...
Improved recovery of enzyme activity after
... Hortmon and Udenfriend (I969 Anal. Biochem. 30:391 ) described o method for utilizing the mognerium sol+ of I-aniline-Einophtholene mdgoerium and sodium soltr m fluorescent protein stain. sulfonote (Eortmon Organic Chemicolr ) os o mpid meonr for viwolizotion of protein bonds in ocrylomide gels. Th ...
... Hortmon and Udenfriend (I969 Anal. Biochem. 30:391 ) described o method for utilizing the mognerium sol+ of I-aniline-Einophtholene mdgoerium and sodium soltr m fluorescent protein stain. sulfonote (Eortmon Organic Chemicolr ) os o mpid meonr for viwolizotion of protein bonds in ocrylomide gels. Th ...
Transport by Carriers
... What moves in and out of cells by osmosis? What controls this process? What are two types of membrane proteins that assist with transport of substances across the membrane? ...
... What moves in and out of cells by osmosis? What controls this process? What are two types of membrane proteins that assist with transport of substances across the membrane? ...
Western blot

The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot) is a widely used analytical technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. It uses gel electrophoresis to separate native proteins by 3-D structure or denatured proteins by the length of the polypeptide. The proteins are then transferred to a membrane (typically nitrocellulose or PVDF), where they are stained with antibodies specific to the target protein. The gel electrophoresis step is included in western blot analysis to resolve the issue of the cross-reactivity of antibodies.There are many reagent companies that specialize in providing antibodies (both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies) against tens of thousands of different proteins. Commercial antibodies can be expensive, although the unbound antibody can be reused between experiments. This method is used in the fields of molecular biology, immunogenetics and other molecular biology disciplines. A number of search engines, such as CiteAb, Antibodypedia, and SeekProducts, are available that can help researchers find suitable antibodies for use in western blotting.Other related techniques include dot blot analysis, immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry where antibodies are used to detect proteins in tissues and cells by immunostaining, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).The method originated in the laboratory of Harry Towbin at the Friedrich Miescher Institute. The name western blot was given to the technique by W. Neal Burnette and is a play on the name Southern blot, a technique for DNA detection developed earlier by Edwin Southern. Detection of RNA is termed northern blot and was developed by George Stark at Stanford.