Protein phosphorylation remains as a black box in signal
... 500 protein kinases are encoded in the human genome and are classified into 7 major groups based on their catalytic domain sequences, with each kinase playing distinct roles through its specific substrates. Although several kinases have been well-characterized and demonstrated to be physiologically ...
... 500 protein kinases are encoded in the human genome and are classified into 7 major groups based on their catalytic domain sequences, with each kinase playing distinct roles through its specific substrates. Although several kinases have been well-characterized and demonstrated to be physiologically ...
Chapter 3 Biological Molecules
... All have a variable “R” group • Some R groups are hydrophobic • Some are hydrophilic • Cysteine R groups can form disulfide bridges ...
... All have a variable “R” group • Some R groups are hydrophobic • Some are hydrophilic • Cysteine R groups can form disulfide bridges ...
Prior Art - Cabic.com
... The claims are directed to patent eligible subject matter with a specific, substantial, and credible utility. Claim 1 would be rejected under 35 U.S.C. §112, ¶1 as lacking written description and also as lacking enablement. Claim 2 complies with both the enablement and written description requ ...
... The claims are directed to patent eligible subject matter with a specific, substantial, and credible utility. Claim 1 would be rejected under 35 U.S.C. §112, ¶1 as lacking written description and also as lacking enablement. Claim 2 complies with both the enablement and written description requ ...
enzymes - Issaquah Connect
... The time it takes to break down a given amount of substrate into a given amount of product. Example: –The more enzyme present, the faster the substrate will be broken down. ...
... The time it takes to break down a given amount of substrate into a given amount of product. Example: –The more enzyme present, the faster the substrate will be broken down. ...
PPT - AePIC
... Conformational changes Protein folding Molecular recognition (drug design) Ion transport The method is based on the Newton’s equation of motion: ...
... Conformational changes Protein folding Molecular recognition (drug design) Ion transport The method is based on the Newton’s equation of motion: ...
BSCS Ch 1 review cdmodified - JBHA-Sci-US-tri1
... Amino acids link in specific sequences to form protein up to hundreds of amino acids long Each amino acid is joined to the next by a peptide bond (Covalent bonds) A polypeptide contains more than 10 amino acids ...
... Amino acids link in specific sequences to form protein up to hundreds of amino acids long Each amino acid is joined to the next by a peptide bond (Covalent bonds) A polypeptide contains more than 10 amino acids ...
National Library of Medicine BuiMing 38A
... diverge from each other. The best alignment between two homologous (i.e. evolutionarily related, and therefore similar) sequences may contain gaps in one or both sequences. BLAST is unable to insert gaps into its alignments. If it encounters non-mate g portions in the sequences being compared, it ge ...
... diverge from each other. The best alignment between two homologous (i.e. evolutionarily related, and therefore similar) sequences may contain gaps in one or both sequences. BLAST is unable to insert gaps into its alignments. If it encounters non-mate g portions in the sequences being compared, it ge ...
Supplementary Methods
... that is trapped in cells when cleaved by intracellular esterases and is then converted into the fluorescent product 2’,7’-dichlorofluorescein (DCF) in the presence of H2O2 and other ROS molecules. Thus, it allows for the measurement of oxidative stress within cells. This procedure was carried out as ...
... that is trapped in cells when cleaved by intracellular esterases and is then converted into the fluorescent product 2’,7’-dichlorofluorescein (DCF) in the presence of H2O2 and other ROS molecules. Thus, it allows for the measurement of oxidative stress within cells. This procedure was carried out as ...
Proteins and Albumin
... amido black (napthol black) method, and the Ponceau S stain. Silver also reacts with proteins, producing a dark brown complex; however, the chemical mechanism for this reaction is unknown. Albumin is the most abundant protein (constituting approximately 50% of the total proteins) in serum and is mea ...
... amido black (napthol black) method, and the Ponceau S stain. Silver also reacts with proteins, producing a dark brown complex; however, the chemical mechanism for this reaction is unknown. Albumin is the most abundant protein (constituting approximately 50% of the total proteins) in serum and is mea ...
148KB - University of California, Berkeley
... nor an inductive effect account for the observed 10-fold effect of substituting the 2⬘-OH with a 2⬘-H [1]. To explain their results, the authors turned to quantitative structure activity relationships (QSAR). This analytical technique has been pioneered in pharmacology, where it is frequently applie ...
