Cellular Functions PP
... The protons then diffuse through a special proton channels called ATP synthase, down the concentration gradient back into the matrix of the mitochondria, creating ATP in the process. Chemiosmosis is the coupling of the protonmotive force and ATP synthesis. The final electron acceptor is Oxygen which ...
... The protons then diffuse through a special proton channels called ATP synthase, down the concentration gradient back into the matrix of the mitochondria, creating ATP in the process. Chemiosmosis is the coupling of the protonmotive force and ATP synthesis. The final electron acceptor is Oxygen which ...
Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
... number using a spectrophotometer, spectrofluorometer, or other optical device. This test is determining the "cut-off" point between a positive and negative result. • Unknowns that generate a signal that is stronger than the known sample are called "positive"; those that generate weaker signal are ca ...
... number using a spectrophotometer, spectrofluorometer, or other optical device. This test is determining the "cut-off" point between a positive and negative result. • Unknowns that generate a signal that is stronger than the known sample are called "positive"; those that generate weaker signal are ca ...
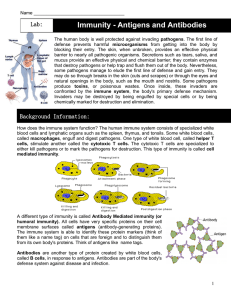
Antigens and Antibodies
... that destroy pathogens or help trap and flush them out of the body. Nevertheless, some pathogens manage to elude the first line of defense and gain entry. They may do so through breaks in the skin (cuts and scrapes) or through the eyes and natural openings in the body, such as the mouth and nostrils ...
... that destroy pathogens or help trap and flush them out of the body. Nevertheless, some pathogens manage to elude the first line of defense and gain entry. They may do so through breaks in the skin (cuts and scrapes) or through the eyes and natural openings in the body, such as the mouth and nostrils ...
Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics (CESG)
... products contains the SP6 promoter, the TMV omega translational enhancer, and the His6 tag from our pEU-HisFlexivector. The other PCR product contains the target ORF with the 3’ extension mini-Phe. The mini-Phe forms a stem-loop structure in the RNA, which we found increases protein expression. The ...
... products contains the SP6 promoter, the TMV omega translational enhancer, and the His6 tag from our pEU-HisFlexivector. The other PCR product contains the target ORF with the 3’ extension mini-Phe. The mini-Phe forms a stem-loop structure in the RNA, which we found increases protein expression. The ...
Getting things where they need to go: Protein Targeting
... deform PM for clathrin coated vesicles. May suggest that using a helix to deform membrane is common mechanism for budding/fission ...
... deform PM for clathrin coated vesicles. May suggest that using a helix to deform membrane is common mechanism for budding/fission ...
Active transport - CHS Science Department Mrs. Davis
... Membrane Proteins Transporters are transmembrane proteins that use energy to move molecules across a membrane. ...
... Membrane Proteins Transporters are transmembrane proteins that use energy to move molecules across a membrane. ...
FREE Sample Here
... important, its knock-out will result in lethality. On the other hand, if it's very important its function will be duplicated by another protein, and there will be no obvious phenotype for the knock-out." Please explain this statement in your own words. ...
... important, its knock-out will result in lethality. On the other hand, if it's very important its function will be duplicated by another protein, and there will be no obvious phenotype for the knock-out." Please explain this statement in your own words. ...
Section 2 Molecules of Life
... 2) The enzyme changes shape weakening the bonds of the substrate. 3) The substrate turns into something different (products) and is released from the enzyme. ...
... 2) The enzyme changes shape weakening the bonds of the substrate. 3) The substrate turns into something different (products) and is released from the enzyme. ...
The Biotechnology Age: Issues and Impacts
... • 2. Enzymes: activity make and burn energy. Stimulate growth and biomass production. • 1000’s different enzymes -> unique activities ...
... • 2. Enzymes: activity make and burn energy. Stimulate growth and biomass production. • 1000’s different enzymes -> unique activities ...
The Fluid Mosaic Model - Chatsworth High School
... between different cells. It was unclear how the proteins in the model would permit the membrane to change shape without bonds being broken. Membrane proteins are largely hydrophobic and therefore should not be found where the model positioned them: in the aqueous cytoplasm and extracellular envi ...
... between different cells. It was unclear how the proteins in the model would permit the membrane to change shape without bonds being broken. Membrane proteins are largely hydrophobic and therefore should not be found where the model positioned them: in the aqueous cytoplasm and extracellular envi ...
Lattice Models of Protein Folding
... In Conclusion---Technical First intermediate resolution simulations of spontaneous “fibril” formation Our results qualitatively agree with experimental data in general, and specifically with those obtained by Blondelle et al. (Biochemistry, 1997) on polyalanines. Next step: Extending PRIME to ...