... nor an inductive effect account for the observed 10-fold effect of substituting the 2⬘-OH with a 2⬘-H [1]. To explain their results, the authors turned to quantitative structure activity relationships (QSAR). This analytical technique has been pioneered in pharmacology, where it is frequently applie ...
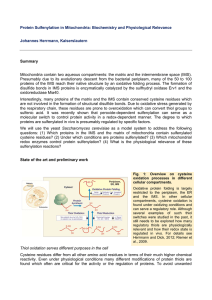
Protein Sulfenylation in Mitochondria: Biochemistry and
... and the intermembrane space of mitochondria (IMS), dedicated machineries exist which introduce stable disulfide bonds into newly synthesized proteins. In this case, thiol oxidation can significantly contribute to the resistance of proteins against thermal denaturation or proteolytic degradation (Rie ...
... and the intermembrane space of mitochondria (IMS), dedicated machineries exist which introduce stable disulfide bonds into newly synthesized proteins. In this case, thiol oxidation can significantly contribute to the resistance of proteins against thermal denaturation or proteolytic degradation (Rie ...
Making Attachments: Curli Production in Bacterial Communities
... More details on each protein subunit Congo red binding assay Experimental design ...
... More details on each protein subunit Congo red binding assay Experimental design ...
Noppl40 Shuttles on Tracks
... competing peptide (lane 2). In the absence of competing peptide Noppl40 was efficiently removed from the SDS extract (lane 3) and immunoprecipitated (lane 4). Similar results were obtained when =P-labeled proteins of whole cells were analyzed (not shown). Considering that Nopp140 is not a major cell ...
... competing peptide (lane 2). In the absence of competing peptide Noppl40 was efficiently removed from the SDS extract (lane 3) and immunoprecipitated (lane 4). Similar results were obtained when =P-labeled proteins of whole cells were analyzed (not shown). Considering that Nopp140 is not a major cell ...
Supplemental Information
... Multifunctional enzyme that, as well as its role in glycolysis, plays a part in various processes such as growth control, hypoxia tolerance and allergic responses. May also function in the intravascular and pericellular fibrinolytic system due to its ability to serve as a receptor and activator of p ...
... Multifunctional enzyme that, as well as its role in glycolysis, plays a part in various processes such as growth control, hypoxia tolerance and allergic responses. May also function in the intravascular and pericellular fibrinolytic system due to its ability to serve as a receptor and activator of p ...
Cas9 Protein Product Analysis Certificate
... 1) Plate 100,000 to 200,000 of target cells (e.g. 293T cells) into a single well of a 12-well plate in 1 ml of appropriate growth medium. Include a single well of cells as negative control. 2) Next day, or when cells are 50-60% confluent, transfect target cells with the Cas9 protein and gRNA (and ap ...
... 1) Plate 100,000 to 200,000 of target cells (e.g. 293T cells) into a single well of a 12-well plate in 1 ml of appropriate growth medium. Include a single well of cells as negative control. 2) Next day, or when cells are 50-60% confluent, transfect target cells with the Cas9 protein and gRNA (and ap ...
Immunity and Vaccination: biology homework revision question
... A new technique for vaccinating people involves injecting them with DNA. Viruses have proteins on their coats that are coded for by their DNA. The genes for producing viral proteins can be isolated and inserted into loops of DNA (plasmids). Plasmids can enter human cells which will then produce the ...
... A new technique for vaccinating people involves injecting them with DNA. Viruses have proteins on their coats that are coded for by their DNA. The genes for producing viral proteins can be isolated and inserted into loops of DNA (plasmids). Plasmids can enter human cells which will then produce the ...
Human PDX-1/IPF1 Antibody
... view shows lysates of βTC6 mouse beta cell insulinoma cell line, loaded at 0.2 mg/mL. A specific band was detected for PDX1/IPF1 at approximately 48 kDa (as indicated) using 10 µg/mL of Goat AntiHuman PDX1/IPF1 Antigen Affinitypurified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2419) followed by 1: ...
... view shows lysates of βTC6 mouse beta cell insulinoma cell line, loaded at 0.2 mg/mL. A specific band was detected for PDX1/IPF1 at approximately 48 kDa (as indicated) using 10 µg/mL of Goat AntiHuman PDX1/IPF1 Antigen Affinitypurified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2419) followed by 1: ...
(PUNCH-P) reveals cell cycle
... metabolic labeling of cells with radioactive amino acids. For high-resolution identification and quantification of proteins, metabolic labeling was combined with mass spectrometric (MS) analysis, and the radioactive amino acids were replaced by stable isotope-labeled (SILAC [stable isotope labeling ...
... metabolic labeling of cells with radioactive amino acids. For high-resolution identification and quantification of proteins, metabolic labeling was combined with mass spectrometric (MS) analysis, and the radioactive amino acids were replaced by stable isotope-labeled (SILAC [stable isotope labeling ...
91.510_ch8_part1
... of a protein. Its size is often 10 to 20 amino acids. Simple motifs include transmembrane domains and phosphorylation sites. These do not imply homology when found in a group of proteins. PROSITE (www.expasy.org/prosite) is a dictionary of motifs (there are currently 1600 entries). In PROSITE, a pat ...
... of a protein. Its size is often 10 to 20 amino acids. Simple motifs include transmembrane domains and phosphorylation sites. These do not imply homology when found in a group of proteins. PROSITE (www.expasy.org/prosite) is a dictionary of motifs (there are currently 1600 entries). In PROSITE, a pat ...
CATALYSIS OF BIOCHEMICAL REACTIONS
... 2. A and B collide; collision distorts or stresses bonds to the point where they can rearrange electrons; generally, this requires more potential energy (since without stress, one expects electrons to find a lowenergy, stable state): extra energy is “activation ...
... 2. A and B collide; collision distorts or stresses bonds to the point where they can rearrange electrons; generally, this requires more potential energy (since without stress, one expects electrons to find a lowenergy, stable state): extra energy is “activation ...
Protein Conformation and Function
... • The amino acids in a chain are often referred to as residues. – Ex. Ala-gly-lys 3 residue amino acids • The amino acid residue with the free COOH group is called the C-terminal, and the amino acid residue with the free NH2 group is called the N-terminal. • Peptide and protein chains are always wr ...
... • The amino acids in a chain are often referred to as residues. – Ex. Ala-gly-lys 3 residue amino acids • The amino acid residue with the free COOH group is called the C-terminal, and the amino acid residue with the free NH2 group is called the N-terminal. • Peptide and protein chains are always wr ...
Protein translocation across mitochondrial membranes
... Thus, the AAC precursor appears to be “promiscuous” in its use of receptors. It can be recognized both by MOM72 and MOM19. Direct interaction of precursor proteins with MOM72 and MOM 19 was demonstrated by co-immunoprecipitation of MOM72 with bound precursor or crosslinking of precursor with h.10M19 ...
... Thus, the AAC precursor appears to be “promiscuous” in its use of receptors. It can be recognized both by MOM72 and MOM19. Direct interaction of precursor proteins with MOM72 and MOM 19 was demonstrated by co-immunoprecipitation of MOM72 with bound precursor or crosslinking of precursor with h.10M19 ...
Western blot

The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot) is a widely used analytical technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. It uses gel electrophoresis to separate native proteins by 3-D structure or denatured proteins by the length of the polypeptide. The proteins are then transferred to a membrane (typically nitrocellulose or PVDF), where they are stained with antibodies specific to the target protein. The gel electrophoresis step is included in western blot analysis to resolve the issue of the cross-reactivity of antibodies.There are many reagent companies that specialize in providing antibodies (both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies) against tens of thousands of different proteins. Commercial antibodies can be expensive, although the unbound antibody can be reused between experiments. This method is used in the fields of molecular biology, immunogenetics and other molecular biology disciplines. A number of search engines, such as CiteAb, Antibodypedia, and SeekProducts, are available that can help researchers find suitable antibodies for use in western blotting.Other related techniques include dot blot analysis, immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry where antibodies are used to detect proteins in tissues and cells by immunostaining, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).The method originated in the laboratory of Harry Towbin at the Friedrich Miescher Institute. The name western blot was given to the technique by W. Neal Burnette and is a play on the name Southern blot, a technique for DNA detection developed earlier by Edwin Southern. Detection of RNA is termed northern blot and was developed by George Stark at Stanford.