... In Conclusion---Technical First intermediate resolution simulations of spontaneous “fibril” formation Our results qualitatively agree with experimental data in general, and specifically with those obtained by Blondelle et al. (Biochemistry, 1997) on polyalanines. Next step: Extending PRIME to ...
RED &WHITE BLOOD CELLS
... Caused by the inability to detoxify oxidizing agents. It is the most common disease producing enzyme deficiency in the world. It is X-linked disorder. ...
... Caused by the inability to detoxify oxidizing agents. It is the most common disease producing enzyme deficiency in the world. It is X-linked disorder. ...
Microbiology: A Systems Approach, 2nd ed.
... • VDRL (Veneral Disease Research Lab) test • Double diffusion (Ouchterlony) method • Immunoelectrophoresis ...
... • VDRL (Veneral Disease Research Lab) test • Double diffusion (Ouchterlony) method • Immunoelectrophoresis ...
... butter. All of its carbon to carbon bonds are single. Too much of this can increase the chance of cardiovascular disease 11. What are unsaturated fats? A fat that contains fewer numbers of hydrogen (less stored energy) and is liquid at room temperature, found in vegetable oils, nuts, and seeds. Atle ...
Ch 3
... • Loosely defined group of molecules with one main chemical characteristic – They are insoluble in water • High proportion of nonpolar C—H bonds causes the molecule to be hydrophobic • Fats, oils, waxes, and even some vitamins ...
... • Loosely defined group of molecules with one main chemical characteristic – They are insoluble in water • High proportion of nonpolar C—H bonds causes the molecule to be hydrophobic • Fats, oils, waxes, and even some vitamins ...
Protein PreTest
... (yellow) The regulation of the body functions (blue) To build and repair 3. Another function of protein is: (red) To provide energy (yellow) The regulation of the body functions (blue) To build and repair 4. A complete protein is: (red) From a source which has all 9 essential amino acids (yellow) Fr ...
... (yellow) The regulation of the body functions (blue) To build and repair 3. Another function of protein is: (red) To provide energy (yellow) The regulation of the body functions (blue) To build and repair 4. A complete protein is: (red) From a source which has all 9 essential amino acids (yellow) Fr ...
Supplement_2_-_PLoS_
... PKD2 activated by phorbol esters efficiently phosphorylated the exogenous substrate histone H1. ...
... PKD2 activated by phorbol esters efficiently phosphorylated the exogenous substrate histone H1. ...
View PDF
... Lipids are a compound made up of __________ and __________. (look at the drawing) NOT ON TEST/not covered in notes: Explain the terms saturated-__________________________________________________ Monounsaturated-__________________________________________________________ Polyunsaturated-______________ ...
... Lipids are a compound made up of __________ and __________. (look at the drawing) NOT ON TEST/not covered in notes: Explain the terms saturated-__________________________________________________ Monounsaturated-__________________________________________________________ Polyunsaturated-______________ ...
BIOGRAPHICAL SKETCH Abhijeet Kapoor Postdoctoral Research
... My PhD studies focused on using computational techniques such as coarse-grained and all-atom simulations to understand functional motions in Ras proteins, an oncology target of exceptional importance. The primary focus of the work was to develop a generic coarse-grained model of proteins, use it to ...
... My PhD studies focused on using computational techniques such as coarse-grained and all-atom simulations to understand functional motions in Ras proteins, an oncology target of exceptional importance. The primary focus of the work was to develop a generic coarse-grained model of proteins, use it to ...
Western blot

The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot) is a widely used analytical technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. It uses gel electrophoresis to separate native proteins by 3-D structure or denatured proteins by the length of the polypeptide. The proteins are then transferred to a membrane (typically nitrocellulose or PVDF), where they are stained with antibodies specific to the target protein. The gel electrophoresis step is included in western blot analysis to resolve the issue of the cross-reactivity of antibodies.There are many reagent companies that specialize in providing antibodies (both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies) against tens of thousands of different proteins. Commercial antibodies can be expensive, although the unbound antibody can be reused between experiments. This method is used in the fields of molecular biology, immunogenetics and other molecular biology disciplines. A number of search engines, such as CiteAb, Antibodypedia, and SeekProducts, are available that can help researchers find suitable antibodies for use in western blotting.Other related techniques include dot blot analysis, immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry where antibodies are used to detect proteins in tissues and cells by immunostaining, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).The method originated in the laboratory of Harry Towbin at the Friedrich Miescher Institute. The name western blot was given to the technique by W. Neal Burnette and is a play on the name Southern blot, a technique for DNA detection developed earlier by Edwin Southern. Detection of RNA is termed northern blot and was developed by George Stark at Stanford.